* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture15
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Haplogroup I-M438 wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Viral phylodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
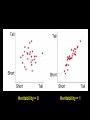
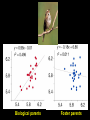
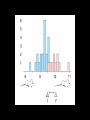
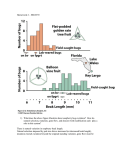
Quantitative genetics Darwin’s tenets: Heritable variation + Differential survival/reproduction = Evolution Heritability = 0 Heritability = 1 Phenotypic variation: total variation in a trait (VP) Genetic variation: variation among individuals due to variation in their genes (VG) Environmental variation: variation among individuals due to variation in their environments (VE) Broad sense heritability: fraction of the total variation in a trait that is due to variation in genes Heritability = VG VG = VP VG + VE Phenotypic variation: VP Genetic variation: VG Environmental variation: VE Biological parents Foster parents Genetic variation: variation among individuals due to variation in their genes (VG) Additive variation: variation among individuals due to the additive effects of genes (VA) Dominance variation: variation among individuals due to gene interactions such as dominance (VD) VG = VA + VD Narrow sense heritability: a measure of the (additive) genetic variation in a trait Heritability, h2 = VA VP = VA VA + VD + VE Genetic variation: VG Phenotypic variation: VP Additive variation: VA Environmental variation: VE Dominance variation: VD Selection differential: difference between the mean of the selected individuals and the mean of the population (S) Evolutionary response: predicted response of the population to selection (R) R = h2 S O* - O Slope = h2 = R = P* - P S P: average midparent value for the entire population P*: average midparent value for the selected individuals O: average midoffspring value for the entire population O*: average midoffspring value for the selected individuals Slope = h2 = R S