* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Disruption of Genetic Equilibrium
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
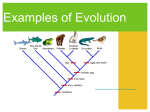
Disruption of Genetic Equilibrium Objectives List the five conditions that cause evolution to occur Describe stabilizing, directional, disruptive, and sexual selection Introduction Evolution is the change in the population’s genetic material over generations Population’s allele or genotype frequencies change Any violation of the conditions necessary for HardyWeinberg can result in evolution Five conditions that cause evolution to occur Mutation Migration Genetic Drift Nonrandom Mating Natural Selection Mutation Mutations are changes in DNA sequences Mutations occur constantly but at a very low rate under normal conditions Exposure to mutagens (mutation-causing agents) can increase mutation rates Most mutations are harmful Beneficial mutations are an important part of evolution Migration Immigration is the movement of individuals into a population Emigration is the movement of individuals out of a population Immigration and emigration can change gene frequencies Gene flow is the process of genes moving from one population to another Genetic Drift Genetic drift is where allele frequencies in a population change as a result of random events Genetic drift can occur in small populations when an allele becomes more or less common Genetic drift can be caused by: An individual in a small population carrying a particular allele and having more decedents that other individuals Founder effect: when a small group of individuals colonizes a new habitat Nonrandom Mating Many species do not mate randomly Mate selection is often influenced by geographic proximity Assortative mating is the selection of a mate based similarity of characteristics Mate probably has similar genes Can result in offspring with disorders caused by recessive genes Natural Selection Most significant factor that disrupts genetic equilibrium The most fit members of a population pass on their genetics to the next generation 4 Main Types of Natural Selection Stabilizing Selection Directional Selection Disruptive Selection Sexual Selection Stabilizing Selection Individuals with the average form of a trait have the highest fitness Individuals in the middle of the bell curve Extreme forms of a trait lower the fitness of the individual Example: A lizard that is too big is easily spotted and killed by a predator. A lizard that is too small is too slow to escape a predator. Directional Selection Individuals that display a more extreme form of a trait have greater fitness than individuals with an average form of the trait Individuals at one end of the curve have a higher fitness those individuals in the middle or at the other end Disruptive Selection Individuals with either extreme variation of a trait have greater fitness than individuals with the average form of the trait Individuals at the upper and lower ends of the curve have a higher fitness those individuals near the middle Sexual Selection Females choose the males they mate with based on certain traits Extreme traits indicate quality of genes Example: Female deer choose males with the biggest antlers. However, big antlers make the males easier to see by predators. As long as the male survives long enough to reproduce, his genes will be passed on. Notes Review List the five conditions that cause evolution to occur Mutation Migration Genetic Drift Nonrandom Mating Natural Selection Notes Review Describe stabilizing, directional, disruptive, and sexual selection Stabilizing Selection: Individuals with the average form of a trait have the highest fitness Directional Selection: Individuals that display a more extreme form of a trait have greater fitness than individuals with an average form of the trait Disruptive Selection: Individuals with either extreme variation of a trait have greater fitness than individuals with the average form of the trait Sexual Selection: Females choose the males they mate with based on certain traits