* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Crossing the Plasma Membrane
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
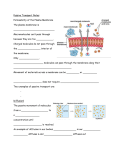
Plasma Membrane Two key components of the membrane: phospholipids proteins The plasma membrane is semi-permeable (selectively permeable) It controls what goes into and out of the cell Two forms of transport: Passive Transport Active Transport • No energy needed • ENERGY used • WITH the gradient (high to low) • AGAINST the gradient • Examples: • Examples: – Diffusion – Osmosis – Endocytosis – Exocytosis Phospholipids • The phospholipids line up to form a double membrane • Small, uncharged particles are able to pass right between the phospholipids • This is called simple diffusion Proteins • There are also proteins embedded between the phospholipids. • These proteins function as gates, allowing larger or charged molecules to get in/out of the cell • Only molecules which are “recognized” are allowed thru these proteins • This is facilitated diffusion Passive transport: Diffusion Higher Concentration Lower Concentration Molecules collide – pass thru membrane Passive Transport: Osmosis • The movement of water • Water moves TOWARDS the molecules • Think of it as “water wants to dissolve stuff” • Which way will water move in each case? Passive Transport: Osmosis ISOtonic HYPERtonic HYPOtonic The effect of osmosis on cells HYPERTONIC ISOTONIC HYPOTONIC Passive transport: osmosis Osmosis Which way will water move? Hypertonic or Hypotonic? Crossing the Plasma Membrane Active transport AGAINST the gradient requires energy Figure 3.8 Active Transport • Endocytosis – Pino– Phago- • Exocytosis Ion pumps: Thru a protein, but using energy Figure 3.9 Crossing the Plasma Membrane Passive Transport Active Transport Crossing the Plasma Membrane Passive Transport Active Transport • No energy needed • ENERGY used • WITH the gradient • AGAINST the gradient • Diffusion • Can be through a protein • Osmosis • Endocytosis • Exocytosis Post test • What is the job of the plasma membrane? • What is semi-permeable? • What is the difference between active transport and passive transport? • What is osmosis? • What will happen to a cell when placed in a hypertonic solution? Hypotonic solution?