* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Biology Notes
Liver support systems wikipedia , lookup
Ascending cholangitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatic encephalopathy wikipedia , lookup
Wilson's disease wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Glycogen storage disease type I wikipedia , lookup
Intestine transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Liver cancer wikipedia , lookup
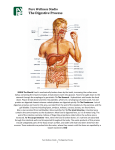
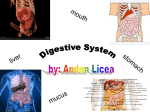
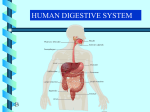
Chapter 9 Human Biology Notes Digestive System & Nutrition I. Functions of the Digestive System A. Ingestion = B. Digestion = C. Movement = D. Absorption = E. Elimination = ## Study Diagram on page 169 II. Two types of digestion… both occur at the same time 1. mechanical = large pieces are broken into smaller pieces 2. chemical = enzymes break down polymers into monomers II. Anatomy of the Digestive System A. Mouth has taste and pressure receptors which send messages to the brain 1. hard and soft palates 2. three pairs of salivary glands produce saliva which contains.. Salivary amylase (enzyme) = Mumps = a viral infection of the salivary glands B. Teeth 1. begin mechanical digestion by… 2. bolus = Chewed food mixed with saliva by tongue into a portion small enough to swallow C. Pharynx is where air passages and food passages cross 1. swallowing is a reflex reflex = 2. the epiglottis is a flap of tissue that… 3. gagging is also a reflex which is activated when… ** Problems with the Mouth, Teeth and Pharynx - dental caries are cavities - gingivitis - tonsillitis and strep throat - cancer D. Esophagus = 1. peristalsis = 2. sphincter muscles are circular smooth muscles that act as… ** Problems with the esophagus (Health Focus, page 174) - acid reflux is caused by… - acid reflux can be prevented by… E. Stomach 1. location is upper left side of abdominal cavity 2. function 3. stomach is protected from its own acids and enzymes by… 4. gastric juice contains… Pepsin (protease enzyme) and Hydrochloric acid (HCl) ** Problems with the stomach - ulcers = sores in the lining of the stomach that do not heal easily - nausea and vomiting are reflexes used to empty the stomach when… F. Small Intestine 1. duodenum = 2. what juices are added to food here Bile from the liver…. Enzymes from the pancreas… Enzymes from the small intestine lining… **3. all digestion is finished in the small intestine 4. villi = **5. almost all nutrients are absorbed into the blood and lymph vessels by the end of the small intestine 6. Regulation of Digestive Secretions - nerves and hormones control the release of all digestive juices - gastrin = hormone that increases stomach muscle activity and release of ______ - GIP = homone released as food enters the duodenum, it slows down _________ - Secretin and CCK = hormones released as food enters the duodenum, they increase… - all hormones and juices are released only when food is present in the stomach or small intestine - Negative feedback and homeostasis at work!! G. Large Intestine – large in diameter, shorter in length than the small intestine 1. includes…colon, cecum, appendix, rectum 2. functions: Defication is a reflex = a rapid, involuntary response to a stimulus 3. Feces contain… 4. Bacteria in the Large Intestine are mostly “good guys” * Problems with the Large Intestine - polyps - diarrhea - constipation III. Three Accessory Organs – Pancreas, Liver, Gall Bladder A. Pancreas 1. location: behind the stomach (posterior) 2. function: 3. Pancreatic enzymes are released into the duodenum - pancreatic amylase - trypsin (a protease) - lipases B. Liver (hepato..) 1. location: upper right part of the abdominal cavity 2. hepatic portal system is.. a special circulation from the small intestine to the liver 3. Gatekeeper functions of the liver (see Table 9.2, page 178) 1) destroys old red blood cells excreting bilirubin 2) detoxifies blood by removing toxins 3) stores iron and fat-soluble vitamins (ADEK) 4) makes plasma proteins 5) stores and releases glucose as needed to maintain blood sugar 6) produces urea when amino acids are metabolized (sent to kidneys) 7) helps regulate cholesterol levels by making HDL and LDL ** Liver Problems - jaundice is a yellowing of the tissues due to a build up of bilirubin (a yellow/green substance produced when red blood cells are broken down) This is a symptom of… - hepatitis is an inflammation/infection of liver tissue - cirrhosis is chronic liver damage usually due to alcohol abuse * liver damage can be repaired if it is not too great C. Gall Bladder 1. location: underneath the liver on the upper right side of the abdomen 2. function ** Gall Bladder Problems - Gall stones can form when bile becomes too concentrated and forms crystals. Bile has many salts and cholesterol which can crystalize Surgery is often required and a person can live quite well without a gall bladder IV. Digestive Enzymes (Table 8.1, page 176) A. enzymes are proteins B. Enzymes to know… 1. salivary amylase 2. pepsin (a protease) 3. Pancreatic amylase 4. trypsin (a protease) 5. lipase One Enzyme Problem is lactose intolerance… Lactose is a double sugar requiring the enzyme lactase to break it apart People who are lactose intolerant do not make the enzyme lactase The undigested lactose makes it to the colon where bacteria break it down for their food causing… V. Nutrition – Check out your BMI on page 184 and information on Fad Diets on page 183, page through the information on the vitamin and mineral charts at the end of the chapter V. Homeostasis – the liver is the most important metabolic organ