* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download White blood cells - The Silver Sword
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
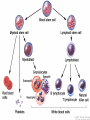
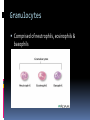
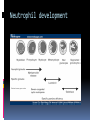
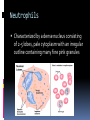
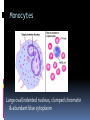
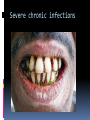
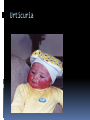
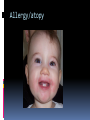
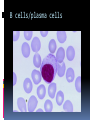
Dr Q Sedick WHITE BLOOD CELLS Haemopoeisis Haemopoeisis starts with a pluripotential stem cell that gives rise to separate cell lineages. Leucocytes May be divided into 2 groups: 1.Phagocytes:granulocytes & monocytes 2.Immunocytes:lymphocytes & plasma cells Phagocytes & immunocytes serve to protect the body against infection using immunoglobin and complement systems. Granulocytes Comprised of neutrophils, eosinophils & basophils Neutrophil development Granulopoeisis Many growth factors are involved in the maturation process Includes IL-1/IL-3/IL-5/IL-6/IL-11/GM-CSF/GCSF/M-CSF GF stimulate proliferation and differentiation and also affect the function of mature cells on which they act Neutrophils Characterized by a dense nucleus consisting of 2-5 lobes, pale cytoplasm with an irregular outline containing many fine pink granules Neutrophil granules Consists if primary & secondary granules Primary : myeloperoxidase/acid phosphatase/acid hydrolases Secondary: collagenase/lactoferrin & lysozyme Monocytes Large oval/indented nucleus, clumped chromatin & abundant blue cytoplasm Neutrophil/monocyte functions 1. Chemotaxis-phagocytes are attracted to bacteria by chemotactic substances released from the damaged tissues/by complement or by leucocyte adhesion molecules 2. Phagocytosis-neutrophils & monocytes have FC and C3B receptors which aid in opsonization of bacteria Neutrophil/monocyte function 3. Secretion of growth factors & chemokines- aid in pro-inflammatory processes 4. Killing and digestion: via oxygen-dependant and oxygen- independent pathways Eosinophils Consists of 2-3 nuclear lobes/ red-staining coarser cytoplasmic granules Enter inflammatory exudates Special role in allergic responses/defense against parasites and removal of fibrin formed during inflammation Basophils Dark cytoplasmic granules which overly the nucleus Contain heparin and histamine-released on degranulation Have IGE attachment sites In tissues-mast cells Defects of leucocytes NEUTROPHIL LEUCOCYTOSIS: >7,5 X 10^9/L 1. Bacterial infections, e.g. : periodontitis 2. Inflammation and tissue necrosis, 3. Metabolic disorders 4. Neoplasm's 5. Acute haemorrhage/ haemolysis 6. Drugs e.g. :lithium Leucocytosis… 7. Haematological malignancies: CML/myeloproliferative disorders/polycythaemia vera/myelofibrosis/AML 8. Treatment with myeloid growth factors 9. Asplenia 10. Rare inherited disorders, e.g.: Down syndrome The leukemoid reaction Reactive and excessive leucocytosis characterised by the presence of immature cells in the peripheral blood Seen in severe chronic infections/severe haemolysis & metastatic cancer Severe chronic infections Malignancy Eosinophilia >0,4 x 10^9/l Causes are as follows: 1. Allergy / atopy 2. Parasitic disease 3. Skin diseases- urticuria 4. Drug-induced 5. Asthma & pulmonary syndromesassociation with nasal polyps Urticuria Eosinophilia 6. Vasculitidis-polyarteritis nodosa 7. Malignancies-metastatic and haematological 8. Chronic eosinophilic leukaemia 9. Hypereosinophilic syndrome Allergy/atopy Basophilia >0,1 x 10^9/l Causes include reactive and malignant Reactive: infections like small pox & chicken pox Myeloproliferative disorders-Chronic myeloid leukaemia Monocytosis >0,8 x 10^9/l 1. Chronic bacterial infections 2. Protozoan infections 3. Collagen vascular disease-SLE 4. Lymphoma 5. Myelodysplasia Neutropaenia <2,5 x 10^9/l 1. Infections of the mouth & throat(bacterial/viral) 2. Immune-SLE,hypersensitivity,anaphylaxis 3. Drug-induced 4. Congenital - Kostmanns syndrome 5. Bone marrow failure Lymphocytes Lymphocytes are the immunologically competent cells that assist the phagocytes in defense of the body against infection They are involved in processes such as antigen specificity and immunological memory Lymphocyte development Consists of T and B cells B cells: Derives from the stem cell,matures in the bone marrow and circulates in the peripheral blood until antigen recognition On activation B cells secrete immunoglobulin and is known as plasma cells B cells/plasma cells T cells T CELLS: Derive from the thymus and differentiates into mature T cells during its passage to the bone marrow Involved in immunological processes such as cell mediated cytotoxicity Lymphocytosis Acute infections-infectious mononucleosis/rubella/pertussis/mumps/herpes/CMV/ HIV 2. Chronic infections-TB/brucellosis/syphillus 3. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemias 4. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia/NHL 1. Infectious mononucleosis