7-OMENTUM-2016-Final
... From the Parietal Peritoneum Abdominal pain originating from the parietal peritoneum is therefore of the somatic type, it is usually severe, and can be accurately localized. From the Visceral Peritoneum The visceral peritoneum, including the mesenteries, is innervated by autonomic nerves. It is due ...
... From the Parietal Peritoneum Abdominal pain originating from the parietal peritoneum is therefore of the somatic type, it is usually severe, and can be accurately localized. From the Visceral Peritoneum The visceral peritoneum, including the mesenteries, is innervated by autonomic nerves. It is due ...
L8 & L9- Bile salt & Enterohepatic circulation2014-12
... Parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves supply the biliary system. Parasympathetic (vagal) stimulation results in contraction of the gallbladder and relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi, as well as increased bile formation. Bilateral vagotomy results in reduced bile secretion after a meal, suggestin ...
... Parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves supply the biliary system. Parasympathetic (vagal) stimulation results in contraction of the gallbladder and relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi, as well as increased bile formation. Bilateral vagotomy results in reduced bile secretion after a meal, suggestin ...
11 L8, Hepathobiliary function, B
... defined as the total bile acid pool. In healthy people, the bile acid pool ranges from 2 to 4 g. The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in this pool is physiologically extremely important. By cycling several times during a meal, a relatively small bile acid pool can provide the body with suffic ...
... defined as the total bile acid pool. In healthy people, the bile acid pool ranges from 2 to 4 g. The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in this pool is physiologically extremely important. By cycling several times during a meal, a relatively small bile acid pool can provide the body with suffic ...
Bilirubin
... Jaundice is the most common reason to check bilirubin levels. Most newborns have some jaundice. The doctor or nurse will often check the newborn's bilirubin level. See: Newborn jaundice The test may also be done in older infants, children, and adults who develop jaundice. A bilirubin test wi ...
... Jaundice is the most common reason to check bilirubin levels. Most newborns have some jaundice. The doctor or nurse will often check the newborn's bilirubin level. See: Newborn jaundice The test may also be done in older infants, children, and adults who develop jaundice. A bilirubin test wi ...
Nutritional Implications of Gastrointestinal and Liver Metabolism in
... contributed to our understanding of nutrient availability. These procedures are also used to study specific metabolic processes within tissue types and across tissue beds. ISOLATED TISSUE PREPARATIONS The use of everted gut sacs made from intestinal segments was first developed by Wilson & Wiseman ( ...
... contributed to our understanding of nutrient availability. These procedures are also used to study specific metabolic processes within tissue types and across tissue beds. ISOLATED TISSUE PREPARATIONS The use of everted gut sacs made from intestinal segments was first developed by Wilson & Wiseman ( ...
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
... Peritoneal versus Retroperitoneal (transverse section) • Most of the internal organs are surrounded by visceral peritoneum: INTRAPERITONEAL Structures. • Some organs (e.g. kidneys) are between peritoneum on one surface, and the body wall on the other: RETROPERITONEAL Structures. ...
... Peritoneal versus Retroperitoneal (transverse section) • Most of the internal organs are surrounded by visceral peritoneum: INTRAPERITONEAL Structures. • Some organs (e.g. kidneys) are between peritoneum on one surface, and the body wall on the other: RETROPERITONEAL Structures. ...
Digestive System - CCBC Faculty Web
... Regulation of Gastric Secretion • Neural control is accomplished by the ANS and local enteric nerve reflexes. – Autonomic control starts in the CNS. ° The parasympathetic division works through the Vagus (X) nerve and stimulates activity. ° The sympathetic division works through thoracic spinal ner ...
... Regulation of Gastric Secretion • Neural control is accomplished by the ANS and local enteric nerve reflexes. – Autonomic control starts in the CNS. ° The parasympathetic division works through the Vagus (X) nerve and stimulates activity. ° The sympathetic division works through thoracic spinal ner ...
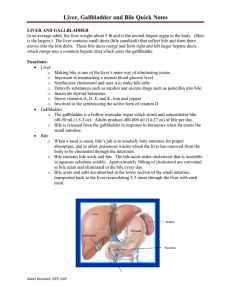
Liver, Gallbladder and Bile Quick Notes
... pain, and usually a trip to the hospital. What happens when your gallbladder is removed? • Bile acids and salts leak into the small intestine throughout the day. o There is no coordination to release bile when fat is present in the stomach. • A pseudo-gallbladder may form, but there has to be enough ...
... pain, and usually a trip to the hospital. What happens when your gallbladder is removed? • Bile acids and salts leak into the small intestine throughout the day. o There is no coordination to release bile when fat is present in the stomach. • A pseudo-gallbladder may form, but there has to be enough ...
What is BILE? - UMK CARNIVORES 3
... ii. As a result, toxins can build up over time, creating many complications and illnesses such as infection, inflammation and cancer. But can be adjusted, treated by taking bile salts orally once a day as a natural supplement to restore your digestive tract back to a clean and pristine condition. ...
... ii. As a result, toxins can build up over time, creating many complications and illnesses such as infection, inflammation and cancer. But can be adjusted, treated by taking bile salts orally once a day as a natural supplement to restore your digestive tract back to a clean and pristine condition. ...
approved
... because the permanent infoldings of the mucous membrane, the plicae circulares, are larger, more numerous, and closely set in the jejunum, whereas in the upper part of the ileum they are smaller and more widely separated and in the lower part they are absent. 3. The jejunal mesentery is attached to ...
... because the permanent infoldings of the mucous membrane, the plicae circulares, are larger, more numerous, and closely set in the jejunum, whereas in the upper part of the ileum they are smaller and more widely separated and in the lower part they are absent. 3. The jejunal mesentery is attached to ...
The peritoneum
... Four-layered fold of peritoneum, the anterior two layers descend from the greater curvature of stomach and superior part of duodenum and hangs down like an apron in front of coils of Small intestine, and then turns Upward and attaches to the transverse colon. If an infection occurs in the intestine, ...
... Four-layered fold of peritoneum, the anterior two layers descend from the greater curvature of stomach and superior part of duodenum and hangs down like an apron in front of coils of Small intestine, and then turns Upward and attaches to the transverse colon. If an infection occurs in the intestine, ...
File
... Four-layered fold of peritoneum, the anterior two layers descend from the greater curvature of stomach and superior part of duodenum and hangs down like an apron in front of coils of Small intestine, and then turns Upward and attaches to the transverse colon. If an infection occurs in the intestine, ...
... Four-layered fold of peritoneum, the anterior two layers descend from the greater curvature of stomach and superior part of duodenum and hangs down like an apron in front of coils of Small intestine, and then turns Upward and attaches to the transverse colon. If an infection occurs in the intestine, ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... digest proteins. 5. Zymogen granules are granules that store pancreatic enzymes. 6. The function of trypsinogen is to be converted to trypsin. 7. The functions of nucleases are to digest nucleic acids. C. Regulation of Pancreatic Secretion 1. Parasympathetic fibers cause the pancreas to release panc ...
... digest proteins. 5. Zymogen granules are granules that store pancreatic enzymes. 6. The function of trypsinogen is to be converted to trypsin. 7. The functions of nucleases are to digest nucleic acids. C. Regulation of Pancreatic Secretion 1. Parasympathetic fibers cause the pancreas to release panc ...
Chapter 01 FlexArt
... nerves to the medulla oblongata (green arrow), where they inhibit parasympathetic action potentials (pink arrow), thereby decreasing gastric secretions. 3 Local reflexes activated by H+ or lipids also inhibit gastric secretion (orange arrows). 4 Secretin and cholecystokinin produced by the duodenum ...
... nerves to the medulla oblongata (green arrow), where they inhibit parasympathetic action potentials (pink arrow), thereby decreasing gastric secretions. 3 Local reflexes activated by H+ or lipids also inhibit gastric secretion (orange arrows). 4 Secretin and cholecystokinin produced by the duodenum ...
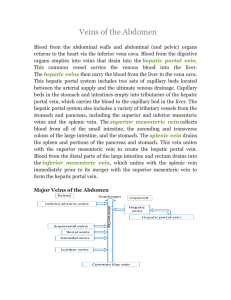
Veins of the Abdomen
... Veins of the Abdomen Blood from the abdominal walls and abdominal (and pelvic) organs returns to the heart via the inferior vena cava. Blood from the digestive organs empties into veins that drain into the hepatic portal vein. This common vessel carries the venous blood into the liver. The hepatic v ...
... Veins of the Abdomen Blood from the abdominal walls and abdominal (and pelvic) organs returns to the heart via the inferior vena cava. Blood from the digestive organs empties into veins that drain into the hepatic portal vein. This common vessel carries the venous blood into the liver. The hepatic v ...
I. Introduction
... synthesizing lipoproteins, phospholipids, and cholesterol. 4. The liver plays a key role in protein metabolism by deaminating amino acids, forming urea, synthesizing plasma proteins, and converting amino acids to other forms of amino acids. 5. The liver stores glycogen, iron, and vitamins A,D, and B ...
... synthesizing lipoproteins, phospholipids, and cholesterol. 4. The liver plays a key role in protein metabolism by deaminating amino acids, forming urea, synthesizing plasma proteins, and converting amino acids to other forms of amino acids. 5. The liver stores glycogen, iron, and vitamins A,D, and B ...
Chapter 17: Digestive System
... 4. The liver plays a key role in protein metabolism by deaminating amino acids, forming urea, synthesizing plasma proteins, and converting amino acids to other forms of amino acids. 5. The liver stores glycogen, iron, and vitamins A,D, and B12. 6. Liver cells help destroy worn out red blood cells. 7 ...
... 4. The liver plays a key role in protein metabolism by deaminating amino acids, forming urea, synthesizing plasma proteins, and converting amino acids to other forms of amino acids. 5. The liver stores glycogen, iron, and vitamins A,D, and B12. 6. Liver cells help destroy worn out red blood cells. 7 ...
I. Introduction
... digest proteins. 5. Zymogen granules are granules that store pancreatic enzymes. 6. The function of trypsinogen is to be converted to trypsin. 7. The function of nucleases are to digest nucleic acids. C. Regulation of Pancreatic Secretion 1. Parasympathetic fibers cause the pancreas to release pancr ...
... digest proteins. 5. Zymogen granules are granules that store pancreatic enzymes. 6. The function of trypsinogen is to be converted to trypsin. 7. The function of nucleases are to digest nucleic acids. C. Regulation of Pancreatic Secretion 1. Parasympathetic fibers cause the pancreas to release pancr ...
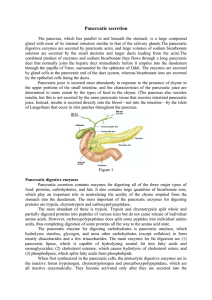
Pancreatic secretion
... can be autocatalytically activated by trypsin that has already been formed from previously secreted trypsinogen. Chymotrypsinogen is activated by trypsin to form chymotrypsin, and procarboxypolypeptidase is activated in a similar manner. It is important that the proteolytic enzymes of the pancreatic ...
... can be autocatalytically activated by trypsin that has already been formed from previously secreted trypsinogen. Chymotrypsinogen is activated by trypsin to form chymotrypsin, and procarboxypolypeptidase is activated in a similar manner. It is important that the proteolytic enzymes of the pancreatic ...
NVCC Bio 212 - gserianne.com
... •Water-soluble through diffusion, except B12 (active transport) • Vitamin K (large intestine) – with other lipids • absorbed into blood ...
... •Water-soluble through diffusion, except B12 (active transport) • Vitamin K (large intestine) – with other lipids • absorbed into blood ...
SKELETAL SYSTEM LAB
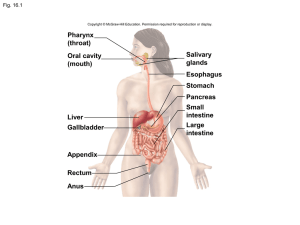
... cm (10 in.) long and extends from the laryngopharynx through the esophageal hiatus in the diaphragm and ends in the superior portion of the stomach.) _____ stomach (This is a J-shaped organ that lies under the diaphragm. The superior part is connected to the esophagus. The inferior part empties into ...
... cm (10 in.) long and extends from the laryngopharynx through the esophageal hiatus in the diaphragm and ends in the superior portion of the stomach.) _____ stomach (This is a J-shaped organ that lies under the diaphragm. The superior part is connected to the esophagus. The inferior part empties into ...
Chapter 15
... – The large intestine does not digest or absorb nutrients, but it does secrete mucus. – The large intestine absorbs electrolytes and water. – The large intestine contains important bacteria which synthesize vitamins and use cellulose. ...
... – The large intestine does not digest or absorb nutrients, but it does secrete mucus. – The large intestine absorbs electrolytes and water. – The large intestine contains important bacteria which synthesize vitamins and use cellulose. ...
Alaskan Husky encephalopathy - UC Davis School of Veterinary
... findings have been defined and permit antemortem presumptive diagnosis [12, 21, 43, 45, 49]. Investigations of LS have revealed an array of biochemical and genetic abnormalities, clearly demonstrating that the characteristic complex of neuropathological features traditionally required to make this d ...
... findings have been defined and permit antemortem presumptive diagnosis [12, 21, 43, 45, 49]. Investigations of LS have revealed an array of biochemical and genetic abnormalities, clearly demonstrating that the characteristic complex of neuropathological features traditionally required to make this d ...
Chapter 25 - digestive - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... 1) epithelium: glandular epithelial cells, secrete digestive juices & goblet cells that secrete mucus. This changes with the location of the digestive tract. Eg) esophagus: stratified squamous ; stomach: simple columnar with goblet cells; small intestine; simple columnar with microvilli & goblet cel ...
... 1) epithelium: glandular epithelial cells, secrete digestive juices & goblet cells that secrete mucus. This changes with the location of the digestive tract. Eg) esophagus: stratified squamous ; stomach: simple columnar with goblet cells; small intestine; simple columnar with microvilli & goblet cel ...
Hepatic encephalopathy

Hepatic encephalopathy (HE), also known as portosystemic encephalopathy, is the occurrence of confusion, altered level of consciousness, and coma as a result of liver failure. In the advanced stages it is called hepatic coma or coma hepaticum. It may ultimately lead to death.It is caused by accumulation in the bloodstream of toxic substances that are normally removed by the liver. The diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy requires the presence of impaired liver function and the exclusion of an alternative explanation for the symptoms. Blood tests (ammonia levels) may assist in the diagnosis. Attacks are often precipitated by an intercurrent problem, such as infection or constipation.Hepatic encephalopathy is reversible with treatment. This relies on suppressing the production of the toxic substances in the intestine and is most commonly done with the laxative lactulose or with non-absorbable antibiotics. In addition, the treatment of any underlying condition may improve the symptoms. In particular settings, such as acute liver failure, the onset of encephalopathy may indicate the need for a liver transplant.