Concept of Capillary Collapse in Air Space
... and the decreasing weight like force of attraction per unit area = 1.12 mg/cm2 (8 / 7.12=1.12 mg/cm2). When the distance returned to the long (over than 1 mm) distance between surfaces, observed weight of water returned to the normal first value. Displacement of glass plate by the heavy glass cube d ...
... and the decreasing weight like force of attraction per unit area = 1.12 mg/cm2 (8 / 7.12=1.12 mg/cm2). When the distance returned to the long (over than 1 mm) distance between surfaces, observed weight of water returned to the normal first value. Displacement of glass plate by the heavy glass cube d ...
Chemical fractionation at environmental interfaces
... Fractionation, is of, relating to, or involving a process for separating components of a mixture through differences in physical or chemical properties. In this thesis, it is occasionally used more broadly to mean partitioning, which emphasizes the separation of a species between different phases. A ...
... Fractionation, is of, relating to, or involving a process for separating components of a mixture through differences in physical or chemical properties. In this thesis, it is occasionally used more broadly to mean partitioning, which emphasizes the separation of a species between different phases. A ...
1 3. Molecular mass transport 3.1 Introduction to mass transfer 3.2
... system contains three or more components, as many industrial fluid streams do, the problem becomes unwidely very quickly. The conventional engineering approach to problems of multicomponent system is to attempt to reduce them to representative binary (i.e., two component) systems. In order to unders ...
... system contains three or more components, as many industrial fluid streams do, the problem becomes unwidely very quickly. The conventional engineering approach to problems of multicomponent system is to attempt to reduce them to representative binary (i.e., two component) systems. In order to unders ...
Aggregation and Adsorption at Interfaces
... unfavourable hydrophobic interactions within the bulk phase. There, water molecules interact with one another through hydrogen bonding, so the presence of hydrocarbon groups in dissolved amphiphilic molecules causes distortion of this solvent structure apparently increasing the free energy of the sy ...
... unfavourable hydrophobic interactions within the bulk phase. There, water molecules interact with one another through hydrogen bonding, so the presence of hydrocarbon groups in dissolved amphiphilic molecules causes distortion of this solvent structure apparently increasing the free energy of the sy ...
Growing Negative Pressure in Dissolved Solutes: Raman - HAL-Insu
... of which allows them to resist tensile (pulling) as pressurizing (pushing) forces (pressure, which can be also called strain, is a vectorial quantity)1. One interest to study the tensile (or stretched) liquids is that they are metastable with respect to their vapor: there are superheated liquids. Th ...
... of which allows them to resist tensile (pulling) as pressurizing (pushing) forces (pressure, which can be also called strain, is a vectorial quantity)1. One interest to study the tensile (or stretched) liquids is that they are metastable with respect to their vapor: there are superheated liquids. Th ...
In situ-XAS and catalytic study of acrolein hydrogenation over silver
... Figure 3: Difference spectrum of grazing – normal incidence spectrum taken from Fig. 2 (shown here as shaded area). As a comparison gas-phase spectrum of propionaldehyde is shown after background subtraction. enhanced, if the spectra are normalized at the first, 1sC1,2 1π* transition. (According to ...
... Figure 3: Difference spectrum of grazing – normal incidence spectrum taken from Fig. 2 (shown here as shaded area). As a comparison gas-phase spectrum of propionaldehyde is shown after background subtraction. enhanced, if the spectra are normalized at the first, 1sC1,2 1π* transition. (According to ...
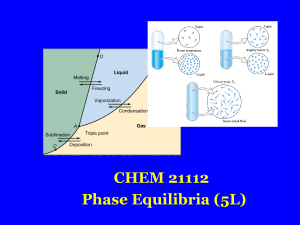
Chapter 6-States of Matter: Gases, Liquids, and Solids
... absorbs a portion of the radiation from the sun, preventing it from reaching the planet's surface. Most importantly, it absorbs the portion of ultraviolet light called UVB(UltraViolet-B). UVB is particularly effective at damaging DNA. It is a cause of melanoma and other types of skin cancer. UVB has ...
... absorbs a portion of the radiation from the sun, preventing it from reaching the planet's surface. Most importantly, it absorbs the portion of ultraviolet light called UVB(UltraViolet-B). UVB is particularly effective at damaging DNA. It is a cause of melanoma and other types of skin cancer. UVB has ...
2.26 MB - KFUPM Resources v3
... pure substances from tables of property data. Describe the hypothetical substance “ideal gas” and the ideal-gas equation of state. Apply the ideal-gas equation of state in the solution of typical problems. Introduce the compressibility factor, which accounts for the deviation of real gases from idea ...
... pure substances from tables of property data. Describe the hypothetical substance “ideal gas” and the ideal-gas equation of state. Apply the ideal-gas equation of state in the solution of typical problems. Introduce the compressibility factor, which accounts for the deviation of real gases from idea ...
Surface Tension
... (which is equivalent to N/m). For example, the amount of work required to create 1 m2 surface is about 72.8 103 J for water. Surface tension is defined as the force at right angle to any line of unit length in the surface. Therefore, surface tension = force/distance. It is expressed in N/m. T ...
... (which is equivalent to N/m). For example, the amount of work required to create 1 m2 surface is about 72.8 103 J for water. Surface tension is defined as the force at right angle to any line of unit length in the surface. Therefore, surface tension = force/distance. It is expressed in N/m. T ...
Supplementary Notes - Word file (264 KB )
... peridotite and liquid komatiite in the pressure range 0~100 kbar, two magnesian silicates of composition closely related to that of the olivine melt. When extrapolating to olivine the observation made by Agee and Walker (1993) that the bulk modulus is essentially invariant with composition in these ...
... peridotite and liquid komatiite in the pressure range 0~100 kbar, two magnesian silicates of composition closely related to that of the olivine melt. When extrapolating to olivine the observation made by Agee and Walker (1993) that the bulk modulus is essentially invariant with composition in these ...
(III) From Aqueous Solutions with Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate
... In the process of solvent sublation using classic glass column [2], made in the form of a cylinder, the bottom of which served as a filter SCHOTT. Scheme SS-column is represented in Figure 1. Through a porous membrane was supplied gas (nitrogen) from the cylinder. The gas flow was controlled by Rota ...
... In the process of solvent sublation using classic glass column [2], made in the form of a cylinder, the bottom of which served as a filter SCHOTT. Scheme SS-column is represented in Figure 1. Through a porous membrane was supplied gas (nitrogen) from the cylinder. The gas flow was controlled by Rota ...
un/scetdg/36/wpxx
... the capacity limitation, as this would have a negative impact on companies using specification 39 cylinders larger than 75 cubic inches in aerosol applications. A 1.25 litres limit is considered by the industry as too restrictive for flammable industrial spray applications, effectively preventing th ...
... the capacity limitation, as this would have a negative impact on companies using specification 39 cylinders larger than 75 cubic inches in aerosol applications. A 1.25 litres limit is considered by the industry as too restrictive for flammable industrial spray applications, effectively preventing th ...
surface properties
... surface of a solid to be made up of elementary spaces each of which could adsorb one gas molecule. Furthermore, it was assumed that all the elementary spaces were identical in their affinity for a gas molecule and that the presence of a gas molecule on one space did not affect the properties of neig ...
... surface of a solid to be made up of elementary spaces each of which could adsorb one gas molecule. Furthermore, it was assumed that all the elementary spaces were identical in their affinity for a gas molecule and that the presence of a gas molecule on one space did not affect the properties of neig ...
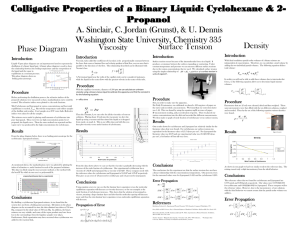
Colligative Properties of an Cyclohexane/1
... the meter and recorded a measurement. We found that our correction factor was 1.42. This was found by using the equation mg/R; m=mass of paper, R=measurement reading, and g=acceleration of gravity. Then we placed our various concentrations into the dish and recorded the different measurements. We th ...
... the meter and recorded a measurement. We found that our correction factor was 1.42. This was found by using the equation mg/R; m=mass of paper, R=measurement reading, and g=acceleration of gravity. Then we placed our various concentrations into the dish and recorded the different measurements. We th ...
tension, compression and shear fatigue of a closed cell foam
... The specimens were tested using a sinusoidal load in load control at 2 Hz at a load ratio R = 0.1. The crack length was monitored using a travelling microscope and measured on one surface only. Tests were done by injecting paint into the crack front, then propagating the crack some distance (several ...
... The specimens were tested using a sinusoidal load in load control at 2 Hz at a load ratio R = 0.1. The crack length was monitored using a travelling microscope and measured on one surface only. Tests were done by injecting paint into the crack front, then propagating the crack some distance (several ...
states of matter
... point increases on moving from HCl to HI. This means that London forces are predominant. This is so because London forces increase as the number of electrons in a molecule increases and in this case number of electrons is increasing from HCl towards HI. ...
... point increases on moving from HCl to HI. This means that London forces are predominant. This is so because London forces increase as the number of electrons in a molecule increases and in this case number of electrons is increasing from HCl towards HI. ...
AAN025_V1 Interfacial rheometry
... face) tension. What gives rise to the surface or in- the gas phase. The average residence time of a molecule at the surface of a liquid is in the order of terfacial tension? microseconds. Let’s consider a gas-liquid interface. In the liqThe surface tension can be defined as the force uid phase the m ...
... face) tension. What gives rise to the surface or in- the gas phase. The average residence time of a molecule at the surface of a liquid is in the order of terfacial tension? microseconds. Let’s consider a gas-liquid interface. In the liqThe surface tension can be defined as the force uid phase the m ...
Properties of Pure Substance
... Predict the pressure of nitrogen gas at T=175 K and v=0.00375 m3/kg on the basis of (a) the ideal gas equaYon of state and (b) the van der Waals equaYon of state, (c) t ...
... Predict the pressure of nitrogen gas at T=175 K and v=0.00375 m3/kg on the basis of (a) the ideal gas equaYon of state and (b) the van der Waals equaYon of state, (c) t ...
Chemistry - Chap 12 Homework Answers 2014
... 7. What is vapor pressure? On a microscopic basis, how does a vapor pressure develop in a closed flask containing a small amount of liquid? What processes are going on in the flask? pressure exerted by vapor above a liquid. High energy particles at surface escape and exert the pressure 8. Which subs ...
... 7. What is vapor pressure? On a microscopic basis, how does a vapor pressure develop in a closed flask containing a small amount of liquid? What processes are going on in the flask? pressure exerted by vapor above a liquid. High energy particles at surface escape and exert the pressure 8. Which subs ...
CHAPTER 17
... is therefore no resultant force tending to move it in any direction. On the other hand, at the surface of a liquid there is a net attraction of the vapor molecules into the liquid. ...
... is therefore no resultant force tending to move it in any direction. On the other hand, at the surface of a liquid there is a net attraction of the vapor molecules into the liquid. ...
Generation of 3-Dimensionally Integrated Micro Solution Plasmas and Its Application to Decomposition of Organic Contaminants in Water
... (b) electric field at the center of the bubble indicated by “Probe point” in Fig. 1. cal conductivity is infinite, we cannot expect any electric field in the bubbles because the surface of the bubbles works as a short circuit to extinguish potential difference on the bubble surface. However, the ele ...
... (b) electric field at the center of the bubble indicated by “Probe point” in Fig. 1. cal conductivity is infinite, we cannot expect any electric field in the bubbles because the surface of the bubbles works as a short circuit to extinguish potential difference on the bubble surface. However, the ele ...
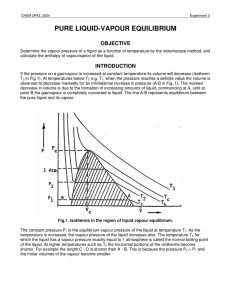
pure liquid-vapour equilibrium - Theoretical and Computational
... in Fig.1 includes all states of the system which correspond to the existence of two phases, liquid and vapour. Part of the shaded area, up to the normal boiling point, Tb, of the liquid, is the subject of this experiment in which the vapour pressure dependence on temperature will be investigated. Th ...
... in Fig.1 includes all states of the system which correspond to the existence of two phases, liquid and vapour. Part of the shaded area, up to the normal boiling point, Tb, of the liquid, is the subject of this experiment in which the vapour pressure dependence on temperature will be investigated. Th ...
Surface Tension in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms
... liquid level in the capillary below that in the chamber and the meniscus is semispherically convex. Maximum bubble pressure method: This method is also called the bubble pressure method. When a gas bubble is produced in a liquid at the tip of a capillary, the curvature initially increases and then d ...
... liquid level in the capillary below that in the chamber and the meniscus is semispherically convex. Maximum bubble pressure method: This method is also called the bubble pressure method. When a gas bubble is produced in a liquid at the tip of a capillary, the curvature initially increases and then d ...
11-16 States of Matter
... Changing from solid to liquid to gas or back the other way occurs by increasing or decreasing energy (heat) in a substance Changing the state does not change the chemical structure. It merely makes the particles in the substance move around faster or slower. Ex: H2O Water …notice that in each stat ...
... Changing from solid to liquid to gas or back the other way occurs by increasing or decreasing energy (heat) in a substance Changing the state does not change the chemical structure. It merely makes the particles in the substance move around faster or slower. Ex: H2O Water …notice that in each stat ...
Foam

A foam is a substance that is formed by trapping pockets of gas in a liquid or solid. A bath sponge and the head on a glass of beer are examples of foams. In most foams, the volume of gas is large, with thin films of liquid or solid separating the regions of gas.An important division of solid foams is into closed-cell foams and open-cell foams. In a closed-cell foam, the gas forms discrete pockets, each completely surrounded by the solid material. In an open-cell foam, the gas pockets connect with each other. A bath sponge is an example of an open-cell foam: water can easily flow through the entire structure, displacing the air. A camping mat is an example of a closed-cell foam: the gas pockets are sealed from each other so the mat cannot soak up water.Foams are examples of dispersed media. In general, gas is present in large amount so it will be divided into gas bubbles of many different sizes (the material is polydisperse) separated by liquid regions which may form films, thinner and thinner when the liquid phase is drained out of the system films. When the principal scale is small, i.e. for a very fine foam, this dispersed medium can be considered as a type of colloid.The term foam may also refer to anything that is analogous to such a foam, such as quantum foam, polyurethane foam (foam rubber), XPS foam, polystyrene, phenolic, or many other manufactured foams.