* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7 - HCC Learning Web
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
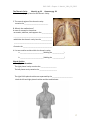
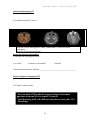
BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define anatomy and physiology. 2. Explain the relationship between anatomy & physiology. 3. List and explain the levels of organization in the human body from the simplest to the most complex level. 4. List the 11 organ systems and describe their functions. 5. Describe homeostasis and explain the importance of negative and positive feedback loops to maintain normal human body functioning. 6. Use anatomical terms to describe body regions, relative positions, body sections, and body cavities 7. Describe medical imaging techniques in terms of their function and use in the diagnosis of diseases. Learning Outcome 1: Define Anatomy and Physiology Martini: 1-2 Anatomy is structure, and physiology is function, pg. 4 Openstax: 1.1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology, pg. 16 1. What is Anatomy? The study of _____________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 2. What is Physiology? The study of _________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW Anatomy: the study of body ___________________ Physiology: the study of ______________________ 1 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 Learning Outcome 2: Explain the relationship between anatomy & physiology. Martini: 1-4 Anatomy and physiology are closely integrated, pg. 5 Openstax: 1.1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology, pg. 17 1. Explain how anatomy and physiology are related to each other: 1a. The shape of a structure ______________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 1b. Physiological processes are explained in terms of __________________________ Learning Outcome 3: List and explain the levels of organization in the human body from the simplest to the most complex level. . Martini: 1-4 Levels of organization progress from molecules to a complete organism, pg. 6 Openstax: 1.2 Structural Organization of the Human Body, pg. 17 1. List the six (6) levels of organization of the human body, from the simplest to the most complex level: 1. _____________________________ 2. _____________________________ Simplest to Fig. 1-1 or or 3. _____________________________ 4. _____________________________ 5. _____________________________ 6. _____________________________ Most Complex 2. Describe the levels of organization in the human body. Chemical Level: composed of ____________, _________________________ and ___________________________ Atoms: _______________________________________________________________ List examples of atoms: Molecules: combination of ______________________________________ List examples of molecules: 2 OS Fig. 1.3 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 Cellular Level Cell: __________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ List examples of cells found in the human body: What is an organelle? Tissue Level Tissue: ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Name the four (4) main body tissues: Organ Level Organ: _____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ List an organ and the type of tissues it is made of: Organ: ___________ Type of tissues in this organ: Organ System Level Fig. 1-1 or OS Fig. 1.4 Organ System:_______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ How many organ systems does a human have? _____ organ systems List examples of organ systems: Organism Level Organism: ____________________________________________ 3 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 LABEL the levels of organization in the human body from the most complex to the simplest level of organization (SEE Fig. 1-1 or OS Fig. 1.3) REVIEW 1. List from the Largest (most complex) to the smallest (simplest) level of organization: Largest 1. ____ A. Molecules Smallest 2. ____ B. Organ 3. ____ C. Atom 4. ____ D. Organism 5. ____ E. Organ System 6. ____ F. Organelles and Cells 7. ____ G. Tissue 2. Arrange in order from the simplest to the most complex level of organization: 4 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 Learning Outcome 4: List the 11 organ systems and describe their functions. Martini: Figure 1-1, pg. 8-9 Openstax: Fig 1.4 & Fig 1.5, pg. 19-20 1. KNOW the name of the 11 organ systems and Function/s of each. ? Review questions about Organ Systems 1. Describe the function/s for each organ system: Organ System Function/s Integumentary Skeletal Muscular Nervous Endocrine Cardiovascular Lymphatic Respiratory Digestive Urinary Reproductive Male Reproductive System: Female Reproductive System: 5 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 2. Match each organ system with its functions: ____ a. nervous system ____b. endocrine system ____c. urinary system ____d. cardiovascular system ____e. muscular system ____f. respiratory system ____g. digestive system ____h. skeletal system ____i. integumentary system ____j. lymphatic system & immunity ____k reproductive system 1.regulates body activities through hormones transported in blood to different target organs in the body. 2. produces gametes; releases hormones to gonads 3. protects against disease; returns fluids blood 4. protects body by forming a barrier to the outside environment; helps regulate body temperature 5. transports oxygen and nutrients to cells; protects against disease; carries wastes away from cells 6. regulates body activities through nerve impulses; receives sensory information; interprets and responds to the information 7. carries out the physical and chemical breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients 8. exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between air and blood 9. supports and protects the body; provides internal framework; provides a place for skeletal muscle attachment 10. powers movement of the body and stabilizes body position 11. eliminates wastes; regulates volume & chemical composition of blood Learning Outcome 5: Describe homeostasis and explain the importance of negative and positive feedback loops to maintain n normal human body functioning. Martini: 1-5 Homeostasis is the state of internal balance, pg. 7 Openstax: 1.5 Homeostasis, pg. 27 1. What is homeostasis? The body’s ability to maintain ___________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 1a. List examples of stable physiological conditions: A. ___________________________________ Normal physiological range: B. ____________________________________ Normal physiological range: 6 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 C. ____________________________________ Normal physiological range: ? Why is homeostatic regulation of physiological conditions important for an organism? 2. The body regulates its internal environment through _________________________ 2a. List the two Feedback Systems: A. ________________________________________________________________ B. _________________________________________________________________ 3. BOTH, Negative and Positive Feedback System, have three basic components: A. _______________________________ Fig. 1-2 OS Fig. 1.10 B. _______________________________ C. _______________________________ 3a. Describe each component of the Feedback Systems: A. Sensor or Receptor -It is a ____________________________ -Monitors ____________________________________________________________ -Sends input to ________________________________________________________ B. Control Center -Sets ________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ -Evaluates ___________________________________________________________ -Sends output (as nerve signals, hormones, etc) to ___________________________ -Examples of Control Centers: ___________________________________________ C. Effector -Receives ____________________________________________________________ -Produces a response that changes _______________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ -Example of Effectors: __________________________________________________ 7 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 4. Negative feedback Martini, pg. 10 4a. What is negative feedback? OpenStax: pg. 27 4b. Describe examples of negative feedback mechanism: 5. Remember these details about negative feedback mechanism: 5a. It is a process in which the body senses a ________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 5b. Body is brought back into ___________________________________________ 5c. Negative feedback is the _______________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 5d. Homeostatic mechanisms using negative feedback normally ignore _______ _____________ and they maintain a normal ______________ rather than a ____ __________________________________ Fig. 1-3b 8 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 6. Positive feedback Martini, pg. 12 6a. What is Positive Feedback? OpenStax: pg. 28 6b. Positive feedback mechanisms occur in the body when: _______________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 6c. List examples of positive feedback mechanisms: Childbirth – A Positive Feedback Mechanism Example 7. Remember these details about positive feedback mechanism: 7a. Produces a response that ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 7b. Body is moved away from ___________________________________________ 7c. Positive feedback mechanisms are ____________________________________ 7d. Positive feedback is used to __________________________________________ 9 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 Learning Outcome 6: Use anatomical terms to describe body regions, relative positions, body sections, and body cavities Martini: 1-7 Anatomical Terms, pg. 14 1-8 Body Cavities of the Trunk, pg. 18 Openstax: 1.6 Anatomical Terminology, pg. 29 Body Cavities, pg. 32 1. The standard body “map” or body reference position is the _____________________ Anatomical Position 1. Describe the anatomical position: It is a stance in which a person stands… a) _____________ b) Face: ________________________________________________ c) Feet: ________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ d) Arms and Hands ______________________________________ e) Palms of Hands _______________________________________ Fig. 1-5 OS Fig. 1.12 2. A body that is lying down is described as either: ___________________________________ 2a. Prone describes _______________________________________ 2b. Supine describes _______________________________________ 3. Anatomical Terms: Anatomical Landmarks, Anatomical Regions, and terms of Anatomical Directions. 3a. Anatomical Landmarks: Fig. 1-5 OS Fig. 1.12 Terms used for locating structures _________________________________________ Fig. 1-6 OS Fig. 1.16 3b. Anatomical Regions: Terms used to describe ___________________________________________ Two methods to map the surface of the abdomen and pelvis: 1. ____________________________________________________________ 2. ____________________________________________________________ 10 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 Abdominopelvic Quadrants: 1. How many abdominopelvic quadrants? ______ 2. Label the abdominopelvic quadrants: Fig. 1-6a OS Fig. 1.16 3. Abdominopelvic quadrants are used to describe ______________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 4. More commonly used by ____________________________ Abdominopelvic Regions: 1. Abdominopelvic regions provide a more precise description of __________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Abdominopelvic regions are mainly used by _________________________________ 3. How many? ___ abdominopelvic regions: 11 Fig. 1-6b OS Fig. 1.16 11 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 SUMMARY - Relationship between the abdominopelvic quadrands and regions and location of the internal organs: Fig. 1-6c Fig. 1-7 OS Fig. 1.13 3c. Anatomical Direction 1. Are used to describe _____________________________________________________ 2. USE Fig 1-7 or see page 31 in the Openstak Textbook to complete the table on the following page. KNOW each term in the table, their meaning, and examples of usage. NOTE: As you read the examples in the table on the following page, look at the figure below to orient the location of the examples described in the table. 12 12 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 Directional Terms Definition Examples (Use Fig. on previous page) 7 Superior The heart is superior to the liver. Inferior The stomach is inferior to the lungs. Anterior (or Ventral) The sternum (breastbone) anterior to the heart. Posterior (or Dorsal) The esophagus is posterior to the trachea (windpipe). Medial The pinky is medial to the thumb. Lateral The lungs are lateral to the heart. is Cranial or Cephalic Toward the head The cephalic border of the pelvis is superior to the thigh. Caudal Toward the tail (coccyx in humans) The hips are caudal to the waist Proximal The humerus is proximal to the radius. Distal The fingers are distal to the wrist. Superficial The ribs are superficial to the lungs. Deep The ribs are deep to the skin of the chest and back. 13 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 OS Fig. 1.14 Fig. 1-8 4. Planes and Sections 4a. Plane is ________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 4b. List the three major anatomical planes: a) _________________________________ b) _________________________________ and c) ____________________________ 4c. Describe each major anatomical plane: Sagittal plane: - _________________ plane -Divides the body or structure into _____________________________________ -When a sagittal plane passes directly down the middle of the body or organ it is called _______________________________ -A midsagittal plane divides the body or organ into _________________________ Label the right and left portion of the brain AND the midsagittal plane. -A cut parallel to the midsagittal line is called__________________________ section -It divides the body or organ into ____________________________________________ 14 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 Frontal or plane: a plane that divides the body or structure into ___________________________________________________ portions. Label the anterior and posterior portions of the brain AND the frontal or coronal plane. Transverse or plane: a plane that divides the body or structure into ___________________________________________ portions. Label the superior and inferior portions of the brain AND the transverse plane What is a section? A section is___________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Example of a section: 15 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 5. Body cavities of the Trunk Martini, pg. 18 5a. List functions of body cavities: Openstax, pg. 32 5b. Body cavities have ___________ membranes. What is a serous membrane or __________? 5c. List the body cavities of the trunk: Posterior Anterior Fig. 1-9 OS Fig. 1.15 Lateral Anterior 5d. Name the flat muscular sheet that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity: ____________________________ (label this muscle sheet in the figure above). 16 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 The Thoracic Cavity Martini, pg. 22 Openstax, pg. 33 1. List viscera (organs) found at the thoracic cavity: 2. The central region of the thoracic cavity contains the ___________________________ 3. What is the mediastinum? A mass of connective tissue that: -surrounds, stabilizes, and supports the _____________ ____________________________________________ -subdivides the thoracic cavity into the ____________ ___________________________________________ -Contains the _________________________________ 4. List two smaller cavities within the thoracic cavity: a. __________________________ (holding the _____________) b. __________________________ (holding the _____________) Pleural Cavities a. Two (2) pleural cavities: The right pleural cavity contains the __________________ The left pleura cavity contains the ____________________ The right & left pleural cavities are separated by the _______________________ Label the left and right pleural cavities and the mediastinum: 17 17 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 b. Serous membranes (serosa) at the Thoracic Cavity 1b. What is a serous membrane or serosa? - Thin membrane secreting _____________________________________________ -Lines ______________________________________________________________ -Consists of 2 layers: 2b. List the serous membranes at the pleural cavity: 3b. What is the visceral pleura? Serous membrane covering _____________________________________________ 4b. What is the parietal pleura? Serous membrane that lines the _________________________________________ LABEL: visceral pleura, parietal pleural, right pleural cavity, left pleural cavity Pericardial Cavity a. What is the pericardial cavity? b. List the serous membranes at the pericardial cavity: 1b. What is visceral pericardium? Serous membrane covering _____________________________________________ 2b. What is parietal pericardium? Serous membrane lining the ____________________________________________ 18 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 LABEL the visceral and parietal pericardium in the figure below: Fig. 1-9b OS Fig. 1.17 Heart REVIEW Posterior Anterior LABEL: 1. Pleural cavity 2. pericardial cavity 3. diaphragm 4. thoracic cavity Abdominopelvic Cavity Lateral View 19 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 The Abdominopelvic Cavity Martini, pg. 22 1. The abdominopelvic cavity extends: Openstax, pg. 33 a) from the ___________________________ b) to the _________________________ Label the Abdominopelvic cavity: 2. List the subdivisions of the abdominopelvic cavity: 2. Name the serous membrane of the abdominopelvic cavity: ______________________________________________ 2a What is parietal peritoneum? serous membrane lining _______________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 2b. What is visceral peritoneum? Serous membrane covering ____________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 3. Name the two division of the abdominopelvic cavity: 20 20 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 4. List viscera at abdominal cavity: liver Vertebral Column 5. List viscera at pelvic cavity: 6. Retroperitoneal Organs: some abdominal organs lie between the parietal peritoneum and the muscular wall of the abdominal cavity. LIST SOME RETROPERITONEAL ORGANS: READ: Diagnostic Imaging Techniques (Martini, pg. 20 uterus urinary bladder OS, pg. 34) After reading the above reading assignment, answer the following questions about each medical imaging technique: X-rays 1. X-rays are a form of _____________________________ radiation. 2. When taking an x-ray, areas in the body impenetrable to x-rays such as hard tissues (bones, teeth) appear ______________________ on the exposed film. 3. Soft tissues (fat. Liver, blood, etc.) slightly impede the passage of x-rays and show up in shades of ________________ on the x-ray film. NOTE: To use x-rays to visualize soft tissues, a radiopaque substance (a substance that stops the passage of x-rays such as barium) must be introduced in the body by ingestion. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – Uses a high-energy magnetic field 1. True or False? MRIs are most useful to create a detailed image of soft tissue structures. 2. Is it safe? 21 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 Computed Tomography (CT) 1. How is a CT scan done? 2. Is radiation used for CT scans? From left to right: photograph of frozen, sawed head, CT scan of the same level/plane, MRI scan of the same level/plane Ultrasound Scanning (sonography) 1. Describe how a sonogram is done: 2. Is it safe? Invasive or noninvasive? Painless? 3. Most commonly used to visualize:__________________________________________ Positron Emission Tomography (PET) 1. How is a PET scan done? 2. PET scan is used to study: -Use your notes AND textbook to answer chapter assessment questions at the end Ch 1 in yourAP Textbook. -Visit Mastering A&P to do different activities to assess your Ch 1 Knowledge. 22 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 Test Your Knowledge on Chapter 1… 1. The branch of science that studies the structure (morphology) of body parts is called _____________________________________________________________________ 2. The branch of science that studies what body parts do and how they do it is called _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Circle one: The function of part is (always/sometimes/never) related to its structure. 4. Choose one: Homeostasis means a. maintenance of a stable internal environment. b. integrating the functions of the various organ systems. c. preventing any change in the organism. d. maintenance of a stable external environment. Questions 5-8. Match the structure listed in the first column with the functions listed in the second column. Structure Function ____5. atoms, molecules, macromolecules a. groups of cells that have a ____6. cells common function ____7. tissues b. chemical structure required for life ____8. organisms c. allow life to continue despite changing environments and reproduce to continue the species d. simplest living units 9. List ALL levels of organization of the body in order of increasing complexity, beginning with the atom. 10. List and describe the major body cavities found in the human body. 23 BIOL 2401 Chapter 1 Martini_10th_OS_2013 11. Describe the standard human anatomical position. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 12. Prepare a sketch of a human body, and use lines to indicate each of the following sections: a. sagittal b. transverse c. coronal 13. Write complete sentences using each of the following terms correctly a. superior: ______________________________________________________________ b. inferior: ______________________________________________________________ c. anterior: ______________________________________________________________ d. posterior: _____________________________________________________________ e. medial: _______________________________________________________________ f. lateral: ________________________________________________________________ g. proximal: _____________________________________________________________ h. distal: ________________________________________________________________ i. superficial: ____________________________________________________________ j. deep: _________________________________________________________________ 14. Which of the following positions of body parts is/are in anatomic position? a. palms of hands turned toward sides of body c. arms at side b. standing erect d. face toward left shoulder 15. The peritoneal membranes are located in the _____________________ cavity. 24