* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab 2 Sequence
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene prediction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
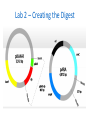
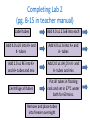
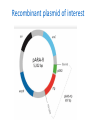
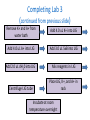
LABORATORY 2 & 3: HOW DO YOU BEGIN TO CLONE A GENE? LSSI Alum, Mary Haus Pre-Assignment http://www.dnaftb.org/34/animation.html • Great background animated storyboard – Could assign as HW if one-toone – Could also complete as pre-lab in computer lab or if you have class sets of tablets or chromebooks – Could complete together in class using teacher computer https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=nfC689ElUVk **Please be aware, sticky ends are not identified correctly, but overall process is. What is a plasmid? • Definition: Small, circular DNA molecules, ranging in size from 1,000 to 200,000 base pairs. • Characteristics: – Can make copies of itself independently of bacterial chromosome using the ori site for initiation. – Can initiate transcription using its promoter sequence. – Often carry antibiotic resistance genes. – Can be passed through bacterial conjugation. Plasmid Features: • Ori (replicating/cloning) • Promoter • Antibiotic resistance • Restriction sites What are restriction enzymes? • Definition: Proteins that restrict the growth of bacteriophage by recognizing and destroying the phage DNA without damaging the host (bacterial) DNA. • Characteristics: Different strains of bacteria possess restriction enzymes that cut at specific DNA sequences called recognition sites and often create sticky ends. What are restriction enzymes? • Importance of restriction enzymes and sticky ends: – Scientists can build designer plasmids that contain specific restriction sites – This allows scientist to cut out and recombine genes to allow for cloning and gene expression. (requires sticky ends) – Sticky ends: want to form hydrogen bonds which scientists use to ligate the DNA together again in desired combinations. Lab 2 – Creating the Digest (cutting up the DNA) • Purpose: to produce the DNA fragments that will be joined to make the recombinant plasmid. – Will need to cut two plasmids • pKAN-R – has the rfp gene, an antibiotic resistance gene for kanamyacin (kan-R), and the promoter sequence (pBAD) • pARA – has an antibiotic resistance gene for ampicillin (ampR) and the arabinose activator (araC) – Arabinose is a sugar that is needed by the promoter to begin transcription of the rfp – Will use 2 restriction enzymes on each plasmid allowing the segment from pKAN-R to later be inserted into the pARA plasmid • BamHI • HindIII Lab 2 – Creating the Digest Lab 2 – Creating the Digest Restriction Digest Fragments BamH I Hind III 4,706 bp BamH I Hind III 4,496 bp Hind III BamH I 806 bp Hind III BamH I 376 bp Safety-Lab 2 • Use laboratory coats, safety glasses and gloves as appropriate • Avoid restrictive clothing and open-toed shoes • No eating or drinking in the lab • Make sure that students are familiar with the operating instructions and safety precautions before they use any of the lab equipment • Check all MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheets) for all chemicals and reagents in the lab before preparing and running the lab www.amgenbiotechexperience.com Lab & Aliquoting Guide-Lab 2 Reagents/Supplies 1.4 ml 2.5X Buffer/class (2.5xB) Aliquot 20ul/group Storage Temp 4o 110 ul of pKAN/class (pKAN) 10ul/group -20o 110 ul of pARA/ class (pARA) 10ul/group -20o 65 ul of Restriction Enzyme/class (RE) 5ul/group -20o 12mL of DI water/ kit (dH20) 1ml/group RT Equipment/Supplies 10 Student boxes with the following: 1 p20 micropipette 1 p200 micropipette 1 p1000 micropipette 1 waste and 1 ice bucket 4 Mini centrifuges 1 Water bath 2 Floating racks www.amgenbiotechexperience.com 1 microfuge rack 1 bag of microfuge tubes 1 bag of microfuge tubes 1 box of refillable tips (2 ul-200 ul) Notes Keep this for all Labs Completing Lab 2 Teacher Tips – *make sure students label with initials/group *Remind them of mixing techniques *Make sure centrifuge is balanced before running *Identify for students when to use a new tip Completing Lab 2 (pg. B-15 in teacher manual) Label tubes Add 4.0 uL 2.5xB into each Add 4.0 uL K into K+ and K- tubes Add 4.0 uL A into A+ and A- tubes Add 2.0 uL RE into K+ and A+ tubes and mix Add 2.0 uL dH2O in K- and A- tubes and mix Centrifuge all tubes Put all tubes in floating rack and set in 37oC water bath for 60 mins. Remove and place tubes into freezer overnight Teacher Video Resources • Mixing two solutions video: https://www.amgenbiotechexperience. com/curriculum/curriculumresources/mixing-two-solutions • Digestion video (different digest, but good techniques): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gs Wo8dCivWs • How restriction enzymes work (good, short): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lW XryzgRces • Longer, overall of lab 2 created for absent students (screen cast): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4 wbStjWEM8A • Fun one from MIT. Covers whole process 1st half good for Labs 2&3: • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nf C689ElUVk ***remember, sticky end issue here What are Ligases? • Definition: Enzymes that • Role in Gene Cloning: catalyze the formation of When the unpaired bases covalent bonds in the of two sticky ends come sugar phosphate together and form backbone. Hydrogen bonds, the DNA Ligase catalyzes the • Ligation is basically the formation of the covalent reaction that joins two bonds between adjacent pieces of DNA together. nucleotides. Lab 3 – Building the Recombinant Plasmid • Purpose: to ligate the DNA fragments you produced during Lab 2 to make new recombinant plasmids. – There are four fragments that will be recombining – There are 10 different possible plasmids produced, each with different combinations (have students predict all possible combinations – key is in teacher guide) – The plasmid of interest is the one containing rfp, pBAD, ampR, and araC • The recombinant plasmid is called pARA - R Recombinant plasmid of interest Safety-Lab 3 • Use laboratory coats, safety glasses and gloves as appropriate • Avoid restrictive clothing and open-toed shoes • No eating or drinking in the lab • Make sure that students are familiar with the operating instructions and safety precautions before they use any of the lab equipment • Check all MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheets) for all chemicals and reagents in the lab before preparing and running the lab www.amgenbiotechexperience.com Lab & Aliquoting Guide-Lab 3 Reagents/Supplies Aliquot Storage Temp 30 ul Ligase/class (Lig) 2ul/group -20o 50 ul 5xB (Ligase B)/ class (5xB) 5ul/group -20o Equipment/Supplies 10 Student boxes with the following: 1 p20 micropipette 1 p200 micropipette 1 p1000 micropipette 1 waste and 1 ice bucket 4 Mini centrifuges 1 Water bath 2 Floating racks www.amgenbiotechexperience.com 1 microfuge rack 1 bag of microfuge tubes 1 bag of microfuge tubes 1 box of refillable tips (2 ul-200 ul) Notes Completing Lab 3 Teacher Tips – *make sure students label with initials/group *Remind them of mixing techniques *Make sure centrifuge is balanced before running *Identify for students when to use a new tip Completing Lab 3 (pg. B-33 in teacher manual) Check reagents Place K+ and A+ into 70oC water bath for 30 mins Label LIG tube with group and class period DIY Water Bath • ***complete paper plasmid activity (see next slide) Paper Plasmid Activity (starts on Pg. 43 in student manual) Modeling Activity: Choose the appropriate restriction enzyme to use to insert the insulin gene Completing Lab 3 (continued from previous slide) Remove K+ and A+ from water bath Add 4.0 uL K+ into LIG Add 4.0 uL A+ into LIG Add 3.0 uL 5xB into LIG Add 2.0 uL dH20 into LIG Mix reagents in LIG Centrifuge LIG tube Place LIG, K+, and A+ in rack Incubate at room temperature overnight Teacher Resources • Making a recombinant (good, short clip): https://www.dnalc.org/view/15476Mechanism-of-Recombination-3Danimation-with-with-basicnarration.html • Recombinant DNA animation: http://www.bioteach.ubc.ca/Teachin gResources/Applications/GMOpkgJKl oseGLampard2.swf • Overall process – Good short animation: http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/re source/biot11.sci.life.gen.genengdna /genetic-engineering-and-workingwith-dna/ • Recombinant DNA quizlet: https://quizlet.com/7435136/recomb inant-dna-technology-flash-cards/ Note on Sequencing Suggested sequences are included in your teacher guides, lessons today were not necessarily presented in this order. • Lab 2 Sequence (pg. B4) • Session 1 – Review, questions, and discussion • Session 2 – “Clone that Gene” paper plasmid activity and questions • Session 3 – Complete lab 3 • Lab 3 Sequence (p B-24) • Session 1 – Review and questions • Session 2 – Complete lab 3