* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Levels of organization
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
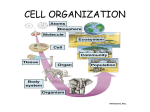
DO NOW Hand in Balance Lab Take out textbook, turn to page 26 LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION CHAPTER 1.3 ORGANISMS CAN BE CLASSIFIED BY THEIR CELL TYPE A domain is a broad category of living things based on characteristics of their cells. Three domains: 1. Archaea: Prokaryotic organisms living in extreme environments. 2. Bacteria: Prokaryotic organisms 3. Eukarya: All eukaryotic organisms (plants, animals, fungi, protists) CELLS IN MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS SPECIALIZE Specialization: specific cells perform specific functions A single cell from a multicellular organism CANNOT survive on its own Example: A nerve cell A MULTICELLULAR ORGANISM IS A COMMUNITY OF CELLS In more complex organisms: Cells are specialized and grouped together Tissue: a group of similar cells that are organized to do a specific job Organ: different tissues working together to perform a particular function Organ System: different organs and tissues working together Humans have 11 major organ systems Organism: highest level of organization NOW: Complete the multiple choice questions in the textbook, pg 35 HW: Complete the study guide vocabulary column 1 HW: COMPLETE THE STUDY GUIDE VOCABULARY COLUMN 1 Column 1