* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FREEZING – is the change of a liquid to a solid. Freezing occurs
Supercritical fluid wikipedia , lookup
Superfluid helium-4 wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Thermal expansion wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Ionic liquid wikipedia , lookup
Van der Waals equation wikipedia , lookup
Sessile drop technique wikipedia , lookup
Freeze-casting wikipedia , lookup
Liquid crystal wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs paradox wikipedia , lookup
Glass transition wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
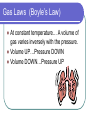
Unit II: Matter Chapter 3: Physical and Chemical Changes Phases of Matter Phase of matter is an important physical property of matter. Matter can exists in four phases: 1) Solid 2) Liquid 3) Gases 4) Plasma Solids Solids have a definite shape and a definite volume. The tiny particles that make up a solid are packed very close together. The particles are only able to vibrate. Crystalline solid In most solids the particles are arranged in regular, repeating patterns called a crystal. Amorphous solids Some solids are not arranged in regular, repeating patterns. These solids do not keep their definite shape permanently. These amorphous solids lose their shape under certain conditions. They act like a slow moving liquid. Amorphous solids Examples: candle wax, window glass and tar. Liquids Liquids have no definite shape, but do have a definite volume. The tiny particles within a liquid are free to flow around on another. Liquid Viscosity Some liquids will flow more easily than others. The resistance of a liquid to flow is called viscosity. High viscosity liquids include: automotive oil, honey Gases Gases have no definite shape,no definite volume. Gases particles tend to spread far out from one another; they can be pushed together. Solids, Liquids, and Gases Gas Laws (Boyle’s Law) At constant temperature… A volume of gas varies inversely with the pressure. Volume UP…Pressure DOWN Volume DOWN…Pressure UP Gas Laws (Charles’ Law) At constant pressure… The volume of gas varies directly with the temperature. Volume UP… Temperature UP Volume DOWN… Temperature DOWN Plasma Is quite rare on Earth. Actually quite common state of matter in the universe, stars and our Sun contain plasma. Plasma phase occurs at extremely high energy. Phase Change Because energy content is responsible for the different phases of matter, substances can be made to change phase by adding or taking energy. Solid – Liquid phase change – is the change of a solid to a liquid. During melting energy is absorbed. The temperature at which a solid changes to liquid is called the melting point. MELTING Solid – Liquid phase change FREEZING – is the change of a liquid to a solid. Freezing occurs when a substance loses energy. The temperature at which a liquid changes to solid is called the freezing point. Liquid –Gas phase changes – is the change of a substance from a liquid to a gas. Energy is absorbed in this process. The process is called evaporation when it takes place at the surface. If energy is supplied until the liquidgas occurs, then the process is called boiling. VAPORIZATION Liquid –Gas phase changes CONDENSATION – is the change of a gas to a liquid. Energy is released during this process. Solid-Gas phase change – when solid surface particles escape directly into gas phase. Example: Dry Ice SUBLIMATION Phases of Matter Phase change diagram Chemical Properties The properties that describe how a substance changes into another NEW substance. Flammability is a chemical property. It describes the ability to burn. Flammabilty Chemical Change Is the process by which the substance changes. Another name for a chemical change is a chemical reaction.