* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6th Grade Science Content Standards
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
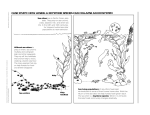
6th Grade Science Content Standards - Focus on Earth Science Ecology (Life Science) Organisms in ecosystems exchange energy and nutrients among themselves and with the environment. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. energy entering ecosystems as sunlight is transferred by producers into chemical energy through photosynthesis, and then from organism to organism in food webs. Kelp beds at the Piedras Blancas enrich ocean water with oxygen while making their own food through photosynthesis. Kelp (a type of seaweed) is an algae. As a producer, kelp uses energy from the sun to conduct photosynthesis and make its own food. Kelp attatches to the seabed through a holdfast, not a root system, but an anchor. A kelp forest, much like the rain forest, can be divided into layers including the canopy, understory, and forest floor. Kelp forests are complex ecosystems that support many interconnected food webs, both as a food source and as habitat. b. over time, matter is transferred from one organism to others in the food web, and between organisms and the physical environment. Elephant seals do not eat anything while on the beach. They fast and metabolize a thick layer of blubber (fat) for their nutritional needs. When at sea, Elephant seals feed on squid, octopus, skate, dogfish, and hagfish. Their predators are Great White Sharks and Orca. c. populations of organisms can be categorized by the functions they serve in an ecosystem. (Producers, Consumers, Decomposers) Kelp and other algae are the producers of the ocean. They use energy from the sun to make their own food. Other sea organisms, some microscopic are consumers, and must get energy from other living things – either plants or animals. Elephant seals are consumers and during the long migration at sea, must develop a thick layer of blubber – enough to sustain them during periods of fasting on land. They are also prey, and must evade great white shark and orca attacks. Gulls and turkey vultures are decomposers that can be seen on the beaches on the Central Coast. Microorganisms are present in every ecosystem. d. different kinds of organisms may play similar ecological roles in similar biomes. A biome includes the living and nonliving (sand, sunlight, water) in a distinct climate zone. Piedras Blancas rookery represents a marine biome. Marine biomes cover three quarters of the earth’s surface, and include oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries. Marine algae supply much of the world’s oxygen supply through photosynthesis. Marine and terrestrial plants require the same conditions for healthy growth: adequate sunshine, nutrients, water and protection form bad weather. Human activities impact both marine and terrestrial biomes through pollution and development. e. the number and types of organisms an ecosystem can support depends on the resources available and abiotic factors, such as quantity of light and water, range of temperatures, and soil composition. The Piedras Blancas rookery is growing in size. Abiotic (nonliving) factors in this ecosystem include the sand and water on this beach. The beach is wide and deep, providing protection from storms and safety from large waves. There is no manufacturing pollution on the Central Coast and human interference is limited. Kelp beds and rocky outcrops at the surf line provide a resting place for adult seals and weaner pups learning to swim. .