* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes #8 PPT - Duplin County Schools
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
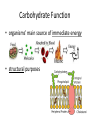
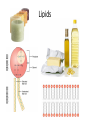
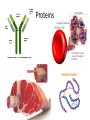
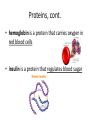
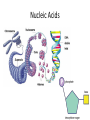
Wednesday February 15, 2017 I can: Agenda Catalyst 1. How will you study more effectively for the next Unit Test? 2. What did you do best on with the Unit 1 Test (what do you think)? What do you need to work more on for the EOC for Ecology? (10) Catalyst (20) GN: Biomolecules (15) Amoeba Sisters Video Recap (15) Biomolecule Puzzle (20) IP: Macromolecules (5) Exit Ticket understand the structure of the four classes of biomolecules HW: IP: Macromolecules Quiz corrections & Extra Credit (Friday) Data Tracking • Biology Master Tracker (Unit 1) – Complete based on test and turn in – Complete HONESTLY. This is for YOU to reflect on. • Growth Chart *GOAL = 80%* – Objectives: • Pre-Benchmark • Quiz 1 (Ecology) • Test 1 (Ecology) Most Missed Questions • • • • • • • • 2 8 14 15 27 39 42 43 Test Corrections / Retakes • Must submit test corrections within one week (due next Thursday, February 23) • Tell me the correct answer and WHY it’s the correct answer • Schedule retest whenever you want (before school, lunch and learn, after school, 1st period) • You keep higher score Big Idea By understanding the chemistry and molecules that make up life, we have deeper insight into how life functions. What do these Macromoleculesstructures all have in common? carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic acids Four groups of molecules make up the building blocks of life. In general, they are called macromolecules (aka organic molecules aka biomolecules). Macromolecules Macromolecules are formed by polymerization, in which large polymers are built by joining small subunits called monomers together. monomers = subunits = building blocks of molecules polymers = monomers joined up by polymerization Carbohydrates Carbohydrate Structure • made up of C, H, and O • polysaccharides are polymers made up of monosaccharides, or simple sugars Carbohydrate Function • organisms’ main source of immediate energy • structural purposes Carbohydrates, cont. • the tough fiber found in plants is made up of the carb cellulose • sugars end in –ose • examples of simple sugars: • complex sugars are called starches Detecting Carbohydrates Simple Sugars • simple sugars turn orange in the presence of Benedict’s solution no carbs carbs present Starches • starches turn deep purple in the presence of iodine, or Lugol’s solution Lipids Lipid Structure • made up of C, H, and O • made up of glycerol and fatty acids – long chains Lipid Functions • make up fats, oils, and waxes • store energy, makes up the cell membrane, and used in waterproof coverings waxy cuticle of leaf = lipids to repel water walrus blubber = lipids to store energy Detecting Lipids brown paper bag test Proteins Protein Structure • made up of C, H, O, N • amino acid subunits form long polypeptide chains – over 20 different amino acids an individual amino acid Protein Function • the most diverse macromolecules • various roles: – speed up reactions (enzymes) – form muscles – transport substances – fight disease Proteins, cont. • hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells • insulin is a protein that regulates blood sugar Protein Detection Biuret’s solution turns from blue to light purple in the presence of protein Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acid Structure • made up of C, H, O, N, and P • subunits: nucleotides – nucleotides are made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base Nucleic Acid Function • store and transmit hereditary information Nucleic Acids, cont. Two examples: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) Write on your board! What are the four classes of biomolecules? Write on your board! Monomers join up to form a ___________. Write on your board! The monomer of carbohydrates are: Write on your board! The monomer of nucleic acids are: Write on your board! Fatty acids and glycerol make up __________ Write on your board! Amino acids join up to form a __________ chain. Write on your board! What biomolecule makes up the cell membrane? Write on your board! What biomolecule is found in a walrus’ blubber? Write on your board! Which biomolecules stores genetic information? Write on your board! This biomolecule is found in your muscles. Write on your board! This biomolecule is used by all cells for energy.