* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Acids and Bases
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Hyaluronic acid wikipedia , lookup
Nitrocellulose wikipedia , lookup
Sulfuric acid wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Acid throwing wikipedia , lookup
Nitric acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
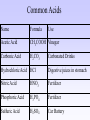
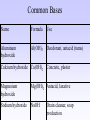
Acids and Bases Dissociation • In water all ionic compounds dissociate into its ionic parts • So NaCl in water dissociates into Na+ and Cl• So H3PO4 dissociates into 3H+ and PO4-3 • Remembers ionic compounds are formed by metals and nonmetals or by metals and polyatomic ions Identifying an Acid • An acid is any compound that + forms an H3O (called hydronium) ion in water • Usually acids have an H in front of the compound • In general they have a sour taste and react with most metals Naming Acids • Look at the acid’s chemical formula, try to name it as if it where an ionic compound • Then eliminate the 1st word • If no “O” is in anion then add hydro to the beginning and trade the –ide for –ic • If the anion has “O” then trade –ate or –ic if the anion ended in –ate originally • If anion has “O” then trade –ite or –ous if the anion ended in –ite originally • Finally add the word “acid” to the end- Name these acids • • • • • • HBr H3N H2SO4 HI HNO3 HNO2 Common Acids Name Formula Use Acetic Acid CH3COOH Vinegar Carbonic Acid H2CO3 Carbonated Drinks Hydrochloric Acid HCl Digestive juices in stomach Nitric Acid HNO3 Fertilizer Phosphoric Acid H3PO4 Fertilizer Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Car Battery Identifying a Base • A base is any compound that forms an OH ion (called hydroxide) in water • Usually bases have an OH at the end of the compound • Bases usually have a bitter taste and a slippery feel Common Bases Name Formula Use Aluminum hydroxide Al(OH)3 Deodorant, antacid (tums) Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 Concrete, plaster Magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 Antacid, laxative Sodium hydroxide NaOH Drain cleaner, soap production Neutralization • When an acid and base react it is called a neutralization reaction • During this reaction a salt and water is always formed • Common salts include but are not limited to: • NaCl, Na2CO3, KCl, KI, MgCl2, CaCO3, and NH4NO3 Proton Donors and Acceptors • Acids are generally defined as proton donors (meaning they give away the H+) • Bases are generally defined as proton acceptors • These alternate definitions of acids and bases help us when compounds react with water or are insoluble Acid Strength • Acids and bases are rated on a pH scale • Where 1 is the strongest acid and 14 is the strongest base • 7 is neutral (water is the only neutral compound) • 1-4 (stronger acid) • 4-7 (weak acid) • 7-10 (weak base) • 10-14 (strong base) Acid Strength (ctd.) • Between any 7 and 6 an acid gets 10 times stronger, between 7 and 5 an acid gets 100 times stronger the scale it logarithmic • Strength is defined as how easily the H+ or the OH- comes off the acid or base, the easier it comes off the stronger the acid or base • Strength is COMPLETELY different than concentration Concentration vs Strength • Concentration refers to how diluted an acid or base is • Concentration DOES NOT change the pH of an acid or base • Hence the pH of 16M HCl is equal to the pH of .001M HCl though there concentrations are extremely different