* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proteins
Rosetta@home wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
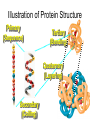
Protein Structure Review of Proteins • Small molecules — 20 kinds – 1 amino group – 1 carboxyl group – 1 "R" group • Joined by peptide bonds to form polypeptide • Different sequence makes different protein • Proteins are amino acid polymers • Many roles in the cell… – Enzymes – Hormones – Structure (muscle, hair, nails) – Cell membrane pumps and channels Amino Acid Carboxylic Acid Group Amine Group R “Alpha” Carbon The “R” Group Placeholder Levels of Protein Structure • Like describing a knot by starting with the strands of the rope – Primary: The amino acid sequence – Secondary: Coiling or folding – Tertiary: folding, kinking, twisting entire structure – Quaternary: Two or more chains together Primary: The amino acid sequence. – This is simply a list of the actual sequence of amino acids in the "backbone" of the protein. – You just start at one end and read off the names of the amino acids in sequence and you have described the primary sequence. Secondary: Coiling of the chain. – The "R" groups get in each other's way and force a twisting of the chain into a coil. Tertiary: Coiling of the coil. – Like if you were to take a screen door spring and tie it in a super knot Quaternary: Two or more chains together – Not all proteins have this level. – It only applies to proteins composed of two or more separate polypeptides glued together. – It refers to how the individual polypeptides are attached. Quaternary Structure Illustration of Protein Structure Primary (Sequence) Tertiary (Bending) Quaternary (Layering) Secondary (Coiling) Denaturation- When an unfavorable change causes a protein to unravel and lose its normal shape 1) A change in temperature 2) A change in pH 3) Some other environmental factor















![Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab [1/13/2016]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010042148_1-49212ed4f857a63328959930297729c5-150x150.png)