* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 4: ATP and Cellular Respiration
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
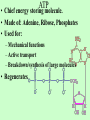
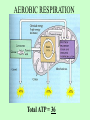
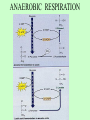
Ch. 8.1 & 9: ATP and Cellular Respiration Energy • Stored in chemical bonds of compounds. • Compounds that store energy: ATP, NADH and FADH2. • When bonds are broken, energy is released. ATP • Chief energy storing molecule. • Made of: Adenine, Ribose, Phosphates • Used for: – Mechanical functions – Active transport – Breakdown/synthesis of large molecules • Regenerates Sources of Energy • Autotrophs – can make own food – photosynthesis – producers • Heterotrophs – get food from others – consumers CELLULAR RESPIRATION C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (energy) • Break down sugars(glucose) to produce energy for cell functions • 2 forms: Aerobic (with O2) Anaerobic (without O2) • Reaction is opposite of Photosynthesis AEROBIC RESPIRATION (3 steps) • Glycolysis-- occurs in the cytoplasm. – Releases 2 ATPs and 2 pyruvates. • Krebs Cycle-- occurs in the mitochondria. -uses the 2 pyruvates from glycolysis -releases 2 ATPs, 6CO2 and many NADH & FADH2 • Electron Transport-- in mitochondria. – Uses the NADH & FADH2 from Krebs – Releases 32 ATPs and 6H2O AEROBIC RESPIRATION Total ATP = 36 ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION • Glycolysis-- yields 2 ATPs and 2 pyruvates – leads to : Alcoholic Fermentation in yeast – or Lactic Acid Fermentation in muscles ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION