* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification, Bacteria, and Viruses Short Answer 1. How does the
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
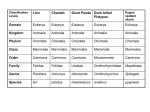
Classification, Bacteria, and Viruses Short Answer 1. How does the diagram show that bacterial cells are different from the cells of eukaryotes? 2. Identify the structure labeled A in the diagram, and describe its function. 3. List the three scientific names of bacterial shapes and describe the shape. Table of Classification Labels Classification Level Aardwolf Grey Wolf Coyote Lion BlueWhale Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia Animalia Animalia Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordata Chordata Chordata Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Order Carnivora Carnivora Carnivora Carnivora Cetacea Family Hyaenidae Canidae Canidae Felidae Balenopteridae Genus Proteles Canis Canis Panthera Balaenoptera Species Proteles cristatus Canis lupus Canis latrans Panther leo Balaenoptera musculus 4. Which of the organisms in the table is least similar to the others? Explain. 5. What classification groups do all organisms in the table have in common? 6. List, in order, from largest to smallest the seven levels of classification 7. What are the two parts of a scientific name for a living organism? Essay 8. Some people believe that taking antibiotics will help them recover more quickly when they have the flu. Explain what is wrong with this reasoning. True/False ____ 9. Vaccines such as penicillin are chemicals that can kill bacteria. _________________________ ____ 10. Unlike the cells of other organisms, the cells of bacteria do not have nuclei. _________________________ ____ 11. Binary fission occurs when a bacterium transfers some of its genetic material to another bacterium. _________________________ Multiple Choice ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 12. Endospores form during a. harsh environmental conditions. c. respiration. b. sunlight hours. d. binary fission. 13. A hidden virus a. attaches to but does not enter the cell. c. immediately takes over the cell's function. b. becomes part of the host cell's genetic d. cannot attach to a host cell. material. 14. Why do scientists organize living things into groups? a. so products from living things can be easily c. so they can make sense of the variety of rocks found in groceries on Earth. b. so that the organisms are easier to study d. so they can find them in the wild more easily 15. Which phrase describes the size of virus particles? a. much larger than cells c. the same size as cells b. smaller than cells d. slightly larger than cells 16. An organism's scientific name consists of a. its class name and its family name. c. its genus name and its species name. b. its phylum name and its species name. d. its kingdom name and its phylum name. 17. What process results in genetically different bacteria? a. conjugation c. asexual reproduction b. binary fission d. respiration 18. Viruses are considered to be nonliving because they a. cannot multiply. c. use energy to grow. b. are not cells. d. produce wastes. 19. What is binomial nomenclature? a. A naming system in which each organism is c. Grouping animals based on how they move given a two-part name b. The naming system developed by Aristotle d. Classifying organisms into seven levels 20. What is a characteristic of archaebacteria? a. Most are disease-causing. c. They use sun to produce food and energy. b. They thrive in extreme environments. d. They live just about everywhere. 21. Which kingdom includes only multicellular heterotrophs? a. protists c. plant b. archaebacteria d. animal 22. Which kingdom includes only prokaryotes? a. fungi c. archaebacteria b. plants d. protists 23. Which of the following is found in the cytoplasm of bacterial cells? a. cell membrane c. flagella b. genetic material d. nucleus 24. Which classification level is broader than the phylum level? a. class c. kingdom ____ ____ ____ ____ b. order d. 25. What is taxonomy? a. the scientific study of how living things are c. classified b. the process used by geologists to classify rocks d. family the name of Aristotle's classification system the process of observing an organism's behavior 26. Why are viruses like parasites? a. They multiply. c. They use energy to develop. b. They make their own food. d. They destroy the cells they enter. 27. What important role do bacteria called decomposers play? a. They slow down food spoilage. c. They produce vitamins. b. They kill harmful bacteria. d. They return basic chemicals to the environment. 28. Which is the broadest classification level? a. kingdom c. phylum b. species d. family Completion 29. An owl and a bat share the same kingdom and phylum; an owl and a robin share the same kingdom, phylum, and class. The owl and ____________________ have more characteristics in common. 30. Bacteria are called ____________________ because their genetic material is not contained in nuclei. 31. A virus can multiply only when it is inside a(n) ____________________. 32. Some bacteria move by using a long, whiplike structure called a(n) ____________________. 33. When bacteria reproduce by ____________________, one cell divides to form two identical cells. 34. A virus that begins to multiply immediately after it enters a cell is called a(n) ____________________ virus. 35. The first part of an organism's scientific name is its classification group called ____________________. 36. Aristotle grouped animals on the basis of how they moved or where they lived. Then ____________________ developed an improved system that depended on grouping organisms on the basis of their observable features. 37. When a(n) ____________________ virus enters a cell, the virus's genetic material becomes part of the cell's genetic material.