* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download antibodies for cancer immunology immunotherapy research
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
12-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
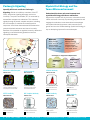
ANTIBODIES FOR CANCER IMMUNOLOGY IMMUNOTHERAPY RESEARCH Immune Checkpoint Blockade STING Pathway Investigate co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory molecules with high-quality, multi-application validated antibodies. Co-inhibitory and co-stimulatory molecules play a critical role in T cell activation and tumor cell recognition and killing. Along with MHC/TCR engagement, co-signaling molecules direct the outcome of T cell activation. In the context of cancer, tumor cells exploit the upregulation of co-inhibitory molecules to promote their own survival and avoid immune recognition. Interrogate the STING Pathway by Western blot, IHC, or Flow. STING (Stimulator of Interferon Genes) is a detector of intracellular viral molecules and double stranded DNA. Activation of STING triggers phosphorylation of downstream NAK/TBK1 and IRF3 to activate immunity and a type I interferon response. The ability of STING agonists to activate a potent anti-tumor immune response has driven increased interest in the pathway for cancer immunotherapy. T cell Costimulatory APC OX40 OX40L CD27 CD27L CD137 CD137L CD28 cGAS CD80/CD86 TCR Type I IFNs +ATP +GTP MHC CTLA-4 cGAMP p65 CD80/CD86 PD1 Coinhibitory dsDNA PD-L1/PD-L2 CD80 PD-L1 GAL9 TIM3 p60 NF-kB STING IRF3 TBK1 P IRF3 P IRF3 VISTA/PD-1H Antibody PD-L1 Antibody IRF3 Antibody (2G3) STING Antibody IHC: VISTA staining of human kidney. IHC: PD-L1 staining of human colon cancer. IHC: IRF3 staining of adenocarcinoma of colon tissue. IHC: STING staining of human breast tumor. NBP1-88967 (3 Publications) LAG-3 Antibody NBP1-97657 Flow: LAG-3 FITC staining in resting and PHA activated lymphocytes. (9 Publications) MAB1561 NBP1-47812 (5 Publication) (1 Publication) PD-1 Antibody NAK/TBK1 Antibody AF1086 NB100-56705 IHC: PD-1 staining of human lymph node. IHC: TBK1 on human testis. (9 Publications) NBP2-24683 (17 Publications) RelA/NFkB p65 Antibody NB100-2176 IHC: RelA staining of human DLBCL showing nuclear expression in the tumor cells. (16 Publications) p: 303.730.1950 • f: 303.730.1966 • [email protected] • www.novusbio.com Purinergic Signaling Quantify ATP levels and Probe Purinergic Signaling. Similar to inhibitory members of the B7 family, adenosine signaling dampens anti-tumor immunity. The purine nucleotide, ATP, is converted by extracellular receptors to adenosine. This molecule signals through G-protein coupled receptors, including Human se the A2A receptor, to mediate immunosuppresive Cd11b+ It has been demonstrated that adenosine 1b+ responses. y1/Ly-6G- HLA-Drreceptor CD14+blockade enhances anti-tumor immunity. C+ Lin- of its potential to regulate immunity, adenosine Because CD66bsignaling CD15- is considered next generation immune checkpoint blockade. e b+ Ly-6G+ - Human Cd11b+ HLA-DrCD14LinCD66b+ CD15+ Pannexin-1 ATP P2X P2Y CD39 ADP AR CD73 ATP 2 Myeloid Cell Biology and The Tumor Microenvironment Understand the tumor microenvironment and myeloid cell biology with Novus antibodies. Suppressive myeloid cells in the tumor microenvironment inhibit anti-tumor immunity. By secreting suppressive and angiogenic molecules, tumor-associated macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote tumor growth and survival. Understanding myeloid cell biology is key to developing improved immunotherapies. Monocytic Granulocytic Mouse monocytic: CD11b+ Gr-1/Ly-6Glo Ly-6Chigh Mouse granulocytic: Human monocytic: Lin- CD11b+ CD14+ CD15– CD33+ CD66b– HLA-DR– Human granulocytic: Lin–CD11b+ CD14– CD15+ CD33+ CD66b+ HLA-DR– CD11b+ Gr-1/Ly-6Ghigh Ly-6Clo 2 NT 3 AMP Adenosine A1 receptor Gi or Go A2A receptor Gs Adenosine A2B receptor Gsor Gq Stimulatory vs. Suppressive Myeloid Cells AMP A3 receptor Gi or Gq Stimulatory Suppressive IL-12hi IL-10lo IL-12lo IL-10hi ROS TGF-B Arginase RNI Adenosine A2a Receptor CD39 Antibody CD11b Antibody ICC/IF: Adenosine A2a receptor antibody staining in the cytoplasm of U251 cells. ICC/IF: CD39 antibody staining in human aortic valve endothelial cells. Flow: Detection of CD11 b/c in fixed Hela cells. CD73 Antibody HIF-1 alpha Antibody CD68 Antibody iNOS Antibody IHC: CD73 antibody staining of human duodenum. WB; HIF-1 alpha analysis of COS-7 nuclear extracts. IHC staining of CD68 in human spleen. WB: iNOS staining in stimulated astrocytes. NB300-597 NBP1-85740 (3 Publications) NBP1-90071 NB100-105 (580 Publications) NB110-40766 (14 Publications) NB100-683 (26 Publications) HLA-DR Antibody NB100-77855 Flow: HLA-DR expression in BDCM cells. (26 Publications) NB300-605 (12 Publications) p: 303.730.1950 • f: 303.730.1966 • [email protected] • www.novusbio.com









![Anti-PCB antibody [3H2AD9] ab110314 Product datasheet 3 Images Overview](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000076345_1-acbfa58e194757c519d151062b812354-150x150.png)
