* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
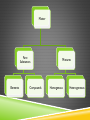
CHAPTER 2 Properties of Matter PROPERTIES OF MATTER Extensive-depends on the amount of matter in a sample ex: volume, mass, texture Intensive-depends on the type of matter in a sample ex: density, viscosity, melting point EXTENSIVE PROPERTIES It depends on the amount of matter in a sample Mass (grams) Weight (newtons) volume (mL or cm3) INTENSIVE PROPERTIES Depends on type of matter Density(at STP) - boiling point texture - melting point odor - color taste - ductility hardness - solubility malleability - tenacity conductivity - brittleness STATES OF MATTER SolidLiquidsGases4th state? What is plasma? 5th state? NOVA Bose Einstein Constant Liquids • Molecules have room to slide over each other • Have no definite shape, but have a definite volume. • Not easily compressed Gases • Molecules move freely to fill the container • Have no definite volume or shape • Easily compressed PHASE CHANGES PHASE CHANGES AND ENERGY Exothermic- heat is released Endothermic- heat is absorbed Is the evaporation of water exothermic or endothermic? Explain. PHASE CHANGES AND ENERGY Entropy- a measure of disorder of a system The more ordered a system is, the more entropy it has – for example a clean, organized room has less entropy than a messy room. Which has more entropy, a solid or a gas? PHYSICAL CHANGES During a physical change, the properties of the material changes, but not the composition of the material Can be classified as reversible or irreversible Examples: MIXTURES Mixture-physical blend of two or more components Heterogeneous ex: Homogenous (solution) ex: ALLOYS Alloy – homogenous mixture of metals Sterling silver- 93% silver 7% copper Surgical steel- Fe – 67%, Cr - 18%, Ni-12%, Mo- 3% Spring steel- Fe- 98.6%, Cr- 1.0% , C- 0.4% SEPARATING MIXTURES What are some ways that we can separate mixtures? • • • • • • • • • Separating mixtures by physical means Filtering By hand Boiling- fractional distillation Freezing Melting Evaporating Dissolving Crystallizing Magnetism SEPARATION OF MIXTURES Distillation Filtration TYPES OF MIXTURES Homogeneous Heterogeneous ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS Element- simplest form of matter with a specific set of properties Compound- contains two or more elements chemically combined Compounds can be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means, elements cannot ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS Elements are represented by symbols Compounds are represented by chemical formulas, groups of element symbols ELEMENT SYMBOLS CHEMICAL SYMBOLS 1st letter always upper case Each element has its own 2nd and 3rd always lower case Represents one atom (or mole) of the element Co vs. CO Ni vs. NI Chemical Formula – the “recipe” for a compound. • Tells what elements are in the compound. • Tells # of atoms of each element. – Ex. H2O = 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen – Ex. NaCl C6H12O6 H2SO4 COMPOUNDS NaCl C6H12O6 Which represents the element, compound and mixture? Element (diatomic) = b Compound = c Mixture = a CHEMICAL CHANGES (RXN) During a chemical change, the composition of matter always changes Reactant Product INDICATORS OF CHEMICAL CHANGE Formation of precipitate Production of a gas Change in pH Energy change Color change Light Matter Pure Substances Elements Compounds Mixtures Homogenous Heterogeneous CONSERVATION OF MASS - During a chemical reaction, the mass of the products is always equal to the mass of reactants - Law of Conservation of Mass Chemical Change = Chemical Reaction Which of the following is not a chemical change? A. Paper being shredded B. Steel rusting C. Charcoal burning D. Newspaper yellowing in SMART the sun Response Qu To set the properties right click and select SMART Response Question Object->Properties.. 2. Which phrase best describes an apple? A. Heterogeneous mixture B. Homogenous compound C. Heterogeneous substance D. Homogenous mixture 3. Which element is paired with the wrong symbol? A. sulfur, S B. nitrogen, N C. potassium, P D. calcium, Ca 4. Which of these properties could not be used to distinguish between table salt and sugar A. Boiling point B. Melting point C. Density D. Color 5. The state of matter characterized by a definite volume and an indefinite shape is a A. Solid B. Liquid C. Mixture D. Gas 6. Which description below correctly identifies air? A. Compound B. Heterogeneous mixture C. Element D. Homogeneous mixture 7. Which description below correctly identifies carbon monoxide? A. Compound B. Heterogeneous mixture C. Element D. Homogeneous mixture 8. Which description below correctly identifies zinc? A. Compound B. Heterogeneous mixture C. Element D. Homogeneous mixture 9. Which description below correctly identifies pepperoni pizza? A. Compound B. Heterogeneous mixture C. Element D. Homogeneous mixture 10. Magnesium metal burns vigorously in oxygen to produce the compound magnesium oxide. Use the Law of Conservation of Mass and the table below to determine the mass of oxygen used in the reaction. Mass of magnesium Mass of oxygen 6.5 g ? Mass of magnesium oxide 10.8 g