* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 49. INTRODUCTION TO ANALYTIC GEOMETRY
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Four-dimensional space wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Event symmetry wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartan connection wikipedia , lookup
Mirror symmetry (string theory) wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Conic section wikipedia , lookup
Hyperbolic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
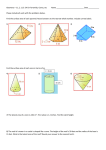
Analytic Geometry Conic Sections Analytic Geometry Analytic geometry, usually called coordinate geometry and earlier referred to as Cartesian geometry or analytical geometry, is the study of geometry using the principles of algebra The Circle The plane that intersects the cone is perpendicular to the axis of symmetry of the cone. The Ellipse The plane that intersects the cone is neither parallel nor perpendicular to the axis of symmetry of the cone and cuts through 2 “sides” The Parabola The plane that intersects the cone is parallel to an element of the cone. The Hyperbola The plane that intersects the cone is parallel to the axis of symmetry of the cone. Where do you see conics in real life? Dimensions a 1D 0 b y x 2D z 3D y x Ordered Pairs Review : (a,b) b (-a,b) II I (a,b) a (-a,-b) III IV (a,-b) Finding the inclination of a line Θ=0 Θ Θ Θ=∏/2 Horizontal Vertical Acute Obtuse Example: make sure you are in radian mode Find the inclination of the line 2x+3y = 6 m= -a/b m= -2/3 Θ Θ = ∏ + arctan (-2/3) Θ = ∏ +(-.588) Θ = 2.554