* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download selected
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Sympatric speciation wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive isolation wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
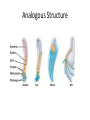
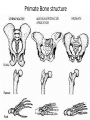
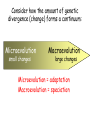
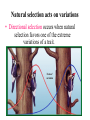
Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Sailed around the world 1831-1836 How did tortoises and birds differ among the islands of the Galapagos? • Each island had its own type of tortoises and birds that were clearly different from other islands Evolution is when organisms change over time. So, modern organisms descended from ancient ones or descended from a common ancestor. Evolution is a Theory – Just like Gravity! • Evolution is a well supported explanation of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world • A theory in science is a well tested hypothesis, not just a guess Artificial Selection • nature provides variation, humans select variations that are useful. • Example - a farmer breeds only his best livestock Selective Breeding Brahman cattle: Good resistance to heat, but poor beef. English shorthorn cattle: Good beef but poor heat resistance. Santa Gertrudis cattle (cross of 2 breeds) RESULT = good beef and resistant to heat! hot weather cow + beefy cow = supercow Natural Selection • The traits that help an organism survive in a particular environment are “selected” in natural selection • Natural selection acts on phenotypes NOT genotypes 11. Natural Selection and Species Fitness • Overtime, natural selection results in changes in the inherited characteristics of a population. • These changes increase a species fitness (survival rate) Evidence of Evolution Fossil Record provides evidence that living things have evolved Fossils show the history of life on earth and how different groups of organisms have changed over time Recent Fossil Finds – Modern whales retain reduced pelvic bones and, in some cases, upper and lower limb bones. However, these structures no longer play a role in locomotion. Homologous Structures – Homologous bones, as shown by colorcoding, support the differently-shaped front limbs of modern vertebrates. Analogous Structure Founder effect & Bottleneck effect Primate Bone structure Evidence of Evolution 2. Geographic Distribution of Living Species Similar animals in different locations were the product of different lines of descent What is an adaptation? • An adaptation is a change in an animal’s physical structure or behavior that helps an animal to survive in their habitat. – Examples: The shape of a bird’s beak, number of fingers and toes, or the color of an animal’s fur. • Physical adaptations do not develop during one lifetime, but over many generations. Consider how the amount of genetic divergence (change) forms a continuum: Microevolution small changes Macroevolution large changes Microevolution = adaptation Macroevolution = speciation The Evolution of Species • Significant changes in the gene pool could lead to the evolution of a new species over time. • The evolution of new species, a process called speciation. It is a process typically caused by the genetic isolation from a main population resulting in a new genetically distinct species. Evolution – change over time. The question is… How much time? Gradualism- a proposed explanation stating that new species arise from the result of slight modification over many generation. This evolutionary change is slow, gradual, and continuous. Punctuated Equilibrium – A proposed explanation stating that species generally stable over long periods of time. Occasionally there are rapid changes that affect some species which can quickly result in a new species. Why do organisms become extinct? II. Extinction – occurs when the environment changes and the adaptive characteristics of a species are insufficient to allow its survival. If our environment is constantly changing, why doesn’t extinction occur more often? Isolating Mechanisms Describe the mechanisms which isolate individuals of a population and allow speciation to occur. Prezygotic barriers: • Obstacle to mating or to fertilization if mating occurs geographic isolation behavioral isolation ecological isolation temporal isolation mechanical isolation gametic isolation Prezygotic Isolating Mechanisms Prezygotic barriers: Ecological isolation • Species occur in same region, but occupy different habitats so rarely encounter each other – reproductively isolated 2 species of garter snake, Thamnophis, occur in same area, but one lives in water & other is terrestrial lions & tigers could hybridize, but they live in different habitats: lions in grasslands tigers in rainforest Prezygotic Isolating Mechanisms Prezygotic Isolating Mechanisms Postzygotic Isolating Mechanisms • Examples: – Hybridization between sheep and goats produces embryos that die in the earliest embryonic stages – Leopard frogs of the United States are a group of similar species, and NOT a single species as was long assumed Postmating Isolation • Postzygotic Isolation • These isolations prevent successful reproduction after fertilisation. – Hybrid Inviability – a zygote is formed but does not develop properly. – Hybrid sterility – a hybrid forms but it is sterile Postmating Isolation – Hybrid Breakdown – the hybrid offspring are fertile but produce many infertile or non-viable offspring. Polyploidy • This is the abrupt formation of a new species. It is an important sympatric speciation as it does not involve geographical isolation. • In one generation the parent and the offspring can belong to a different species. • More common in plants. Isolation by Time • A species that disappeared one million years ago obviously can not interbreed with a species living today. Three kinds of natural selection Natural selection acts on variations • Stabilizing selection is a natural selection that favors average individuals in a population. Selection for average size spiders Normal variation Natural selection acts on variations • Directional selection occurs when natural selection favors one of the extreme variations of a trait. Normal variation Natural selection acts on variations • In disruptive selection, individuals with either extreme of a trait’s variation are selected for. Selection for light limpets Normal variation Selection for dark limpets