* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nuclear Chemistry - Northwest ISD Moodle
Fallout shelter wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion–fission hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive decay wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Background radiation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Ionizing radiation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
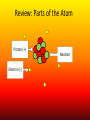
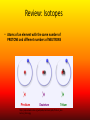
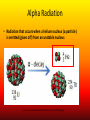
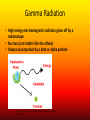
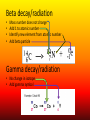
Nuclear Chemistry Review: Parts of the Atom Proton (+) Electron (-) Neutron Review: Isotopes • Atoms of an element with the same number of PROTONS and different numbers of NEUTRONS https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6c/Protium_deu terium_tritium.jpg About The Atom • Nucleus includes NEUTRONS and PROTONS • PROTONS give the atom its identity • Held together by a very strong nuclear force o One of the four fundamental forces in our universe o Incredibly powerful o Releasing nuclear force results in a nuclear reaction Nuclear Stability • Stability of an atom depends on the ratio of protons and neutrons • Too many/too few neutrons can lead to instability • More than 82 protons means an unstable/radioactive nucleus • Nucleus can become stable by releasing energy o More unstable nucleus = more energy released Radioactivity • The process by which an unstable nucleus becomes stable • Radioisotopes: isotopes with unstable nuclei • Ex: Carbon-14, Uranium 235, Thorium-230, Thorium-234 • Radioactive decay- when an unstable nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation • Results in a smaller, more stable nucleus Types of Radiation • Alpha Radiation • Beta Radiation • Gamma Radiation https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=images&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwiT64DklOHMAhWh3YMKHeIIDQQjB0IBg&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.tesec-int.org%2FTechHaz-site%252008%2Ftechnological_hazard%2520Inter%2520Matter.htm&psig=AFQjCNHKYIJcZWH2_vIVTNmqO4KwqXzMg&ust=1463576163223562 Alpha Radiation • Radiation that occurs when a helium nucleus (α particle) is emitted (given off) from an unstable nucleus http://www.emc2-explained.info/Emc2/Decay_htm_files/1968.jpg Beta Radiation • Fast moving electrons emitted from a radioactive source • Neutron decomposes into an electron and a proton • Electron is released (β particle) http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/outreach/isotopes/images/beta_decay.jpg Gamma Radiation • High energy electromagnetic radiation given off by a radioisotope • No mass (not matter like the others) • Always accompanied by a beta or alpha particle http://images.tutorvista.com/cms/images/38/alpha-beta-gammadecay.PNG Type of Radiation Energy Level Atomic Changes Example Nuclear Equations • Used to represent the type of radiation occurring from a nuclear reaction Alpha decay/radiation • • • • Subtract 4 from mass number Subtract 2 from atomic number Identify new element from atomic number Add alpha particle Beta decay/radiation • • • • Mass number does not change Add 1 to atomic number Identify new element from atomic number Add beta particle Gamma decay/radiation • No change in isotope • Add gamma symbol Fission And Fusion • Nuclear Fission: the SPLITTING of a nucleus into smaller fragments • Occurs when the nuclei of certain radioisotopes are bombarded with neutrons • Can unleash enormous amounts of energy • Each time a nucleus splits energy is released • More atoms = bigger boom https://youtu.be/4pQDcQxZA8E Fission And Fusion • Nuclear Fusion: occurs when two light nuclei combine to produce a nucleus of greater mass • Energy released by sun is the result of fusion • Requires a starting temp above 40,000,000 K