* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prokaryotes - AP Biology Overview
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
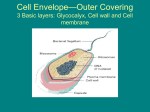
Prokaryotes Cell wall Polysaccharides - Archaea Peptidoglycan - Bacteria o Gram positive – simple cell wall with LOTS of peptidoglycan o Gram negative – complex cell wall with little peptidoglycan More pathenogenic and disease causing – can be resistant to antibiotics Capsule – covers outer cell wall – sticky protection from host cells Fimbriae – short numerous hairs that attach prokaryotes to one another Pili – longer hair – can be used for conjugation – DNA transfer from one bacteria to another Movement Flagella – propulsion Taxis – response toward a stimulus Reproduction Binary Fission – rapid o Genetic Recombination – Conjugation, transduction, transformation Adaptation Can withstand harsh conditions Can produce endospores – resistant “dormant cells” (capsules) that can withstand extreme conditions for long periods of time Nutrition Autotrophs o Photoautotrophs – photosynthesis o Chemoautotrophs – use inorganic chemicals in place of sunlight to manufacture organic compounds Heterotrophs o Photoheterotrophs – use light for energy, but must get carbon from an organic compound o Chemoheterotrophs – must consume to get energy and carbon Metabolism Nitrogen o Nitrogen fixation – take atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) – symbiotic relationship with some plants Oxygen o Obligate aerobes – use O2 for respiration and cannot grow without it o Facultative anaerobes – use O2 if present, but can also grow using fermentation o Obligate anaerobes – are poisoned by O2 – can only do fermentation or anaerobic respiration