* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
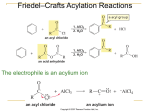
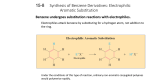
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS By PUAN AZDUWIN BINTI KHASRI Criteria for Aromaticity 1. A compound must have an uninterrupted cyclic cloud of 𝜋 electrons above and below the plane of the molecule 2. The p cloud must contain an odd number of pairs of p electrons. BENZENE Benzene is an aromatic compound because it is cyclic and planar, every carbon in the ring has a p orbital, and the 𝜋 cloud contains three pairs of 𝜋 electrons. Hückel’s Rule For a planar, cyclic compound to be aromatic, its uninterrupted p cloud must contain (4n + 2) p electrons, where n is any whole number Monocyclic hydrocarbons with alternating single and double bonds are called annulenes: Cyclobutadiene and cyclooctatetraene are NOT AROMATIC, because they have an even number of p electron pairs not aromatic not aromatic aromatic Cyclopentadiene does not have an uninterrupted ring of p orbital-bearing atoms Cyclopentadienyl cation has an even number of p electron pairs Cyclopentadienyl anion has an uninterrupted ring of p orbital-bearing atoms and an odd number of p electron pairs 5 The resonance hybrid shows that all the carbons in the cyclopentadienyl anion are equivalent These compounds consist of fused benzene rings and are aromatic: Any compound consisting of fused benzene rings is aromatic 7 Aromatic Heterocyclic Compounds A compound does not have to be a hydrocarbon to be aromatic. A HETEROCYCLIC compound has ring atoms other than carbon Example:Heterocyclic Compounds Antiaromaticity A compound is antiaromatic if it is a planar, cyclic, continuous loop of p orbitals with an even number of pairs of p electrons Antiaromatic compounds are highly unstable, but the nonplanar versions are stable A compound is classified as being antiaromatic if it fulfills the first criterion for aromaticity but does not fulfill the second criterion. EXAMPLE: Antiaromaticity Nomenclature of Monosubstituted Benzenes Some are named by attaching “benzene” after the name of the substituent: 11 Some have to be memorized: A benzene substituent is called phenyl. A benzene substituent with a methylene group is called benzyl. 13 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions 1. Halogenation 2. Nitration 3. Sulfonation 4.Friedel–Crafts acylation 5.Friedel–Crafts alkylation General Mechanism for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution of Benzene Carbocation intermediate 1. Halogenation of Benzene LEWIS ACID CATALYST LEWIS ACID CATALYST 16 Lewis acid weakens the Br–Br (or Cl–Cl) bond, which makes the halogen a better electrophile: 17 Mechanism for bromination B: Bromide or Benzene The catalyst is regenerated: 19 2. Nitration of Benzene Nitration of benzene with nitric acid requires sulfuric acid as a catalyst. 20 Nitronium ion formation: Mechanism for Nitration; 21 3.Sulfonation of Benzene Fuming sulfuric acid (a solution of in sulfuric acid) or concentrated sulfuric acid is used to sulfonate aromatic rings Mechanism for sulfonation Sulfonation of benzene is a reversible reaction. Mechanism for desulfonation Reaction coordinate diagram for the sulfonation the desulfonation sulfonation of B DESULFONATION B-A RATE DETERMINING STEP A C-B has a smaller rate constant than B-A (because once B is formed, its easier for B to get to C Desulfonation of and proceed to A) SULFONATION benzene A-B RATE DETERMINING STEP Has a smaller rate constant (Higher energy hill, thus slower reaction) than B-C C benzenesulfonic acid Friedel–Crafts Acylation vs Friedel– Crafts Alkylation 4.Friedel–Crafts Acylation Reactions Either an acyl halide or an acid anhydride can be used for Friedel–Crafts acylation. Mechanism for Friedel–Crafts acylation: Must be carried out with more than one equivalent of AlCl3: 27 5.Friedel–Crafts Alkylation of Benzene The Friedel–Crafts alkylation reaction substitutes an alkyl group for a hydrogen. 28 Mechanism for Friedel–Crafts alkylation: 29 The carbocation will rearrange to a more stable species: However, 100% of the 2-methyl-2-phenylbutane product can be obtained if a bulky alkyl halide is used: 31 Friedel–Crafts alkylation will not produce a good yield of an alkylbenzene containing a straight-chain group, because the carbocation will rearrange: Acylium ions, however, do not rearrange: 32 Methodologies Used for the Reduction Step There are more general methods available to reduce a ketone carbonyl group to a methylene group 33 Using Coupling Reactions to Alkylate Benzene The Gilman reagent: The Stille reaction: The Suzuki reaction: The resulting halide product can undergo a nucleophilic substitution reaction: Oxidation of an alkyl group bonded to a benzene ring Provided that a hydrogen is bonded to the benzylic carbon, 36 The same reagent that oxidizes alkyl substituents will oxidize benzylic alcohols: 37 However, aldehydes or ketones can be generated if a milder oxidizing agent is used: 38 Reducing a Nitro Substituent 39 It is possible to selectively reduce just one of the two nitro groups: 40 Summary of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions 41 Summary of Friedel–Crafts Reactions 42 THE END