* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viruses and Diseases in the Civil War Miss Sabia
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
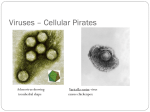
Viruses and Diseases in the Civil War Miss Sabia Objectives Be able to summarize both the lytic and lysogenic cycle. Be able to compare the structure and characteristics of viruses and bacteria. Be able to properly perform a swab technique. The Main Killers Typhoid Pneumonia Measles Tuberculosis malaria Pathogens Microbes that cause diseases… VIRUSES and BACTERIA Bacteria Earliest form of life (3 billion years ago) Prokaryotic cells (no organelles, no nucleus) Single celled have a cell wall Bacteria 3 shapes: Cocci (spherical) Bacilli (rod shaped) Spirilla (spirals) Bacteria Use flagella to “swim” or produce thick coats of slime to “slide” around How Bacteria Infect Give off chemicals called toxins that can make us sick Our body fights off bacterial infections using antibodies Viruses Single-celled Not considered living Cannot reproduce on their own They are not made up of cells They cannot respond to the external environment Cannot move on their own Called “particles” or “agents” About 4,000 different types of viruses Viruses Have genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a capsid Some viruses have a viral envelope covering their capsid (taken from host cell) sneaky How Viruses Infect Lytic cycle 1. entry into cell 2. replicate DNA 3. make viral proteins 4. assemble new generation 5. exit from infected cell—host cell bursts open (lyses) and virus is released into the environment, host cell dies http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3DP-MAhr0YY How Viruses Infect Lysogenic cycle (sneaky!) 1. entry into cell 2. DNA incorporated into host cell’s DNA 3. host cell copies chromosomes 4. host cell divides and replicates—all new cells have virus’ DNA incorporated into their own 5. steps 3-5 from lytic cycle http://wrate.me.vccs.edu/courses/env108/lesson2_4.h tm Microbiology Lab—Microbes Around Us Swab Demo:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2U6usyE80i o Note: we will not be wetting our swabs in distilled deionized water as the video says