* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 29-30
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
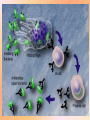
Immunology Dr. Hal Sternberg MCB 135E Lecture 29-30 DEVELOPMENT OF IMMUNE SYSTEM • - GESTATIONAL TOLERANCE • (PREVENTING REJECTION) • - FETAL/NEONATAL PROTECTION • - VACCINATION/IMMUNIZATION VACCINATIONS • • • • • • • • • BIRTH BCG (BACILLUS CALMETTE-GUERIN) ORAL POLIO HEPATITIS 6 WEEKS DPT (DIPHTHERIA, TETANUS, PERTUSSIS ORAL POLIO 2ND DOSE HEPATITIS 2ND • 10 WEEKS DPT (DIPHTHERIA, TETANUS, PERTUSSIS) ORAL POLIO 3RD • • • 14 WEEKS DPT 3RD ORAL POLIO 4TH • • • 6-9 MONTHS ORAL POLIO 5TH HEPATITIS B • • 9 MONTHS MEASLES • • • • 15-18 MONTHS MMR (MEASLES, MUMPS, RUBELLA) DPT booster dose ORAL POLIO 6TH • • • 5 YEARS DPT 2ND booster ORAL POLIO 7TH • • • 10 YEARS TT (TETANUS) 3RD booster HEPATITIS B booster • • 15-16 YEARS TETANUS booster Progression of Vaccine Development ** ….. ….. ** Taken from the Scientist;17(2004) Function of Immune System is PROTECTION against: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Bacteria Virus Fungus/ multicellular parasites Cancer Toxins ( 5,000 daltons--protein/lipid/CHO/nucleic acids) Tissues and Organs Important for Immune Function •Cells derived from stem cells: liver, bone marrow • Cells are stored, multiply, interact, and mature in: thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, blood •Transport: lymphatic vessels Accessory Organs •Appendix, tonsils, intestines Cell Types 1. Lymphocytes: derived in bone marrow from stem cells include both T cells and B cells. 1012 QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Lymphocytes (cont.) A) T cells: stored & mature in thymus-migrate throughout the body -Killer Cells Perform lysis (infected cells) Cell mediated immune response -Helper Cells Enhance T killer or B cell activity -Suppressor Cells Reduce/suppress immune activity May help prevent auto immune disease Lymphocytes (cont.) B) B-Cells: stored and mature in spleen • secrete highly specific Ab to bind foreign substance (antigen: Ag), form Ab-Ag complex • responsible for humoral response • perform antigen processing and presentation • differentiate into plasma cells (large Ab secretion) 2. Neutrophils- found throughout body, in blood -phagocytosis of Ab-Ag CX QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 3. Macrophages- throughout body, blood, lymphatics -phagocytose non-specifically (non Ab coated Ag) -phagocytose specifically AbAg CX -have large number of lysosomes (degradative enzyme) -perform Ag processing and presentation -present Ag to T helper cell -secrete lymphokines/ cytokines to stimulate T helper cells and immune activity 4. Natural Killer Cells-in blood throughout body -destroy cancer cells -stimulated by interferons QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Macrophage Bacteria Bacterial Infection Complement Series of enzymes which are sequentially activated and result in lysis of cell membrane of infected cell at bacterium Permeabilizes membrane leaky Complement binding and activation ~35 enzymes and factors involved in cascade QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. CDC involves: 1) recognition, 2) attachment of complement-fixing antibodies to tumor specific surface antigens, 3) complement activation, 4) formation of MAC resulting in transmembrane pores (perforins) that disrupt the osmotic barrier of the membrane and lead to osmotic lysis. Viral Infection 5 classes of Ig IgG: 150,000 m.w. most abundant in blood, cross placental barrier, fix complement, induce macrophage engulfment IgA: associated with mucus and secretory glands, respiratory tract, intestines, saliva, tears, milk variable size IgM: 900,000 m.w. 2nd most abundant , fix complement, induce macrophage engulfment, primary immune response 5 Classes of Ig IgD: Low level in blood, surface receptor on Bcell IgE: Binds receptor on mast cells (basophils) secretes histamine, role in allergic reactions Increased histamine leads to vasodilation, which leads to increase blood vessel permeability. This induces lymphocyte immigration swelling and redness. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Thymus Involution Repertoire of lymphocytes shift with aging (membrane components shift) ORGAN AND T-CELL DEVELOPMENT • YOLK SAC • • • BONE MARROW • (4-5 Weeks ) • • • LIVER (4 Weeks) THYMUS (7-10 Weeks) BLOOD LYMPH • (14 Weeks) • SPLEEN • (16 Weeks) • T-cells migrate and appear in tissues with development and increase in number throughout Gestation B-CELLS • FIRST appear in immature state - Liver at 7 weeks • LATER –appear mature by 14-20 weeks • CAN DIFFERENTIATE INTO IMMUNOLOGICALLY COMPETENT ANTIBODY-PRODUCING PLASMA CELLS NATURAL KILLER CELLS • FIRST APPEAR IN FETAL BONE MARROW AROUND 13 WEEKS GESTATION • FIRST APPEAR IN FETAL BONE MARROW AROUND 13 WEEKS GESTATION • FOUND THROUGHOUT BODY • NK CELLS HAVE DIMINISHED ACTIVITY BEFORE BIRTH COMPARED TO ADULT • STIMULATED BY INTERFERON AFTER 27 WEEKS COMPLEMENT PROTEINS • ARISE FROM LIVER • FIRST DETECTED 5-6 WEEKS GESTATION • INCREASE GRADUALLY IN CONCENTRATION • AT ABOUT 28 WEEKS COMPLEMENT PROTEINS ARE AROUND 2/3 THAT OF ADULT CONCENTRATIONS • INDIVIDUAL VARIATION SEVERE COMBINED IMMUNODEFICIENCY DISEASE (SCID) CHARACTERISTICS: GENERALLY CAUSED BY DEFECT OF SINGLE GENE NEEDED FOR TCELL AND B-CELL FUNCTION —SUBJECT EXHIBITS NO CELL MEDIATED RESPONSE ––SUBJECT CANNOT MAKE ANTIBODIES ABOUT 25% OF CASES INVOLVES DEFECTIVE GENE FOR THE ENZYME ADENOSINE DEAMINASE (REQUIRED FOR PURINE BREAKDOWN) SEVERE COMBINED IMMUNODEFICIENCY DISEASE (SCID) • TREATMENT OPTIONS: • • • GERM FREE ENVIRONMENT BONE MARROW TRANSPLANT ROUTINE INJECTIONS OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE (ADA) • • • GENE THERAPY USING SUBJECTS OWN CELLS (RETROVIRUS CONTAINING ADA TO “INFECT” SUBJECTS BONE MARROW STEM CELLS) ENZYME