* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dihybrid Problems - Milan Area Schools
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
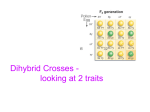
Dihybrid Crosses Name: Dihybrid crosses are 16 square punnetts that predict the chance of offspring having 2 different traits. Let's call them trait A and trait B. Hints for solving dihybrid crosses: * Use the 1,3 1,4 2,3 2,4 Rule * Number the alleles in the parent genotype 1 -4 * Match 1 and 3 together, 1 and 4 together, 2 and 3 together, 2 and 4 together * You should have 2 letters in each square along the top and on the side (the parent genotypes) * Place the letters in the inner squares just like you did for the shorter Punnett squares * There should be 4 letters in each of the inner squares * Put the 2 similar letters next to each and put capital letters first Finding Genotype Probabilities: * Find all the different letter combinations * (There will never be more 9 different combinations) * Count how many you have of each kind * Your probability will be the number of that combination / 16 Finding Phenotype Probabilities: * There will never be more than 4 different phenotype combinations * Count the number of offspring with dominant trait A and dominant trait B * find those with dominant A, recessive B * find those with recessive B, dominant A * find those with recessive A and recessive B * your probability will be the number of each combination / 16 Problems - 1st one is partially done for you – we will finish it together in class. 1. G-Normal, g – Green N- Long Nosed, n – Short Nosed Cross GgNn x GgNn. Give the genotype and phenotypes of the offspring. Be sure to list expected probabilities of each phenotype (ie. 3/16). Parent 1: GgNn (normal, long-nose) 1234 GN (1,3) Gn (1,4) gN (2,3) GN GGNN Gn GGNn GGnn gN GgNN GgNn ggNN gn GgNn Ggnn ggNn Parent 2: GgNn (normal, long-nose) 12 34 gn (2,4) ggnn Genotypes GGNN = /16 GGNn = /16 GGnn = /16 GgNN = /16 GgNn = /16 Ggnn = /16 ggNN = /16 ggNn = /16 ggnn = / 16 Phenotypes normal, long nose = normal, short nose = green, long-nose = green, short-nose = /16 /16 /16 /16 2. 3. G-Normal, g – Green N- Long Nosed, n – Short Nosed Cross GGNn x ggnn. Give the genotype and phenotype ratios of the offspring. Be sure to list expected probabilities of each phenotype (ie. 3/16). Genotypes In peas, a gene for tall plants, T, is dominant over its allele for short plants, t. The gene for smooth peas, S, is dominant over its allele for wrinkled peas, s. Calculate both the genotypes and phenotypes for the following cross: TtSS x ttSs Genotypes 4. Phenotypes Phenotypes Long noses are recessive to short noses. Attached ear lobes are dominant to detached ear lobes. What would the resultant offspring be of a cross between a homozygous short nosed, homozygous attached ear person and a heterozygous short nosed, heterozygous attached ear person? Give the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring as well as the ratios. S = short nose s = long nose A = attached earlobe Parent 1:_________ Parent 2: ________ a = detached earlobe Genotypes 5. Phenotypes 2 Vietnamese pigs were mated together. If all offspring contained the same genotype RrTt (round, squiggly tailed), what were the genotypes of the two parent pigs? (there may be more than one correct answer) Genotypes RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt 6. In the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, vestigial (stubby) wings and hairy bodies are produced by two recessive genes located on different chromosomes. The normal alleles, long wings and hairless bodies, are dominant. Suppose a vestigial-winged hairy male is mated with a homozygous normal female. What types of offspring would be expected? L= long wing l = stubby (vestigial) wing H = hairless body Parent 1(male): _________ Parent 2 (female): ________ h = hairy body Phenotypes (Offspring types) 7. Suppose a hairy female with vestigial wings is crossed with a vestigial-winged male heterozygous for the hairless characteristic. What will be the genotypes and phenotypes in the F1? Genotypes 8. Phenotypes A rare recessive gene in the gerbil (d), is lethal (deadly) in the homozygous condition. Geneticists have noticed that if these gerbils also contain the dominant allele (N), they will survive (a condition known as epistasis). The alleles D and N are coded for on different genes. If you mate a ddNn male with a Ddnn female, how many offspring will be viable (live)? Hint: What combinations are deadly? Remember that dd = deadly unless it is paired with an N. Number of Viable (living) offspring = ________________ 9. In hogs, a gene that produces a white belt around the animal’s body is dominant over its allele for a uniformly colored body. Another gene produces a fusion of the two hoofs on each foot, a condition known as syndactyly; this gene is dominant over its allele which produces normal hoofs. Suppose a uniformly colored hog homozygous for syndactyly is mated with a normal-footed hog homozygous for the belted character. What would be the phenotype of the F1? If the F1 individuals are allowed to breed freely among themselves, what genotypes and phenotypes would be predicted in the F2? (Hint: You can use the trick that I taught in class rather than doing the punnet squares if you like) W = white belt Parent 1: _______________ Parent 2: ________________ w = uniform color H = fused hoofs h = normal hoofs Syndactyly in a human F1 Generation Genotypes Phenotypes Genotypes Phenotypes F2 Generation 10. Write your own problem. Be sure to pick two genes with two variants (alleles) for each. BE creative, they do not need to be real traits. Be sure to solve the problem as well, showing the offspring’s expected genotypes and phenotypes. Genotypes Trait A= ___________________ Trait B = __________________ Ex. Cred. Draw your variations Phenotypes