L8 & L9- Bile salt & Enterohepatic circulation2014-12
... Hepatocyte Arrangement Aids in the Rapid Exchange of Molecules • Hepatocytes are highly specialized cells. • Sinusoidal endothelial cells separates the perisinusoidal space (Disse space). Endothelial cells of the liver lack a basement membrane. They have sievelike plates that permit the ready exc ...
... Hepatocyte Arrangement Aids in the Rapid Exchange of Molecules • Hepatocytes are highly specialized cells. • Sinusoidal endothelial cells separates the perisinusoidal space (Disse space). Endothelial cells of the liver lack a basement membrane. They have sievelike plates that permit the ready exc ...
Reasons for modification and discontinuation of - estudo ATAR-VIH
... problems with adherence, sub-optimal therapy, discontinuation of therapy, and potentially to treatment failure [21]. Clinical trials have reported the frequency and severity of toxicities associated with HAART but similar results from observational studies are less common. In a group of patients sta ...
... problems with adherence, sub-optimal therapy, discontinuation of therapy, and potentially to treatment failure [21]. Clinical trials have reported the frequency and severity of toxicities associated with HAART but similar results from observational studies are less common. In a group of patients sta ...
Ischaemic Heart Disease
... The assumption that direct and indirect bilirubins represent conjugated and unconjugated bilirubins, respectively although in several assays this may be incorrect. The lack of adequate standards for calibration of the direct bilirubin assay. Direct bilirubin assays have used unconjugated bilirubin f ...
... The assumption that direct and indirect bilirubins represent conjugated and unconjugated bilirubins, respectively although in several assays this may be incorrect. The lack of adequate standards for calibration of the direct bilirubin assay. Direct bilirubin assays have used unconjugated bilirubin f ...
book - MUK Publications
... intestines is known as enterocolitis, which may lead todiarrhoea. Acute conditions affecting the bowels include infectious diarrhoea and mesenteric ischaemia. Causes of constipation may include faecal impaction and bowel obstruction, which may in turn be caused by ileus, intussusception, volvulus. I ...
... intestines is known as enterocolitis, which may lead todiarrhoea. Acute conditions affecting the bowels include infectious diarrhoea and mesenteric ischaemia. Causes of constipation may include faecal impaction and bowel obstruction, which may in turn be caused by ileus, intussusception, volvulus. I ...
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction
... • Sclerosing inflammation of the bile duct or biliary tree (cholangitis) in cats (characterized by thickening or hardening of the biliary and/or liver tissues)—clinically may mimic blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction) since disease may involve extrahe ...
... • Sclerosing inflammation of the bile duct or biliary tree (cholangitis) in cats (characterized by thickening or hardening of the biliary and/or liver tissues)—clinically may mimic blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction) since disease may involve extrahe ...
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction
... • Sclerosing inflammation of the bile duct or biliary tree (cholangitis) in cats (characterized by thickening or hardening of the biliary and/or liver tissues)—clinically may mimic blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction) since disease may involve extrahe ...
... • Sclerosing inflammation of the bile duct or biliary tree (cholangitis) in cats (characterized by thickening or hardening of the biliary and/or liver tissues)—clinically may mimic blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction) since disease may involve extrahe ...
extrahepatic_bile_duct_ostruction
... • Sclerosing inflammation of the bile duct or biliary tree (cholangitis) in cats (characterized by thickening or hardening of the biliary and/or liver tissues)—clinically may mimic blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction) since disease may involve extrahe ...
... • Sclerosing inflammation of the bile duct or biliary tree (cholangitis) in cats (characterized by thickening or hardening of the biliary and/or liver tissues)—clinically may mimic blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction) since disease may involve extrahe ...
Ch11 - ISpatula
... adjective endocrine indicates that a particular gland’s secretions are internal, e The rather than external; that is, secretions are not expelled through a duct. Glands that do expel their secretions through a duct are called exocrine glands. You will learn more about the endocrine system in Chapter ...
... adjective endocrine indicates that a particular gland’s secretions are internal, e The rather than external; that is, secretions are not expelled through a duct. Glands that do expel their secretions through a duct are called exocrine glands. You will learn more about the endocrine system in Chapter ...
8. Russell JA, Walley KR, Gordon AC, et al. Interaction of
... duration and reduced dose, when used together in the treatment of septic shock but it did not alter plasma vasopressin levels. Further trials are needed to assess the clinical effectiveness of vasopressin as the initial vasopressor therapy with or without corticosteroids. ISRCTN66727957 ...
... duration and reduced dose, when used together in the treatment of septic shock but it did not alter plasma vasopressin levels. Further trials are needed to assess the clinical effectiveness of vasopressin as the initial vasopressor therapy with or without corticosteroids. ISRCTN66727957 ...
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Obstruction
... Monitor blood work (serum chemistry profile, especially total bilirubin values [reflect effectiveness of relief of bile-duct obstruction—should decline to near normal within days] and liver enzymes [decline slowly]) Complete blood count (CBC)—repeat every two to three days initially, if patient ...
... Monitor blood work (serum chemistry profile, especially total bilirubin values [reflect effectiveness of relief of bile-duct obstruction—should decline to near normal within days] and liver enzymes [decline slowly]) Complete blood count (CBC)—repeat every two to three days initially, if patient ...
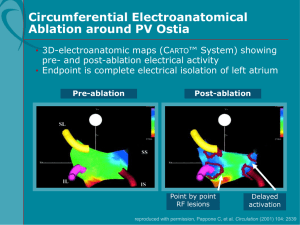
Section III: Catheter Ablation for the Treatment of AFib
... • Operator located away from X-ray exposure, not ...
... • Operator located away from X-ray exposure, not ...
Octreotide - Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA)
... diagnosis many patients have advanced disease at the time of diagnosis. Clinical incidence is probably higher than stated in the literature. Non Functioning tumours: Asymptomatic NETs in the distal small intestine are discovered while searching for a primary in patients with newly discovered liver m ...
... diagnosis many patients have advanced disease at the time of diagnosis. Clinical incidence is probably higher than stated in the literature. Non Functioning tumours: Asymptomatic NETs in the distal small intestine are discovered while searching for a primary in patients with newly discovered liver m ...
Formoterol Turbuhaler as reliever medication in patients with acute asthma
... Formoterol is the only long-acting b2-agonist that has been approved for use as both maintenance and reliever therapy for chronic symptomatic asthma. As a result, some patients may be using formoterol as their only b2-agonist bronchodilator. In the event of acute asthma worsening, such patients must ...
... Formoterol is the only long-acting b2-agonist that has been approved for use as both maintenance and reliever therapy for chronic symptomatic asthma. As a result, some patients may be using formoterol as their only b2-agonist bronchodilator. In the event of acute asthma worsening, such patients must ...
11 L8, Hepathobiliary function, B
... hemobilirubin (unconjugated bilirubin) which is rapidly transported to hepatocytes for further metabolism (even when bound to albumin, it’s called free bilirubin). 3. The liver removes bilirubin from the circulation rapidly, mediated by a carrier protein (receptor), and conjugates it with glucuronic ...
... hemobilirubin (unconjugated bilirubin) which is rapidly transported to hepatocytes for further metabolism (even when bound to albumin, it’s called free bilirubin). 3. The liver removes bilirubin from the circulation rapidly, mediated by a carrier protein (receptor), and conjugates it with glucuronic ...
Albumin (Latin: albus, white) refers generally to any protein with
... In critical illness, there is a stronger correlation between colloid oncotic pressure and Total protein than with albumin. In these patients the decreased albumin is compensated for by an increase in acute phase proteins. Unquestionably there is increased leakage of albumin and this drags fluid with ...
... In critical illness, there is a stronger correlation between colloid oncotic pressure and Total protein than with albumin. In these patients the decreased albumin is compensated for by an increase in acute phase proteins. Unquestionably there is increased leakage of albumin and this drags fluid with ...
Prevention and Management of Gastroesophageal Varices and
... tissue and regenerative nodules. In addition to this structural resistance to blood flow, there is an active intrahepatic vasoconstriction that accounts for 20–30% of the increased intrahepatic resistance (8), and that is mostly due to a decrease in the endogenous production of nitric oxide (9, 10). ...
... tissue and regenerative nodules. In addition to this structural resistance to blood flow, there is an active intrahepatic vasoconstriction that accounts for 20–30% of the increased intrahepatic resistance (8), and that is mostly due to a decrease in the endogenous production of nitric oxide (9, 10). ...
Liver biopsy
... Data derived from multiple randomized clinical trials or meta-analyses Data derived from a single randomized trial, or nonrandomized studies Only consensus opinion of experts, case studies, or standard-of-care ...
... Data derived from multiple randomized clinical trials or meta-analyses Data derived from a single randomized trial, or nonrandomized studies Only consensus opinion of experts, case studies, or standard-of-care ...
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
... back on itself forming a double Membrane: mesentery Functions of mesentery:(1)Provides support: Intestines: Mesentery & Mesocolon. Stomach: Omenta. Liver: Falciform ligament. (2) Prevents intestinal twisting (3) Stores fat (4) Pathway for vessels & nerves 2. Visceral Layer: covers the organs. Perito ...
... back on itself forming a double Membrane: mesentery Functions of mesentery:(1)Provides support: Intestines: Mesentery & Mesocolon. Stomach: Omenta. Liver: Falciform ligament. (2) Prevents intestinal twisting (3) Stores fat (4) Pathway for vessels & nerves 2. Visceral Layer: covers the organs. Perito ...
Pediatric PSC Medical Issues
... of autoimmune features in pediatric PSC compared to the adult disease may have important implications for treatment and outcome, and results of drug trials in adults are not necessarily applicable to children with PSC. (children are not small adults). ...
... of autoimmune features in pediatric PSC compared to the adult disease may have important implications for treatment and outcome, and results of drug trials in adults are not necessarily applicable to children with PSC. (children are not small adults). ...
Long-Term Management of the Successful Adult Liver
... and microbiological confirmation (grade 1, level A). a. Blood cultures are most helpful for the diagnosis of Candida bloodstream infections (class 1, level B) and Blastomyces (grade 1, level B). b. Cryptococcal antigen testing of cerebrospinal fluid or blood is most helpful for the diagnosis of Cryp ...
... and microbiological confirmation (grade 1, level A). a. Blood cultures are most helpful for the diagnosis of Candida bloodstream infections (class 1, level B) and Blastomyces (grade 1, level B). b. Cryptococcal antigen testing of cerebrospinal fluid or blood is most helpful for the diagnosis of Cryp ...
National Medical Policy
... significant quality-of-life issues can be given priority for listing for deceased donor organs, absent any absolute contraindications to liver transplantation. These patients should be referred as early as possible to a transplant facility that performs a reasonably high volume of liver transplantat ...
... significant quality-of-life issues can be given priority for listing for deceased donor organs, absent any absolute contraindications to liver transplantation. These patients should be referred as early as possible to a transplant facility that performs a reasonably high volume of liver transplantat ...
Bilirubin
... The excess amount transferred to intestine to be excreted in urine and stool. However 95% of the secreted bile is reabsorbed by the small intestine. This bile is then resecreted by the liver into the small intestine. This process is known as enterohepatic circulation About half of the conjuga ...
... The excess amount transferred to intestine to be excreted in urine and stool. However 95% of the secreted bile is reabsorbed by the small intestine. This bile is then resecreted by the liver into the small intestine. This process is known as enterohepatic circulation About half of the conjuga ...
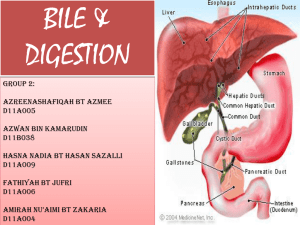
What is BILE? - UMK CARNIVORES 3
... ii. As a result, toxins can build up over time, creating many complications and illnesses such as infection, inflammation and cancer. But can be adjusted, treated by taking bile salts orally once a day as a natural supplement to restore your digestive tract back to a clean and pristine condition. ...
... ii. As a result, toxins can build up over time, creating many complications and illnesses such as infection, inflammation and cancer. But can be adjusted, treated by taking bile salts orally once a day as a natural supplement to restore your digestive tract back to a clean and pristine condition. ...
Hyaluronic Acid Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma
... (VAS) for pain, and Lysholm knee score; and (3) difference in intra-articular biochemical marker concentrations. Results: There were 49 patients randomized to treatment with PRP and 50 randomized to treatment with HA. No difference was seen between the groups in the primary outcome measure (WOMAC pa ...
... (VAS) for pain, and Lysholm knee score; and (3) difference in intra-articular biochemical marker concentrations. Results: There were 49 patients randomized to treatment with PRP and 50 randomized to treatment with HA. No difference was seen between the groups in the primary outcome measure (WOMAC pa ...
Medical Terminology
... Rect/al: Pertaining to the rectum Rect/o/cele: Herniation of the rectum Rect/o/scope: Instrument for examining the rectum Col/o/rect/al: Pertaining to the colon and rectum Rect/o/scopy: The process of examining the rectum with a rectoscope Rect/o/scopic (adj.): Pertaining to rectoscopy ...
... Rect/al: Pertaining to the rectum Rect/o/cele: Herniation of the rectum Rect/o/scope: Instrument for examining the rectum Col/o/rect/al: Pertaining to the colon and rectum Rect/o/scopy: The process of examining the rectum with a rectoscope Rect/o/scopic (adj.): Pertaining to rectoscopy ...
Liver support systems

Hepatic insufficiency implies the inability of the liver to carry out its metabolic, excretory and detoxifying functions owing to a decrease in the number of functional hepatocytes or because their normal activity is altered.Hepatic insufficiency can be acute or chronic. Acute liver failure (ALF) is produced without a previous liver disease whereas the chronic liver failure is the consequence of a liver disease evolution over a long period of time, independently of its etiology and degree.The incidence of acute liver failure is estimated to be of 1-6 cases per million of person. ALF can be subclassified into hyperacute, acute and subacute based on when hepatic encephalopathy occurs following the onset of jaundice (O`Grady et al., 1993), and this classification can sometimes help to identify the etiology, potential complications and patient prognosis (Table 1).In hyperacute and acute liver failure the clinical picture develops rapidly with progressive encephalopathy and multiorgan dysfunction such as hyperdynamic circulation, coagulopathy, acute renal and respiratory insufficiency, severe metabolic alterations and cerebral edema that can lead to brain death. In these cases the mortality without liver transplantation (LTx) ranges between 40-80%. LTx is the only effective treatment for these patients although it requires a precise indication and timing to achieve good results. Nevertheless, due to the scarcity of organs to carry out liver transplantations, it is estimated that one third of patients with ALF die while waiting to be transplanted.On the other hand, a patient with a chronic hepatic disease can suffer an acute decompensation of liver function following a precipitating event such as variceal bleeding, sepsis and excessive alcohol intake among others that can lead to a condition referred to as acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF).Both types of hepatic insufficiency, ALF and ACLF, can potentially be reversible and liver functionality can return to a level similar to that prior to the insult or precipitating event.LTx is the only treatment that has shown an improvement in the prognosis and survival with most severe cases of ALF. Nevertheless, cost and donor scarcity have prompted researchers to look for new supportive treatments that can act as “bridge” to the transplant procedure. By stabilizing the patient’s clinical state, or by creating the right conditions that could allow the recovery of native liver functions, both detoxification and synthesis can improve, after an episode of ALF or ACLF.Basically, three different types of supportive therapies have been developed: bio-artificial, artificial and hybrid liver support systems (Table 2).Bio-artificial liver support systems are experimental extracorporeal devices that use living cell lines to provide detoxification and synthesis support to the failing liver. Bio-artificial liver (BAL) Hepatassist 2000 uses porcine hepatocytes11 whereas ELAD system employs hepatocytes derived from human hepatoblastoma C3A cell lines.9, Both techniques can produce, in fulminat hepatic failure (FHF), an improvement of hepatic encephalopathy grade and biochemical parameters. Nevertheless, they are therapies with high complexity that require a complex logistic approach for implementation; a very high cost and possible inducement of important side effects such as immunological issues (porcine endogenous retrovirus transmission), infectious complications and tumor transmigration have been documented. Other biological hepatic systems are Bioartificial Liver Support (BLSS)12 and Radial Flow Bioreactor (RFB).15 Detoxification capacity of these systems is poor and therefore they must be used combined with other systems to mitigate this deficiency. Today its use is limited to centers with high experience in their application.Artificial liver support systems are aimed to temporally replace native liver detoxification functions and they use albumin as scavenger molecule to clear the toxins involved in the physiopathology of the failing liver. Most of the toxins that accumulate in the plasma of patients with liver insufficiency are protein bound, and therefore conventional renal dialysis techniques, such as hemofiltration, hemodialysis or hemodiafiltration are not able to adequately eliminate them.Between the different albumin dialysis modalities, single pass albumin dialysis (SPAD) has shown some positive results at a very high cost; it has been proposed that lowering the concentration of albumin in the dialysate does not seem to affect the detoxification capability of the procedure. Nevertheless, the most widely used systems today are based on hemodialysis and adsorption. These systems use conventional dialysis methods with an albumin containing dialysate that is latter regenerate by means of adsorption columns, filled with activated charcoal and ion exchange resins. At present, there are two artificial extracorporeal liver support systems: the Molecular Adsorbents Recirculating System (MARS)10 from Gambro and Fractionated Plasma Separation and Adsorption (FPSA), commercialised as Prometheus (PROM) from Fresenius Medical Care.13 Of the two therapies, MARS is the most frequently studied, and clinically used system to date.