* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Myers Update 2011A
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
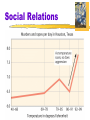
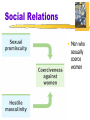
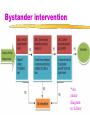
Myers’ PSYCHOLOGY Seventh Edition in Modules Module 55 Social Relations Social Relations Prejudice- mixture of beliefs an unjustifiable (and usually negative) attitude toward a group and its members involves stereotyped beliefs, negative feelings, and a predisposition to discriminatory action Stereotype a generalized (sometimes accurate, but often over generalized) belief about a group of people Social Relations What comes to mind when you first see this picture? Social Relations Does perception change with race? Social Relations Americans today express much less racial and gender prejudice Social Roots of Prejudice Why does prejudice arise? Social Inequalities “Haves” and “HaveNots” Haves can develop attitudes that justify the way things are “Prejudice rationalizes inequalities” Self fulfilling prophecy- Gordon Allport Self-Fulfilling Prophecy Steps to Self-Fulfilling Prophecy • Perceiver has expectations about how the target will behave * Perceiver then behaves in a way that is likely to elicit the expected target behavior * Target indeed behaves in a way that confirms perceiver’s expectations * Perceiver sees predicted behavior - Objective perceiver might also see it • NOTE: you cannot have a self-fulfilling prophecy with yourself Good Example:You expect your new roommate to be shy so you don’t speak much to him after he moves in, and he therefore does seem shy Wrong Example:Because you get a bad grade on your first exam you give up and stop studying at all, leading you to fail the course Us and Them John Turner & Michael Hogg- Social identities Ingroup “Us”- people with whom one shares a common identity Outgroup “Them”- those perceived as different or apart from one’s ingroup Social Relations Ingroup Bias tendency to favor one’s own group Scapegoat Theory theory that prejudice provides an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame Ex:Nazi’s blaming Jews for all problems. Just-World Phenomenon tendency of people to believe the world is just people get what they deserve and deserve what they get Ex:When told about a rape victim, people would respond that she had it coming, or that her behavior must have invited rape. Social Relations Vivid cases (9/11 terrorists) feed stereotypes Just- World Phenomenon The tendency of people to believe the world is just and that people therefore get what they deserve and deserve what they get. Hindsight bias also plays a part Genetic & Neural Influences Genetic: Animals have been bred for aggressiveness Twin studies suggest that genes influence human aggression as well Neural: Animal and human brains have neural systems that, when stimulated, inhibit or produce aggressive behavior Social Relations Aggression any physical or verbal behavior intended to hurt or destroy Behavior emerges from interaction of biology and experience Freud- our species has a volcanic potential to erupt in aggression Frustration-Aggression Principle principle that frustration – the blocking of an attempt to achieve some goal – creates anger, which can generate aggression Social Relations Social Relations Men who sexually coerce women Do Video Games Teach or Release Violence? Social Relations Conflict perceived incompatibility of actions, goals, or ideas Social Trap a situation in which the conflicting parties, by each rationally pursuing their self-interest, become caught in mutually destructive behavior Social Relations Social trap Person 1 Person 2 Choose B Choose A Choose A Choose B Optimal outcome by pursuing our self-interest and not trusting others, we can end up losers Biased Perceptions Probable outcome Individuals or groups of nations can have deep psychological roots (self-serving bias & fundamental attribution error) Social RelationsAttractiveness Mere Exposure Effect repeated exposure to novel stimuli increases liking of them Proximity- most powerful predictor of friendship Conceptions of attractiveness vary by culture Social Relations Passionate Love an aroused state of intense positive absorption in another usually present at the beginning of a love relationship Companionate Love deep affectionate attachment we feel for those with whom our lives are intertwined Social Relations Equity a condition in which people receive from a relationship in proportion to what they give to it. Self-Disclosure revealing intimate aspects of oneself to others Ex: People who engage in deep, personal conversations have a tendency toward intimacy over small talk conversations with others. Altruism unselfish regard for the welfare of others Became a major concern after vile acts of sexual violence Social Relations Bystander Effect tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present Social Relations The decision-making process for bystander intervention Bystander intervention *An easier diagram to follow Social Relations Social Exchange Theory the theory that our social behavior is an exchange process, the aim of which is to maximize benefits and minimize costs Superordinate Goals shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation Social Relations Graduated and Reciprocated Initiatives in Tension-reduction (GRIT) a strategy designed to decrease international tensions Ex. League of Nations! one side announces recognition of mutual interests and initiates a small conciliatory act opens door for reciprocation by other party