* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Shear wave splitting wikipedia , lookup
Seismic communication wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
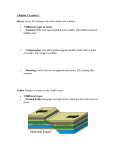
Earthquakes – Video Notes #4 Objective 14: I can define earthquakes seismology and seismologists. : the and that result from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface. Seismology: the study of : the scientists who study earthquakes Earthquakes: Earthquakes form because of its response to called – the building, tilting, and breaking of the Earth’s crust. The point beneath the surface where the rocks break and move is called the . The focus is the underground origin of an earthquake. Directly above the focus, on the Earth’s surface is the epicenter . During an earthquake, the most . Earthquake waves reach the shaking is found at the epicenter. Objective 15: I can describe the 3 types of faults. : is a break in Earth’s crust where slabs of crust slip past each other. faults: the rocks on either side of the fault sideways with little up-or-down motion and are produced by each other plate motion. : the fault is at an angle, so one block of rock lies above the fault while the other block lies below the fault and produced by plate motion. the : the fault has the same structure as a normal fault, but the blocks move in direction. Use the video to help you label this 3 types of faults. Objective 16: I can identify folding and the types of folding. Folding: bends in rock that form when compression shortens and thickens part of Earth’s crust. Anticline: a fold in rock that bends upward into an arch. (horizontal stress) Syncline: a fold in rock that bends downward in the middle to form a bowl. (horizontal) Monocline: rock layers are folded so that both ends of the fold are horizontal. Objective 17: I can describe how Earthquakes travel through seismic waves – P waves, S waves, and Surface waves. Seismic waves: vibrations that travel through Earth carrying the energy released during an earthquake. : the first waves that expand and compress the ground like an accordion that causes particles of rock to move in a back and forth direction. P waves travel through and . : After P waves come, these waves come and vibrate side to side and up and down – they shake the ground back and forth. They causes rock particles to move in a side-to-side direction and they only travel through . : move more most than P waves and S waves, but they produce the damage. Objective 18: I can define wave properties – frequency, wavelength, amplitude and speed. THIS SHOULD BE REVIEW!!!!! :-) : the number of waves produced in a given amount of time. : the distance from any point on a wave to an : The point on the next wave. distance that the particles of a wave’s medium vibrate from their rest position. Speed: Fill the rest of the answers. The illustration to the right shows a wave. Label each part in the space below: a. _________________ b. _________________ c. _________________ d. _________________ .