* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme kinetics wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
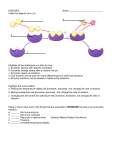
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Objectives • Identify the parts of a chemical reaction. • Relate energy changes to chemical reactions. – interpret energy diagrams • Summarize the importance of enzymes in living things. – – – – enzymes (definition) “lock and key” model effect of temp. and pH on enzyme activity effect of concentration on enzyme activity Chemical Reactions • Definition – process by which atoms or groups of atoms in substances are reorganized into different substances • Chemical bonds are broken and/or formed. Chemical Equations • Reactants Products “yields” • Read the following: C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6H20 + 6CO2 glucose oxygen water carbon dioxide Energy of Reactions • Energy – needed to start chemical reactions • Activation Energy (Ea) – minimum amount of energy needed for reactants to form products • Energy Change ( H) – (Energy of Reactants - Energy of Products) – Exothermic (H) • energy of products lower than energy of reactants – Endothermic (+ H) • energy of products higher than energy of reactants Energy Diagram Exothermic Reaction Energy Diagram Endothermic Catalysts CATALYSTS HELP CHEMICAL ___________ REACTIONS _______________ HAPPEN FASTER DECREASING the Catalysts work by ____________ ACTIVATION ENERGY required ___________________________to get a chemical reaction started. – NOTE: – does not increase the amount of product – does not get used up in the reaction Enzymes • Enzymes – types of proteins – act as biological catalysts – speed up the rate of reaction in biological processes (by lowering activation energy) – most are specific to one reaction Enzymes • Naming Enzymes • many end in _____ • beginning of the name tells what it does • Examples: • DNA Polymerase • “polymerizes” • joins monomers to make DNA • Protease • breaks down proteins • ATP synthase • synthesizes ATP Energy Diagram Enzymes • Substrate – reactants that bind to the enzyme • Active Site – location where the substrate binds on the enzyme • Enzymes combine with the substrate in the active site to form the enzyme-substrate complex Enzymes • Lock & Key Model: – substrate and active site -> complimentary shapes (puzzle pieces that fit together) • Enzymes exhibit specificity: – enzymes only fit with a particular substrate – due to the shape of the active site Enzyme Demonstration 5) Product Released; enzyme free to react again 1) Substrate 2) Fits into active site 4) Reaction takes place 3) Enzyme-Substrate Complex Enzymes • Factors that affect enzyme activity – pH – temperature – concentration (amt.) of substrate – concentration (amt.) of enzyme Enzymes • Optimal pH (dependent on enzyme) • Too low -> decreased rate of reaction • Too high -> enzyme denatures (breaks apart) Denatured Proteins • When a protein loses its shape (its tertiary (3-D) structure) • Cause: -high temperature (like on the stove) -pH extremes (like in your stomach) • Effect: -Losses its ability to function -Properties can change (become insoluble, change color) Denatured Proteins changesthe • Denaturing an enzyme _______ _______ shape of the ______________ ACTIVE SITE so enzyme ______________ ____________ CAN’T BIND to SUBSTRATE Denatured Proteins • As a result, the reaction occurs at a reduced rate or stops all together. Enzymes • Optimal Temp. • Temp , Activity • Temp too high-> protein denatures (breaks apart) Enzymes Predict what would happen if… (1) you added more enzyme to the reaction? (2) you added more substrate to the reaction? WHITEBOARDS! How does the amount of the substrate and the amount of enzyme affect the rate of reaction? Lab: Understanding Enzymes Objectives: • Understand the function of enzymes in the human body. • Observe the function of several commercially important enzymes. • Predict the effect of enzyme concentration, temperature, and pH on enzyme activity rate. • Understand the structure of enzymes & how denaturation occurs. • Graph enzyme activity rates and different enzyme concentrations. Enzyme Inhibitors • Competitive Inhibition – plug up active site->substrate can’t bind • Non-Competitive Inhibition – bind to enzyme (not in active site) --> change shape of active site Enzyme Inhibitors • May be – Permanent - covalent bond – Reversible - hydrogen bond • Examples – – – – – Nerve gas Penicillin Cyanide Aspirin AZT Online Tutorials for additional information & visuals • http://resources.emb.gov.hk/biology/eng lish/virtual_lab/flash/enzyme_lab.html • http://www.bbc.co.uk/education/asguru/ biology/02biologicalmolecules/01protein s/11enzymes/index.shtml • http://www.tvdsb.on.ca/westmin/science /sbi3a1/digest/enzymes.htm Note: Not required. Can you… • …identify the parts of a chemical reaction? • …relate energy changes to chemical reactions? – interpret energy diagrams? • …summarize the importance of enzymes in living things? – enzymes (definition)? – “lock and key” model? – effect of temp. and pH on enzyme activity?