* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prostista[1]
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
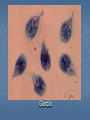
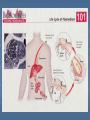
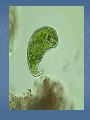
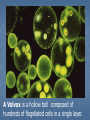
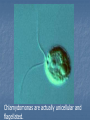
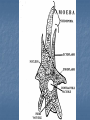
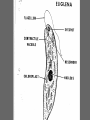
Kingdom Protista If you look at a drop of pond water under a microscope, all the "little creatures" you see swimming around are protists. All protists have a nucleus Protists are either plant-like, animal-like or fungus-like. Plant-like protists are autotrophs – they contain chloroplasts and make their own food. Animal-like and fungus-like protists and are heterotrophs. Protozoans are animal-like protists (heterotrophs) grouped according to how they move. The word protozoa means "little animal." They are so named because many species behave like tiny animals—specifically, they hunt and gather other microbes as food. All protozoa digest their food in stomachlike compartments called vacuoles <vacyou-ohls>. As they chow down, they make and give off nitrogen, which is an element that plants and other higher creatures can use. Protozoa range in size from 1/5,000 to 1/50 of an inch (5 to 500 µm) in diameter. They can be classified into three general groups based on how they move. The first group is the phylum Rhizopoda. These are amoebae <ah-me-bee>, which can be subdivided into the testate amoebae, which have a shell-like covering, and the naked amoebae, which don't have this covering. Amoebae ooze along by means of pseudopodia (false feet) engulfing food as they go. Amoebae live in water or moist places. They have a cell membrane but no cell wall. The second group is the Flagellates <flahgeh-lets>, of the phylum Zoomastigina. Flagellates are generally the smallest of the protozoa and have one or several long, whip-like projections called flagella poking out of their cells. Flagellates use their flagella to move. It is a flagellate in the intestines of termites which enable them to eat wood. Both organisms benefit…..what kind of relationship do they have? Giardia The third group of protozoans are the ciliates from the phylum Ciliophora. These are generally the largest protozoa. They are covered with hair-like projections called cilia and they eat the other two types of protozoa as well as bacteria. Ciliates are found in every aquatic habitat. The last of the Protozoans come from the phylum, Sporozoa. These are parasitic and nonmotile. For example…… DIATOMS Multicellular algae are classified by color. Giant Kelp are the largest and most complex brown algae. They have hold fasts and air bladders. The last of the multicellular algae are the green algae from the Phylum chlorophyta. Most green algae are found in fresh water habitats. A Volvox is a hollow boll composed of hundreds of flagellated cells in a single layer. Chlamydomonas are actually unicellular and flagellated. There are four phyla in the Protista Kingdom Amoeba Flagellates Ciliates Sporozoans Protozoans are found in many environments. Oceans Ponds Rivers Streams Soil Lakes Ditches Creeks And as Parasites DISADVANTAGES OF PROTOZOANS They can produce diseases such as Malaria and Dysentery. ADVANTAGES OF PROTOZOANS THEY ARE AN IMPORTANT SOURCE OF FOOD FOR A MULTITUDE OF SEA ANIMALS. THEY CONTRIBUTE TO THE FORMATION OF SOIL BY ASSISTING IN THE DECAY OF PLANTS AND ANIMALS. THE HARD COVERING OF MANY PROTOZOANS ACCUMULATES TO FORM ROCKS. THE GREAT PYRAMIDS OF EGYPT THE CHALK CLIFFS OF DOVER ,ENGLAND Amoeba – Comes from the Greek word meaning change. Contractile vacuole- stores water Food vacuole - stores food Pseudopods- helps it move Nucleus- controls the activities of the cell Cell membrane- separates it from it’s environment Ectoplasm and endoplasm -is the liquid part of the cell and it is made up of water, salts and compounds. The paramecium – Phyla Ciliates Cilia used for moving Contractile vacuole stores water Food vacuole stores food Macronucleus and micronucleus controls the activities of the cell. Pellicle covers the cell membrane and acts like a skeleton Trichocysts are defence structures that shoot out like long threads The food enters the oral grooveand falls into the mouth cavity. It then collects in a sac called a gullet. When the gullet gets full it breaks away and becomes a food vacuole. Flagellum helps it move Contractile vacuole stores water Eyespot searches for light Chloroplast cells contains chlorophyll that traps the sunlight. Reservoir stores extra water Nucleus controls the cell’s activities.