* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside Our Earth
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
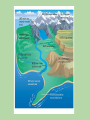
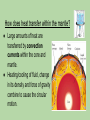
Our Earth Inside and Out And how it works 4.6 billion years in the making Big Question- How do Earth’s land, water, air and life work together to form a system? What Are the Main Parts of the Earth System? ● A system is a group of parts that work together as a whole. ○ involves a constant flow of matter though different parts ○ is driven by energy ○ two main sources of energy: heat from the sun and heat flowing out of Earth as it cools Parts of the Earth System ➔ four main spheres ◆ atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, and the biosphere Can you tell what is in which sphere? p6 How do forces change Earth? Lands are constantly being created and destroyed by competing forces. ● Forces that construct/build up mountains are called constructive forces. They shape the land’s surface by building up mountains and other landmasses. ● Destructive forces destroy and wear away landmasses forces such as ice, rain, wind, and changing temperatures wear down/destroy landmasses. How Do Geologists Learn about Earth's Interior? two main types of evidence ● direct evidence from rock samples ○ Drilling, volcanic rock are clues to conditions deep inside Earth. ● indirect evidence from seismic waves ○ Study how waves travel through Earth - speed and path of wave gives clue to structure. What are the main parts of Earth’s Structure? ● Three main layers of Earth are the crust, the mantle, and the core. ● These layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pressure. ● Pressure results from a force pressing on an area. The temperature and pressure inside Earth increase with depth. Crust - ● layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin ● layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and the ocean floor ● composition of oceanic crust is much like basalt ● composition of continental crust is much like granite What are the main types of landforms found? ❖ Plain - landform made up of nearly flat or gently rolling land. ➢ coastal plain or interior plain (plains of North America are called the Great Plains) ❖ Mountain - landform with high elevation; mountain range are closely related in shape, structure, area, and age. ❖ Plateau - landform that has high elevation and a more or less level surface Mantle ➔ made of rock that is very hot, but solid ➔ nearly 3,000 kilometers thick ➔ Divided into layers based on the physical characteristics ➔ crust and uppermost mantle, a single layer called the lithosphere ➔ soft layer just beneath the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere. How does heat transfer within the mantle? ● Large amounts of heat are transferred by convection currents within the core and mantle. ● Heating/cooling of fluid, change in its density and force of gravity combine to cause the circular motion. Other ways to transfer heat Radiation - transfer of energy/heat that travels through the air. (sun, campfire) Conduction - transfer between materials that are touching. (holding a cup of hot coco) Core ● made mostly of the metals iron and nickel ● two parts—a liquid outer core and a solid inner core ● movements in the liquid outer core create Earth’s magnetic field Modeling and Measuring Earth ● Globes, map projection and maps are all way to model the surface of Earth. ● Degrees measure the distance from the equator to the poles and east/west of the prime meridian. How Do Maps Show Topography? ● Topographic map shows the surface features of an area. ● Use contour lines to represent elevation, relief, and slope