* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbon Cycle
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Iron fertilization wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Carbon pricing in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate-friendly gardening wikipedia , lookup
Blue carbon wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sequestration wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
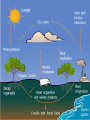
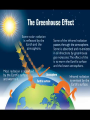
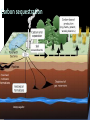
Carbon Cycle What is Carbon and carbon dioxide? Carbon is the fourth most abundant element in the universe and is needed for life. It is the backbone of life on earth we need carbon but that need is also entwined with one of the serious problem facing us today. Carbon dioxide a colorless, odorless, and slightly acid tasting gas, sometimes called carbonic acid gas, the molecule of which consists of one atom of carbon joined to two atoms of oxygen (CO2). What is Carbon Cycle? Carbon cycle The set of biochemical processes by which carbon undergoes chemical reaction, changes form, and moves through different reservoirs on earth, including living organism. The geological component of the carbon cycle is driven by plate tectonics and includes processes like volcanic eruption and burial of carbon rich sediments on the ocean floor. The global carbon cycle is divided into major reservoir of common interconnected by pathway of exchange. 1. The atmosphere 2. The terrestrial biosphere 3. The ocean including dissolved inorganic carbon the living and non living marine biota 4. Sediment including fossil fuel ,fresh water system and non living organic material such as soil carbon Two Types of Carbon Cycle Terrestrial Carbon Cycle Aquatic Carbon Cycle Terrestrial Carbon Cycle Concerned with the movement of carbon through terrestrial ecosystems. Terrestrial plants use atmospheric carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to generate oxygen that sustains animal life. Aquatic Carbon Cycle concerned with the movements of carbon through marine ecosystems. Aquatic plants also generate oxygen but they use carbon dioxide from water. Importance of Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is important because its disruption is what causes global warming at the atmosphere. Too much carbon dioxide accumulates in the atmosphere and the carbon dioxide trap heat inside the planet causing global temperature to rise. Causes The movement of carbon molecules from the co2 pool to the air and water to plants and animals is at various positions along the food chain and respiration return along the pool. Carbon is also returned to the pool through bacterial and fungal agent that causes decay, thus converting the complex carbon containing molecules to their simple component. one important factor: Human activities change the atmosphere's composition. Through burning fossil fuels, industrial production and etc. These human activities increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere which keeps more heat in our atmosphere , facilitating global warming. Factor that leads to global warming 1. Increasing Population Growth 2. Destruction of the forest 3. Burning of fossil fuel 4. Exhaust Fumes/ Smokes and other Gases Mechanisms Photosynthesis Chemical process by which plants containing chlorophyll use sunlight to manufacture their own food by converting carbon dioxide and water to carbohydrates, releasing oxygen as a by-product. Plants Use Carbon Dioxide Plants pull carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and use it to make food Called photosynthesis. The carbon becomes part of the plant (stored food). Respiration The process in which oxygen is used to break down organic compounds into carbon dioxide (CO2 ) and water (H 2 O). Animals Eat Plants When organisms eat plants, they take in the carbon and some of it becomes part of their own bodies. Decomposition The breakdown of complex molecules is a molecule of which dead organisms are composed into simple nutrients that can be reutilized by living organisms. Plants and Animal Die When plants and animals die, most of their bodies are decomposed and carbon atoms are returned to the atmosphere. Some are not decomposed fully and end up in deposits underground (oil, coal, etc.). Combustion It is the sequence of exothermic chemical reactions between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the production of heat and conversion of chemical species. Weathering of rocks It is the breaking down of rocks, soil and mineral as well as artificial material through contact with the earth’s atmosphere, biota, and water. Two important classification of weathering process: Physical or Mechanical Weathering Chemical Weathering Carbon Slowly Returns to Atmosphere Carbon in rocks and underground deposits is released very slowly into the atmosphere. This process takes many years. Cycle Repeats Over and Over and Over and Over … Effects 2 major effect of global warming 1. Increase of temperature on the earth by about 3° to 5° C (5.4° to 9° Fahrenheit) by the year 2100. 2. Rise of sea levels by at least 25 meters (82 feet) by the year 2100. climate change The effects of climate change can be seen around the world. Temperatures, including those coastal waters, have already risen. Globally, extreme weather is predicted to become more common and to have a negative impact on humans, animals and plants Acid Rain Impact HUMAN Humans negatively impact the carbon cycle by extracting fossil fuels from the ground and unbalancing the cycle. climate change Changes in the greenhouse effect , which affects the amount of heat retained by Earth’s atmosphere Variations in the sun’s energy ,reaching Earth Changes in the reflectivity of Earth’s atmosphere and surface. Most places will continue to get warmer especially at night and in winter Sea levels will continue to rise for many centuries Weather patterns will keep changing Increased carbon dioxide levels will affect biological systems independent of climate change. Mitigation To successfully manage carbon for climate purposes it requires increased understanding of carbon cycle dynamics and improvements in the scientific capabilities available for measurement as well as policy needs. Land management Energy Policy Two methods used to balance disrupted carbon cycle Carbon sequestration Deep sea carbon storage Carbon sequestration 3 types of technologies for scrubbing Post-combustion capture Pre-combustion capture oxy-fuel combustion Deep sea carbon storage CONCLUSION and RECOMMENDATION CONCLUSION Human activities changes the natural land surface. Humans causes global climate change through fossil fuel combustion. Earth's systems are dynamic they continually react to changing influences. There are several compelling reasons to begin establishing a global carbon cycle observing system: the well-known need for information on the productivity and changes of terrestrial biosphere to permit sustainable development and resource management. the well-established need for improved knowledge of the carbon cycle, its variability, and its likely future evolution, dictated by the desire to develop the most effective national and global policies to deal with climate variability, change, impact and adaptation. RECOMMENDATION Plant more trees to prevent global warming and other problems. Reduce the use of chemical that can harm our environment. Promotion of family planning to reduce population growth. Promotion of the use of electric vehicle to lessen the CO2 emission. Provide funding for this project. THANK YOU FOR LISTENING AND GOD BLESS