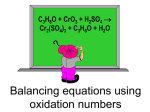* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
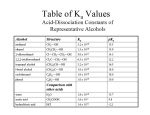
Download alcohol - Portal UniMAP
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
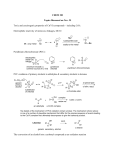
Reactions: OXIDATION & REDUCTION ROHAZITA BAHARI Basic need to know Type of alcohol What is carbonyl group Oxidation Reduction Type of alcohol PRIMARY ALCOHOL SECONDARY ALCOHOL TERTIARY ALCOHOL Carbonyl group What is carbonyl group? Aldehyde Ketone Carboxylic Acid Ester How to remember L: loss E : eO : oxidation Says G : gain E : eR : reduction oxidation reduction Is the loss of electrons (e-) and loss of hydrogen atom Is the gain of electrons (e-) and gain of hydrogen atom Up charge Reduce charge Example: If I have the Fe2+ reacting to form Fe3+, U probably learned that when the oxidation number goes up that is oxidation. Fe 2+ Fe3+ A reaction involving electron transfer Called it as redox reaction example: Fe + CuSO4 FeSO4 + Cu Oxidation-Reduction An oxidation reduction reaction or a redox reaction is one which electron transfer occurs In organic chemistry this tends to have a significance more on par of oxygen content Oxidation reactions as ones in which carbon gains bonds to oxygen Reduction reactions as ones in which carbon atoms lose bonds to oxygen. We can see some different functional groups here a carboxylic acid and an aldehyde and alcohol and just alkane. This is oxidation and reduction . So there are different compounds that will induce different transformations so there are reducing agents that will reduce any of these compounds in this direction and there are oxidizing agents that will oxidize compounds in this direction. oxidation Just to take a look at oxidations. We can oxidize primary or secondary alcohols A tertiary alcohol cannot be oxidized because that carbon cannot already has three bonds to other carbons. So, there are not any bonds that can be replaced to give carbon more bonds to oxygen. It is going to be possible to gain more oxygen here Example: (oxidation) oxidation For oxidation, we usually used PCC, Pyridinium chlorochromate to get aldehyde for primary alcohols & ketone for secondary alcohols It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primary for oxidation of alcohols. We use Jones oxidation (CrO3 + H2SO4) to get carbocyclic acid for primary alcohols and ketones for secondary alcohols. oxidation Why we can’t use tertiary alcohol to form a carbonyl compound? (what is carbonyl compound) Eg: reduction Carbonyl compound to alcohol Use different reducing agents and again these have different strengths. Sodium borohydrate (NaBH4) and Lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) LiAlH4 more stronger than NaBH4. NaBH4 only reduce aldehyde and ketones LiAlH4 can reduce aldehyde, ketones including carboxylic acid and ester. conclusion U need to understand the transformation that agent is capable of producing and be able to apply that to any substrate.