* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Engineering the Genetic Code
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Personalized medicine wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
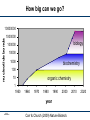
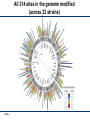
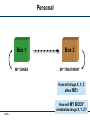
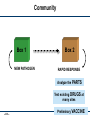
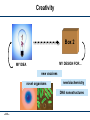
Recoding the Genome Peter Carr 18 August 2011 FAB7 Lima, Peru SS -1 PAC 8/18/11 DNA On-Demand rewrite genomes minimal life genetic circuits metabolic pathways DNA base pairs 103 individual genes assembly scaffolds SS -2 PAC 8/18/11 104 105 vaccines gene therapy 106 How big can we go? nucleotide bonds 10000000 1000000 biology 100000 10000 1000 biochemistry 100 10 1 1950 organic chemistry 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 year SS -3 PAC 8/18/11 Carr & Church (2009) Nature Biotech. 2010 2020 The basic genetic code 4 letters A C G T SS -4 PAC 8/18/11 4 letters X A C G T 64 words (codons) 4 letters X A C G T = AAA AAC AAG AAT ACA ACC ACG ACT ... Second Position SS -5 PAC 8/18/11 Second Position new room for plug & play rearrange to block function By engineering new genetic codes we can: • make universal systems for “plug and play” with new amino acids • block exchange of genes, a “genetic firewall” • produce organisms immune to viruses SS -6 PAC 8/18/11 Multiplex Automated Genome Engineering (MAGE) “Find and replace” with the DNA of the genome SS -7 PAC 8/18/11 Key features of MAGE: • Multiplexed: can address many sites at once • Targeted: modifies specific sequences; changes made can be specific or random • Iterated: weak efficiency can be compensated by automating many cycles of modification • Tunable: can control the range of diversity generated in a population • Clean: no DNA scars, no resistance gene markers, etc. SS -8 PAC 8/18/11 All 314 sites in the genome modified (across 32 strains) SS -9 PAC 8/18/11 Genome Engineering base pairs to megabases SS -10 PAC 8/18/11 Thanks to: Joseph Jacobson • Bram Sterling* • Chris Emig • Sam Hwang George Church (HMS) • Farren Isaacs • Harris Wang • Marc LaJoie Shuguang Zhang (MIT) SS -11 PAC 8/18/11 Funding: NSF Atoms to bits...to atoms to bits transmitter receiver genetic molecules counseling G A T T A C A me you it SS -12 PAC 8/18/11 Box 1 clinical + research Box 2 data health statistics forensics basic experiments research Personal Box 1 Box 2 MY GENES MY TREATMENT How will drugs X, Y, Z affect ME? How will MY BODY metabolize drugs X, Y, Z? SS -13 PAC 8/18/11 Community Box 1 NEW PATHOGEN Box 2 RAPID RESPONSE Analyze the PARTS Test existing DRUGS at many sites SS -14 PAC 8/18/11 Preliminary VACCINE Creativity Box 2 MY DESIGN FOR... MY IDEA new vaccines novel organisms new biochemistry DNA nanostructures SS -15 PAC 8/18/11