Edita Pusvaškienė
... temperature. Thus the temperature for optimum extraction efficiency was determined experimentally. The effect of temperature was studied in the range of 20 - 70oC by exposing SPME fibre in the headspace of the solution containing 10 mg L-1 of each analyte for 15 min. As can be seen in Fig. 4, the ex ...
... temperature. Thus the temperature for optimum extraction efficiency was determined experimentally. The effect of temperature was studied in the range of 20 - 70oC by exposing SPME fibre in the headspace of the solution containing 10 mg L-1 of each analyte for 15 min. As can be seen in Fig. 4, the ex ...
Fluorian garnets from the host rocks of the Skaergaard intrusion
... Fluorine-bearing garnets formed as part of a later, retrograde assemblage altering prismatic wollastonite and pyroxene in amygdule centers. Other retrograde minerals in amygdule centers are fluorite, calcite, quartz, acicular wollastonite, and magnesian hedenbergite. Near the walls of amygdules, pre ...
... Fluorine-bearing garnets formed as part of a later, retrograde assemblage altering prismatic wollastonite and pyroxene in amygdule centers. Other retrograde minerals in amygdule centers are fluorite, calcite, quartz, acicular wollastonite, and magnesian hedenbergite. Near the walls of amygdules, pre ...
ABSTRACT Title of Document:
... in coexisting phases. Therefore, we have investigated the behavior of a PB-b-PEO diblock copolymer of narrow polydispersity (1.04) and roughly equivalent block lengths (54.7 wt% PEO) in the methanol/cyclohexane binary solvent system, which is partially miscible at room temperature and exhibits an am ...
... in coexisting phases. Therefore, we have investigated the behavior of a PB-b-PEO diblock copolymer of narrow polydispersity (1.04) and roughly equivalent block lengths (54.7 wt% PEO) in the methanol/cyclohexane binary solvent system, which is partially miscible at room temperature and exhibits an am ...
ELECTROCHEMICAL STUDY OF CORROSION PROCESSES IN
... partial charge transfer reactions such as the metal dissolution and the reduction of oxygen. On the other hand, CO processes are dominated by direct molecular processes such as the direct reaction of the metal with aggressive species on one site. EES method is used to differentiate two corrosion mec ...
... partial charge transfer reactions such as the metal dissolution and the reduction of oxygen. On the other hand, CO processes are dominated by direct molecular processes such as the direct reaction of the metal with aggressive species on one site. EES method is used to differentiate two corrosion mec ...
feature article
... solvents (oils) (B), nonionic (C) or ionic amphiphiles (D), and salts (E). The mutual solubility between water and oils is very low. However, if an amphiphile is added, the mutual solubility increases until, at a sufficiently high amphiphile concentration, the mixture becomes homogeneous. As experim ...
... solvents (oils) (B), nonionic (C) or ionic amphiphiles (D), and salts (E). The mutual solubility between water and oils is very low. However, if an amphiphile is added, the mutual solubility increases until, at a sufficiently high amphiphile concentration, the mixture becomes homogeneous. As experim ...
Fluid and enthalpy production during regional metamorphism
... constructed to determine the thermal effects of reaction enthalpy and the amount of fluid generated by dehydration metamorphism. The model continental crust contains an average of 2.9 wt % water and dehydrates by a series of reactions between temperatures of 300 and 750 ~ C. Large scale metamorphism ...
... constructed to determine the thermal effects of reaction enthalpy and the amount of fluid generated by dehydration metamorphism. The model continental crust contains an average of 2.9 wt % water and dehydrates by a series of reactions between temperatures of 300 and 750 ~ C. Large scale metamorphism ...
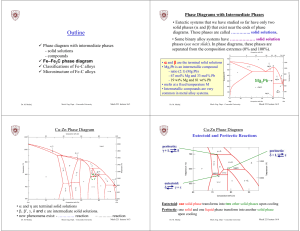
Outline - Concordia University
... • Soft and relatively easy to deform γ -austenite - solid solution of C in …….. Fe • The maximum solubility of C is 2.14 wt % at 1147°C. • Interstitial lattice positions are much larger than ferrite (higher C%) • Is not stable below the eutectic temperature (727 °C) unless cooled rapidly (Chapter 10 ...
... • Soft and relatively easy to deform γ -austenite - solid solution of C in …….. Fe • The maximum solubility of C is 2.14 wt % at 1147°C. • Interstitial lattice positions are much larger than ferrite (higher C%) • Is not stable below the eutectic temperature (727 °C) unless cooled rapidly (Chapter 10 ...
Solutions and solubility
... heat + solid sugar + water = dissolved sugar The equation represents two processes: dissolution going left to right, and crystallization going right to left. When the sugar crystals are dissolving at exactly the same rate that sugar is crystallizing out of solution, the system is at equilibrium. ...
... heat + solid sugar + water = dissolved sugar The equation represents two processes: dissolution going left to right, and crystallization going right to left. When the sugar crystals are dissolving at exactly the same rate that sugar is crystallizing out of solution, the system is at equilibrium. ...
Fluid reservoirs in the crust and mechanical coupling between the... lower crust Bruce E Hobbs , Alison Ord
... An important observation associated with seismic activity on the Nagamachi-Rifu Fault is the existence of tabular, fluid rich zones at mid-crustal levels. These zones resemble the “bright spots” seen in many seismic images of the crust worldwide. The aim of this paper is to develop the mechanical fo ...
... An important observation associated with seismic activity on the Nagamachi-Rifu Fault is the existence of tabular, fluid rich zones at mid-crustal levels. These zones resemble the “bright spots” seen in many seismic images of the crust worldwide. The aim of this paper is to develop the mechanical fo ...
Supercritical Burning of Liquid Oxygen (LOX) Droplet with Detailed
... ignition process and diffusion flame structure. Ignition consists typically of the propagation of a premixed flame which is initiated in the H,-rich hot side. Propagation takes place in a nonhomogeneous hot environment (say 1500 K) with a considerable velocity (typically 50 ms-’ ). Despite the high ...
... ignition process and diffusion flame structure. Ignition consists typically of the propagation of a premixed flame which is initiated in the H,-rich hot side. Propagation takes place in a nonhomogeneous hot environment (say 1500 K) with a considerable velocity (typically 50 ms-’ ). Despite the high ...
Temperature Dependence of Viscosity and Density of cis-1,4/trans
... For the viscosity and density measurements with 2-MP, CP, and CP/IP a home-built prototype cryostat (A) was used, which is described in detail in [7]. The temperature control consisted of a calibrated Pt-100 resistance thermometer (Lauda R46) in combination with a control unit (Haake TP24) (also cf. ...
... For the viscosity and density measurements with 2-MP, CP, and CP/IP a home-built prototype cryostat (A) was used, which is described in detail in [7]. The temperature control consisted of a calibrated Pt-100 resistance thermometer (Lauda R46) in combination with a control unit (Haake TP24) (also cf. ...
Slide 1 - scie
... understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other ...
... understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other ...
No Slide Title
... understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other ...
... understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other ...
chromapp
... understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other ...
... understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other ...
The Physical Chemistry, Theory and Technique of
... fugacity are all relative concepts, e.g., a solution does not have an osmotic pressure unless there is a semipermeable membrane present and another solution on the other side. When talking about these terms, then, reference must be made to the particular system being studied. ...
... fugacity are all relative concepts, e.g., a solution does not have an osmotic pressure unless there is a semipermeable membrane present and another solution on the other side. When talking about these terms, then, reference must be made to the particular system being studied. ...
HC_Chapter_15_-_Solutions_files/Chapter 15 Objectives and Notes
... combined materials that are uniformly distributed throughout the mixture. The component parts do not have to be in a fixed ratio and they do not lose their own identity. a. Because the components are physically mixed together, they can be separated by physical methods such as distillation or crystal ...
... combined materials that are uniformly distributed throughout the mixture. The component parts do not have to be in a fixed ratio and they do not lose their own identity. a. Because the components are physically mixed together, they can be separated by physical methods such as distillation or crystal ...
Liquid-Vapor Equilibria of Llnear Kihara Molecules
... = nu3, and p* = p / ( c / $ ) . The number in parentheses is the accuracy beginning of the run. For a more detailed description of the of the last decimal(s), so 0.375 (15) means 0.375 i 0.015. The estimethod we refer the reader to the original paper^.^^^^^ mated errors were obtained from the standa ...
... = nu3, and p* = p / ( c / $ ) . The number in parentheses is the accuracy beginning of the run. For a more detailed description of the of the last decimal(s), so 0.375 (15) means 0.375 i 0.015. The estimethod we refer the reader to the original paper^.^^^^^ mated errors were obtained from the standa ...
Methods of solubility improvements
... network. The solubilization efficiency of a cosolvent depends upon the extent to which it weakens the structure of water. Cosolvents reduces the interfacial tension between the aqueous solution and hydrophobic solute. Most cosolvents have hydrogen bond donor and/or acceptor groups as well as small h ...
... network. The solubilization efficiency of a cosolvent depends upon the extent to which it weakens the structure of water. Cosolvents reduces the interfacial tension between the aqueous solution and hydrophobic solute. Most cosolvents have hydrogen bond donor and/or acceptor groups as well as small h ...
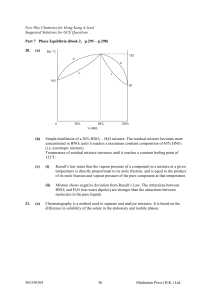
Topic guide 6.2: Phase equilibria
... •• this means that both temperature and pressure can be varied without altering the number of phases. If F = 1, it means that if, say, temperature is altered, then pressure must also be altered to maintain the number of phases in equilibrium. If F = 0, it means that no variable can be altered withou ...
... •• this means that both temperature and pressure can be varied without altering the number of phases. If F = 1, it means that if, say, temperature is altered, then pressure must also be altered to maintain the number of phases in equilibrium. If F = 0, it means that no variable can be altered withou ...
Ch 8 LAN 7th Intro Chem Gases Liquids and Solids
... 1. What are the major intermolecular forces, and how do they affect the states of matter? Be able to explain dipole–dipole forces, London dispersion forces, and hydrogen bonding, recognize which of these forces affect a given molecule, and how these forces are related to the physical properties of ...
... 1. What are the major intermolecular forces, and how do they affect the states of matter? Be able to explain dipole–dipole forces, London dispersion forces, and hydrogen bonding, recognize which of these forces affect a given molecule, and how these forces are related to the physical properties of ...
Pore-Scale Controls on Reaction-Driven Fracturing - DUO
... We will now take a closer look at the pore-scale mechanisms that lead to the stresses and fracture patterns discussed in the preceding section. The key requirement for reactions to take place is that water has access to the reactive surface. In the examples given below, we will show how fracturing c ...
... We will now take a closer look at the pore-scale mechanisms that lead to the stresses and fracture patterns discussed in the preceding section. The key requirement for reactions to take place is that water has access to the reactive surface. In the examples given below, we will show how fracturing c ...
Pore-Scale Controls on Reaction
... We will now take a closer look at the pore-scale mechanisms that lead to the stresses and fracture patterns discussed in the preceding section. The key requirement for reactions to take place is that water has access to the reactive surface. In the examples given below, we will show how fracturing c ...
... We will now take a closer look at the pore-scale mechanisms that lead to the stresses and fracture patterns discussed in the preceding section. The key requirement for reactions to take place is that water has access to the reactive surface. In the examples given below, we will show how fracturing c ...
Book 2,Part 7 - GEOCITIES.ws
... Presence of many other elements increases the boiling point of He. Hence it is possible to have He liquid in the sun even when the temperature is very high. ...
... Presence of many other elements increases the boiling point of He. Hence it is possible to have He liquid in the sun even when the temperature is very high. ...
Supercritical fluid
A supercritical fluid (SCF) is any substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist. It can effuse through solids like a gas, and dissolve materials like a liquid. In addition, close to the critical point, small changes in pressure or temperature result in large changes in density, allowing many properties of a supercritical fluid to be ""fine-tuned"". Supercritical fluids are suitable as a substitute for organic solvents in a range of industrial and laboratory processes. Carbon dioxide and water are the most commonly used supercritical fluids, being used for decaffeination and power generation, respectively.