* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exponents, Factors, and Fractions
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
List of prime numbers wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
P-adic number wikipedia , lookup
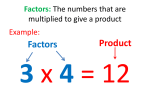
Exponents, Factors, and Fractions Chapter 3 Exponents and Order of Operations Lesson 3-1 Terms • An exponent tells you how many times a number is used as a factor • A base is the number that is multiplied 4 5 4 is the base, 5 is the exponent. It means 4 x 4 x 4 x 4 x 4 It does NOT MEAN 4 x 5 Simplify Using Order of Operations • Simplify 34 •(7-2)3 First: Parentheses Second: Exponents Third: Multiply = = = 34 • 53 81• 125 10,125 Simplify Powers with Negatives -54 and (-5)4 are not equivalent. -54 means the “negative of” 54, so the base is 5, not -5 • -54 = -(5 • 5 • 5 • 5) = -625 But watch out for: here the base is the number in the parentheses (-5)4 = (-5)(-5)(-5)(-5) = 625 Partner Practice • Exponents and Order of Operations Scientific Notation Lesson 3-2 Definition • A number in scientific notation is written as the product of two factors, one greater than or equal to 1 but less than 10, and the other as a power of 10 7,500,000,000,000 = 7.5 x 1012 Example • The moon orbits the earth at a distance of 384,000 km. Write the number in scientific notation First: move the decimal point to get a factor greater than 1 but less than 10 384,000. becomes 3.84000 Then: rewrite as 3.84 x 105 because I moved the decimal point 5 places From Scientific Notation to Standard Form • Mars is 2.3 x 108 miles from Earth Write in standard form: Move the decimal point to the right 8 places 230,000,000 Think, Pair, Share • http://www.worksheetworks.com/pdf/eaf/9c dc46f73b98/WorksheetWorks_Scientific_Nota tion_1.pdf Divisibility Tests Lesson 3-3 Definition A whole number is divisible by another if the remainder is zero Facts/Characteristics all even numbers are divisible by 2 Vocabulary Word Divisible 48 ÷ 4 = 12 47 ÷ 4 = 11 r 3 Examples Non-Examples Divisibility of Whole Numbers A whole number is divisible by • • • • • 2 if it ends in 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3 5 if it ends in 0 or 5 0 if the sum of the digits is divisible by 9 10 if it ends in 0 Prime Factorization Lesson 3-4 Definition Factors are numbers that are multiplied Facts/Characteristics When divided there is no remainder Vocabulary Word 3 x 4 = 12 12÷ 4 = 3 Examples Factor 12 ÷ 5 = 2 r2 Non-Examples Definition Facts/Characteristics A whole number numbers that can be greater than 1 with more divided evenly by more than two factors than just 1 and itself Vocabulary Word 20 1 x 20 2 x 10 4x5 Examples Composite number 19 1 x 19 Non-Examples Definition A whole number with exactly two factors, 1 and the number itself Facts/Characteristics The whole numbers 0 and 1 are neither prime nor composite Vocabulary Word 19 1 x 19 Examples Prime number 20 1 x 20 2 x 10 4x5 Non-Examples Prime Factorization What does this mean??? Writing a composite number as a product of prime numbers gives the prime factorization ….OK, so what does that mean??? And how do I do it?? Method One: Division Ladder • Find the prime factorization of 84 Divide 84 by prime numbers starting with 2 and work your way up. 2) 84 2) 42 3) 21 7 Divide 84 by the prime number 2. Work down. The result is 42. Since 42 is even, divide by 2, again. The result is 21. Divide by the prime number 3. The prime factorization of 42 is 2x2x3x7 Some things to remember… • When using division ladders, start by first dividing with the smallest prime number. For even numbers, that divisor will be 2. • Keep dividing until you reach a prime number as the quotient. Method Two: Factor Trees • Gets us to the same result, just a different way 84 2 42 2 21 3 7 Circle the prime numbers Prime factorization of 84: 2 x 2 x 3 x 7 GCF • The greatest common factor of two or more numbers is the greatest factor shared by all the numbers. • Find the GCF three different ways: • Use a list of factors • Use a division ladder • Use factor trees Simplifying Fractions Lesson 3-5 Definition… • Equivalent fractions are fractions that name the same amount • Form equivalent fractions by multiplying the numerator and denominator by the same nonzero number Simplest Form • Fractions are in simplest form when the only common factor of the numerator and denominator is 1 • Example: 2 is on simplest form since 2 and 3 3 only have the number 1 as a common factor Partner Practice • Get the fractions into simplest form Write the Fraction in Simplest Form Fractions Puzzlers Task Cards Comparing and Ordering Fractions Lesson 3-6 Least Common Denominator • To compare fractions, start with the LCD The Least Common Denominator of two or more fractions is the Least Common Multiple of the denominators Ex: compare 3/4 and 5/6 Compare ¾ and 5/6 Step One: Find LCM for 4 and 6 Option 1: Use a List of Multiples Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24 Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36 12 is the least common multiple for 4 and 6 Compare ¾ and 5/6 • Step Two: Write equivalent fractions using LCM as the common denominator • 3/4 = 9/12 • 5/6 = 10/12 3/4 < 5/6 How to Find LCM Find LCM for 8, 10 and 20 Option 2: Use Prime Factorization Prime Factorization for 8 = 2 x 2 x 2 Prime Factorization for 10 = 2 x 5 Prime Factorization for 20 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 5 Circle each different factor: 2 x 2 x 2 x 5 = 40 LCM for 8, 10 and 20 is 40 Partner Practice • Use either method for practice Find the LCM for each pair What Happens If You Watch TV All Day? Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions Lesson 3-8 Key Terms • A proper fraction has a numerator that is less than its denominator: ⅜ • An improper fraction has a numerator that is greater than or equal to its denominator: 8/5 • A mixed number is a number written with both a whole number and a fraction: 2⅔ Write Mixed Numbers as Improper Fractions • Write 6⅔ as an improper fraction • First: Multiply the whole number by the denominator (6 x 3 thirds = 18 thirds) • Second: Add the numerator (18 thirds + 2 thirds = 20 thirds) Example: 6⅔ = (6 x 3) + 2 = 20 3 3 Write Improper Fractions as Mixed Numbers • Write 9 6 as a mixed number First: divide the numerator by the denominator Second: write the remainder as a fraction Third: simplify 1 6)9 -6 3 9 = 1 3/ 6 = 1⅟2 6 Partner Practice • With your partner, convert Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions Convert Mixed Numbers and Fractions Cryptic Quiz Fractions and Decimals Lesson 3-9 Terminating Decimals • Write fractions as decimals by dividing the numerator by the denominator. • A decimal that stops, or terminates, is a terminating decimal • Ex: 5/8 = 5÷ 8 = 0.625 Repeating Decimal • If when we divide, we discover the same digit or group of digits in the quotient repeats without end, that decimal is a repeating decimal • Ex: 3/11 = 3 ÷ 11 = 0.272727… = 0.27 Practice • convert Rational Numbers Lesson 3-10 Rational Number • A rational number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers, where the divisor is not 0. Examples: ⅝, 0.46, -6 and 3⅟2 All integers are rational numbers as all integers can be written with a denominator of 1 Negative Rational Numbers • Negative Rational Numbers can be written in three ways 6= 6 =6 7 7 7 Compare Negative Rational Numbers • Compare -⅟2 and -3/4 • Option 1: Use a number line. Since -3/4 is farther to the left, it is the smaller number Compare Negative Rational Numbers • Compare -⅟2 and -3/4 • Option 2: make equivalent fractions -⅟2 = - 2/4 Since -3/4 < - 2/4 , then -3/4 < -⅟2 Ordering Rational Numbers • Order these numbers from greatest to least ⅟4, -0.2, -2/9 , 1.1 Step One: convert the fractions to decimals by dividing ⅟4 = 0.25 and -2/9 = -0.22 Now order: -0.22 , -0.2, 0.25, 1.1 Partner Practice http://www.mathworksheetsland.com/6/16expr at/ip.pdf