* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download life process
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
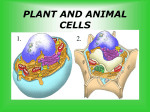
Chapter 1: Life Processes Mrs. Giles 4th Grade Saraland Elementary Lesson 1:Characteristics of Living Things • All living things are made of cells and are able to carry out life processes. • A life process is a function that a living thing performs to stay alive and produce more of its own kind. • Living things also reproduce, or make more living things of their own kind. • What is the difference between a bronze duck and a live duck? A live duck carries out life processes!! Life Processes Life Process Takes in materials such as nutrients and gases. Plants Animals Take in carbon dioxide, water, and minerals Take in oxygen from the air and nutrients from food. Release energy from the food they make Release energy from the food they eat Grow and develop Release energy React to surroundings Give off waste Reproduce Give off oxygen as a waste Give off carbon dioxide product of making food. and other waste. Other processes gives off water and carbon dioxide. Objective: Describe organization of cells into tissues, organs, and organ systems What is a Cell? • A cell is the basic unit that makes up all living things. Cells carry out life processes. • Cells are very tiny and can be seen with a microscope. All living things are made up of at least one cell Complete the web with four characteristics of cells. All organisms -living thingsare made of cells. Cells Cells do the jobs that keep organisms alive. Cells are the smallest part of a living thing. These cells are like tiny building blocks. Plant and Animal Cells Two Types of Cells Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Animal Cell Read/Look at pages A8-A9 in your textbook • Compare both cells. How are their cells alike? How are their cells different? Plant Cell • A plant and animal cell both have a nucleus, chromosomes, mitochondria, cell membrane, vacuole and cytoplasm. • A PLANT CELL ONLY HAS… • A cell wall- These walls help give the plants their shape. • Chloroplast- is where the plant make food. It contains a green material called chlorophyll. A PLANT Cell • Plant cells have a few large vacuoles. An animal cell has several small vacuoles. • The vacuole is a storage container for food, nutrients, or waste. Cell Structures that Both Cells Contain • Nucleus- the control center of the cell- “The POWER HOUSE” • Chromosomes- Tiny blueprints for the cell- DNA • Mitochondria- Power Sources of a cell, Break down and release energy • Cell Membrane- acts like skin; located on the outside of an animal cell; located on the inside of the cell wall of a plant cell. • Cytoplasm- jellylike substance that fills the cell; other parts of the cell float in this. nucleus chloroplasts cytoplasm Cell wall Cell membrane Cell membrane cytoplasm Nucleus Compare and Contrast plant and animal cells. Animal Cells Plant Cells Compare and Contrast plant and animal cells. Animal Cells •Cell membrane •Cytoplasm •Vacuoles- many small ones throughout the cell •Nucleus Plant Cells •Cell wall •Cell membrane •Cytoplasm •Vacuoles- One large •Chloroplasts •Nucleus Organisms How are living things organized? Objective: Describe organization of cells into tissues, organs, and organ systems LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION - Cells work together to form tissues Cardiac cells Bone cells Muscle tissue epithelial tissue Cardiac organ Bone Levels of Organization • Tissue- group of similar cells working together LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION • Tissues work together to form organs Levels of Organization • An organ is a structure that contains at least two different types of tissue functioning together for a common purpose • Example: organ- the lungs LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION - Organ systems work together to form the whole organism Skeletal system Whole organism Muscular system Circulatory system Simple Organisms • Simple organisms contain only one cell.- Single Cell • Examples: bacteria, algae • Bacteria can be harmful. They can make you sick! • Some bacteria are helpful. They break down dead plant and animal material. Some kill bad bacteria. Bacteria is used to turn milk into cheese and yogurt!!! E. Coli Bacteria Diatomssingle celled algae that live in water. Algae- A Simple Organism • Algae and green plants give off oxygen as a waste product of making food. • Algae produce much of the oxygen on Earth. Complex Organism • A complex organism has many different kinds of cells. • Jellies have more than one cell • They have simple bodies • They do not have distinct organs. They do not have a heart or brain!! Complex Organisms • Most of the organisms that you are familiar with have more than one cell. • You are a complex organism!!! • You have many different cells in your body!! Simple and Complex Organisms Simple Organism Complex Organism • Some made of a single cell • Many different kinds of cells • Some made of many similar cells • Different kinds of tissue • Do not have distinct organs • Have organ system Review Questions: 1. How are living things alike? 2. Use the term tissue in a sentence about the bodies of animals. 3. Compare and Contrast How are a person and a wax model of that person alike? How are they different?