* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Hawk Nation Biology
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Mendelian inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
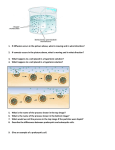
Biology EOC Review Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Characteristics: Prokaryotic Cell No membrane-bound organelles & DNA not contained in a nucleus Unicellular Ex. Eubacteria & Archaebacteria Both Cells Membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, DNA Eukaryotic Cell Has membrane-bound organelles & DNA is contained in a nucleus Living Uni or multicellular Ex. Protista, Fungi, Plant, Animal Explain the Endosymbiotic theory developed by Lynn Margulis in 1985. Prokaryotic cell engulfed another prokaryotic cell and created a eukaryotic cell. The two prokaryotic cells created a mutualistic relationship. This is the beginning of chloroplast and mitochondria. I need to remember…. Prokaryotic cells do not have _membrane __ _bound___ _organelles_ In Eukaryotic cells, the _nucleus__ is surrounded by a membrane. (Just like the ER, Golgi body, Mitochondria, etc) Both types of cells have _ribosomes____ to make proteins. Sample Question: Scientists determined that organisms of the genus Spinoloricus were eukaryotes and not prokaryotes because Spinoloricus cells have — A flagella C cell walls B hereditary material D nuclear membranes Cellular Processes Compare and contrast Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration in the Venn Diagram (include at least 2 facts per section) Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Requires CO2, H2O, sunlight Both part of carbon cycle Requires O2, C6H12O6 Produces O2, C6H12O6 Chemical equations are complementary Produces CO2, H2O, ATP Occurs in chloroplast Occurs in mitochondria I need to remember …. The reactants and products for photosynthesis and cellular respiration are _complementary__. Cellular respiration occurs in _plant__ and __animal___ cells. Plants use __chloroplast__ during photosynthesis to convert _solar energy__ from the sun in order to make _C6H12O6___ and _(OMIT)_ and to release oxygen. _Glucose (cellular respiration)__ is used by both plant and animal cells. Sample Question: Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration? a. Respiration is the reversal of the biochemical pathways of photosynthesis, using the exact same enzymes. b. Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules, while respiration releases it. c. Photosynthesis occurs only in plants and respiration occurs only in animals. d. ATP molecules are produced in photosynthesis and used up in respiration. Cell Transport and Homeostasis I need to remember … __Osmosis_ is the movement of water molecules across a _semi or selectively permeable_ membrane. __Active__ transport needs energy because it is going __against__ the flow. When the number of molecules inside a cell is __equal___ to the number of molecules on the outside of the cell, the cell has reached __equilibrium____ . Sample Question: If the paramecium is then placed in a hypotonic environment, which of the following will occur? A Water will diffuse into the paramecium. B Water will diffuse out of the paramecium. C Salt will be pumped out of the paramecium by the vacuole. D Salt will be pumped into the paramecium by the vacuole. Sample question: A researcher lyses a cell containing the tobacco mosaic virus (TMV). The cell contents are left in a covered test tube overnight. The next day this mixture is sprayed on tobacco plants, laboratory rat and mushroom. Which of the following would be expected to occur? a. All organisms would develop the symptoms of the TMV infection. b. The plants and the rat would be infected by the virus. c. Only the tobacco plants would develop the typical symptoms of TMV infection. d. None of the organisms would show any disease symptoms. A patient has had a serious accident and lost a lot of blood. In an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water, equal to the volume of blood lost, is transferred directly into one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? a. The patient's red blood cells will burst because adding water to the blood makes it hypertonic compared to the red blood cells. b. The patient's red blood cells will shrivel up because adding water to the blood makes it hypotonic compared to the red blood cells. c. The patient's red blood cells will swell because adding water to the blood makes it hypotonic compared to the red blood cells. d. The patient's red blood cells will shrivel up because adding water to the blood makes it hypertonic compared to the red blood cells. Cell cycle I need to remember … The _cell_ _cycle___ is a continuous process of cell _growth__ and _division___. _Interphase__ is the longest phase. Growth results from _mitosis____. _Cancer_ cells can develop during any part of interphase and never stops growing, using all the body’s resources. Sample question: Imagine looking through a microscope at a squashed onion root tip. The chromosomes of many of the cells are plainly visible. In some cells, replicated chromosomes are aligned along the center (equator) of the cell. These particular cells are in which stage of mitosis? A. Telophase B. Prophase C. Anahase D. Metaphase Biomolecules I need to remember … _Monosaccharides_, the smallest carbohydrates, are used as fuel. Carbohydrates main function is _short-term__ __energy__. Lipids store _long-term energy___. A Protein’s function depends on its sequence of _amino __ __acids___. __Nucleic_ _acids___ store and transfer _genetic __, heredity information. Sample Question: Like complex carbohydrates, proteins are biomolecules that serve many functions and can be chemically broken down and restructured. Both proteins and complex carbohydrates are which of the following? A Polymers of smaller subunits C Lipids of large molecules B Sequences of sugars D Nucleotides of DNA Of the four different types of biomolecules, which of them can contain phosphorous in their structure? A. Nucleic acid and lipids C . Protein and carbohydrate B. Nucleic acid and carbohydrate D. Lipid and carbohydrate Components of DNA DNA mRNA 2 Strands 1 A, T, G, C Nitrogen bases A, U, G, C Deoxyribose Sugars Ribose Nucleus Location Nucleus, Cytoplasm I need to remember … DNA contains 4 _nitrogenous__ bases: _adenine_, _thymine__, __guanine__, and _cytosine__. “A” matches with _T_ and “G” matches with _C_. The amount of A & T are _equal_ and the amount of G & C are _equal__. _Weak_ hydrogen bonds hold DNA together. _Mutations in germ cells (gametes)__ are changes in DNA that can be inherited. Not all _mutations_are harmful, some are beneficial. Transcription and Translation protein Amino Acid tRNA anti-codon codon DNA ribosome cytoplasm Nucleus RNA Label all circled numbers! What process creates molecule 2? __Transcription______ Describe what is happening at molecule 5. (Use the names of all numbered molecules involved) ______Ribosomes are the site of translation where tRNA brings the amino acids and amino acids are assembled building polypeptide (protein) chains. _____________________________________________________________________ Sample Question: A mutation is least likely to affect a cell when the mutation — A B C D reverses the order of bases in a DNA strand allows the total number of bases in a DNA sequence to remain the same replaces a base with its complementary base produces a triplet that codes for the same amino acid as the original triplet Meiosis Gametes = sex cells Daughter cells are __haploid__ cells with half the number of chromosomes than the parent cell. A normal human somatic cell has _46_ chromosomes. This process above is_crossing over._ I need to remember … Gametes are produced by the process of _meiosis_. Meiosis results in 4 genetically _different__ cells that are __haploid__ (half the amount of chromosomes). _Crossing_ __over__ happens in Prophase I and increases diversity in species. Sample Question: The segregations and divisions that occurs during meiosis results in a — A B C D decrease in the total number of cells per organism reduction in the number of chromosomes per cell single fertilized egg cell group of genetically identical cells Genetics Complete the following statements with the correct vocabulary word. Dominant Homozygous Recessive Genotype Phenotype Heterozygous Purebred True breeding Hybrid 1. Inheriting two of the same alleles for a trait is called __homozygous__, __true breeding__, or ___purebred____. 2. Inheriting two different alleles for a trait is called __heterozygous or hybrid______. 3. A __dominant_______ allele covers up other traits. 4. Alleles that are hidden or covered up are called: _recessive________. 5. The actual physical expression of a gene is called its __phenotype_____. 6. The actual genes present that are represented by symbols are called its __genotype_______. For each genotype below, indicate whether it is heterozygous (He) or homozygous (Ho) AA _Ho__ Cc _He__ Ee _ He_ Gg _ He_ Bb _ He__ kk _ Ho__ ff _ Ho_ nn _ Ho__ For each of the genotypes below determine what phenotypes would be possible. Brown fur is dominant to black fur. BB __brown______ Bb __brown______ bb __black_______ For each phenotype below, list all of the possible genotypes (remember to use the letter of the dominant trait) Straight hair (H) is dominant to curly (h). Pointed heads (A) are dominant to round heads (a). _HH, Hh straight ___hh curly AA, Aa__ pointed aa___ round Sample Questions: In rats, the allele for a rough coat (R) is dominant over the allele for a smooth coat (r). A heterozygous rat and a homozygous recessive rat are mated. What is the distribution of genotypes for the offspring? a. 100% Rr R r b. 50% Rr and 50% rr Rr c. 75% Rr and 25% rr rr r r Rr rr In pea plants, red flower(R) is dominant over white(r). Cross a true-breeding red flower with a homozygous recessive flower. What is the probability of having a white flower in F2 generation? (Show your work!!!!) R R R r __Key__ RR x rr r __G__ __P__ Rr x Rr Rr Rr 25% White flower R = red Rr = 100% Red = 100% R RR Rr r r = white Rr Rr r Rr rr Compare and contrast Mendel’s Laws of Heredity. Law of Independent Assortment inheritance of one allele is independent of all other alleles Ex. Blonde hair ≠ blue eyes Law of Segregation Mendel Pairs of alleles separate during anaphase Result in genetic diversity of offspring Ex. Each cell will get one allele from the pair E a punnett square using the following information: A dihybrid cross involves the crossing of two traits. Set up E E · Dominant allele for purple corn kernels = R · Recessive allele for yellow corn kernels = r · Dominant allele for starchy kernels = T · Recessive allele for sweet kernels = t Cross a homozygous dominant parent of both traits with a homozygous recessive parent of both traits. Give the genotypic and phenotypic percentage and ratios of the F1 offspring. Key R = purple r = yellow T = starchy t = sweet Cross RT RT RT RT rt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt rt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt rt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt Genotype RrTt = 100% Phenotype Purple, starchy = 100% RRTT x rrtt rt RrTt RrTt RrTt RrTt Incomplete Dominance One trait is not completely dominant over the other (Results: MIXTURE) Non-Mendelian Genetics Codominance Multiple Alleles Both traits seen equally Different genes control certain trait (Results: SPOTTED) Ex. Ex. Red+White = PINK Red +White = SPOTS Sex-linked Traits Trait found on sex chromosome (23rd Chromosome in humans) Ex. Blood Types: A blood – _AA, AO__ B blood – _BB, BO___ Ex. Color Blindness Sex Chromosome: Female _XX___ AB blood – __AB____ Male __XY___ O blood –__OO_____ Heterozygous individuals have two different alleles. Explain with punnett square examples below how heterozygous individuals have different phenotype expressions when comparing Complete Dominance(MENDEL), Incomplete Dominance and Co-dominance. (Use the Phenotypes Red and White to go with two genotype alleles of your choice) COMPLETE DOMINANCE Cross: INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE Cross: Rr x Rr R r R RR Rr r Rr rr CO-DOMINANCE Cross: RW x RW R W R RR RW W RW WW R W R RR RW W RW WW Genotype Phenotype Genotype Phenotype Genotype RR = 25% Rr = 50% rr = 25% Red = 75% White = 25% RR = 25% RW = 50% WW = 25% Red = 25% Pink = 50% White = 25% RR = 25% RW = 50% WW = 25% Sample Questions: Two parents are screening their unborn child for genetic disorders. The doctors return with the following karyotype. What is the diagnosis of the child? A. B. C. D. Turner’s Syndrome – monosomy X Cri du chat – shortened 5 Down Syndrome – trisomy 21 Kleinfelters – sex linked non-disjunction RW x RW Phenotype Red = 25% Spotted = 50% White = 25% The following pedigree shows a genetic disorder in 4 generations of a family. Which disease could apply to this pedigree? A) Marfan Syndrome – 1 in every 3 people are affected, everyone is a carrier B) Albinism – Only homozygous recessives are affected, males are carriers C) Dwarfism – Anyone with a dominant allele is affected, no carriers D) Hemophilia – more males are affected, and women are carriers I need to remember … Mendel used peas plants to study the __inheritance___ of traits. _Homozygous__, purebred, and true-breeding all have the same _allele (letter)__ for a trait. Mendel’s principles of genetics apply to all __living__ organisms. Non-Mendelian traits - _incomplete__ dominance – blending of traits ____Co___ dominance – shows both traits (stripes) Evolution __Homologous___ Structures – same structure, different function. Suggests that organisms have a ___common____ __ancestor___. Fossil Record is evidence of __evolution___. I need to remember … Survival of the _fittest__ refers to an organism’s ability get food successfully and to reproduce and pass on its traits. _Natural___ __selection___ refers to competition, fitness, and having the best adaptations to survive and pass on to offspring. Sample Question: When we say that an individual organism has a greater biological fitness than another individual, we specifically mean that the organism A. lives longer than others of its species. B. competes for resources more successfully than others of its species. C. mates more frequently than others of its species. D. leaves more viable offspring than others of its species. Taxonomy and Classification Levels D omain K ingdom P hylum C lass O rder F amily G enus Cladogram The lizard, pigeon, mouse, and chimp all have what traits in common? ____jaws, lungs, claws or nails_______________________________ S pecies Cladograms show __traits__ not dates. Six Kingdoms Fill in the blanks with the correct kingdom. __Archaebacteria______ – extremophiles (live in extreme locations) ___Eubacteria________ – bacteria that live in the same habits as humans ____Protista_________ – eukaryotic organisms that are not plant, animal or fungus ____Fungi___________ – eukaryotic organisms, hetertrophic, cell wall made of chitin, DO NOT photosynthesis ____Plantae_________ – eukaryotic organisms, autotrophic, cell wall made of cellulose, DO photosynthesis ____Animalia________ – eukaryotic organisms, heterotrophic, no cell walls, almost all are mobile I need to remember … _Binomial__ _nomenclature__ is a two part naming system using the last two levels of classification as the scientific name = __Genus__ & __species___. __Common__ names cause confusion if the names differ by location. Prokaryotic shapes are _coccus__(round), __bacillus___(rod), & __spirillum___(spiral). Bacterial grouping are __Strepto__(chains), __Staphylo____(clusters), & _Diplo__(pairs). Ex) Strepto-coccus = round chains Sample Questions: Methanogens, thermophiles, and halophiles are some of the most primitive life-forms found on Earth and thrive in very harsh environments. These unicellular, prokaryotic organisms most likely belong to which of the following kingdoms? A Fungi B Eubacteria C Protista D Archaebacteria The diagram above shows a model of species divergence among some primates. If this model is correct, the greatest genetic differences would be found in the DNA sequences of which two species? A Tarsius bancanus and Cebus albifrons C Hylobates lar and Pongo pygmaeus B Macaca sylvanus and Macaca mulatta D Pan troglodytes and Lemur catta Plants The ovary in flowers will turn into _ fruit _. Stamen contains __male___ reproductive tissues. Pistil (carpel) contains __female__ reproductive tissues. Stoma controls the amount of water lost through __leaves___. 2 Types of Vascular Tissue: ____Xylem __ carries water and minerals up from roots. ___Phleom___ carries sugars down to the stems and roots. I need to remember … Plants get energy through _photosynthesis (sunlight)_. The _stoma/stomata__ controls water loss. __Xylem___ carries water up from the roots and __phleom__ carries sugars down to the stems and roots. Sample Question: Cells List the seven characteristics that all living things have in common. 1. _Composed of cells_______________________________ 2. _Levels of organization____________________________ 3. _Use energy_____________________________________ 4. _Respond to their environment_____________________ 5. _Grow__________________________________________ 6. _Reproduce_____________________________________ 7. _Adapt to their environment_______________________ Four structures that all cells have in common: What are the 3 parts to the Cell Theory 1. _Cell/plasma membrane____ 1. _All living organisms are composed of one or more cells._ 2. Genetic material (DNA/RNA)_ 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure, function, and organization in all organisms._ 3. _Ribosomes______________ 3. _All cells come from preexisting living cells.__ 4. _Cytoplasm_______________ What disorder results when human body cells lose the ability to respond to internal regulatory signals that control cell growth? __cancer___ During which phase of the cell cycle is damaged DNA repaired? _S phase of interphase_ The Human Body Body System Function Integumentary Protection from outside elements Muscular Movement Skeletal Structure & Support Circulatory Transport nutrients & gases Respiratory Gas exchange Digestive Breakdown food & remove solid waste Excretory Filter blood & remove liquid waste Nervous Control through electrical signals Endocrine Control through hormones Reproductive Make life Lymphatic (Immune) Fight foreign particles/infections I need to remember … How do the circulatory and lymphatic systems work together to fight infection? Lymphatic system makes white blood cells to fight infections, and circulatory system transports white blood cells and carries pathogens back to lymphatic system to rid body of these pathogens/infections. How does the integumentary system help maintain homeostasis? Integumentary system regulates body temperature by either producing sweat if body is too hot or body is too cold. shivers if How do nervous and endocrine systems work together to regulate homeostasis? Nervous system interprets feedback from systems and sends signals to endocrine system or other system to ensure balance is restored in the body. Endocrine system will release hormones to maintain homeostasis. How do digestive, excretory, and circulatory systems work together to transport nutrients and get rid of metabolic waste? Digestive system will breakdown food, and circulatory system will transport nutrients to cells. Circulatory system will then pick up waste material from cells and transport to digestive and excretory systems so wastes can exit body. How do circulatory and respiratory systems work together in gas exchange? Respiratory system will bring in oxygen, and circulatory system will transport oxygen to cells. Circulatory system will pick up carbon dioxide from cell, and respiratory system will get rid of it. Sample Questions: The diagram shows part of one of the many feedback loops required to maintain homeostasis in the human body. Low oxygen content In blood Kidney increased production of erythropoietin Increased production of of red blood cells rib cage This diagram suggests that which of the following could cause a low red-blood-cell count? A B C D The growth of new bone tissue Chronic kidney disease Decreased levels of metabolic waste An increased breathing rate Cell Transport - Function of cell membrane – controls what enters and leaves the cell - Label this molecule What does semi-permeable or selectively permeable mean? Only certain things are allowed to pass across the membrane - What molecule makes up the semi-permeable/selectively permeable membrane? Phospholipid Biomolecules: Identify the following structures: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Amino Acid (Protein) Lipid Nucleotide Carbohydrate (glucose) Describe how the order of monomers (subunits) might affect the function of the biomolecules. Identify and investigate the role of enzymes. 1. What are enzymes? _specialized proteins that do work _ 2. What is their function? _act as catalysts and either speed up or slow down reactions__ 3. What type of macromolecule are enzymes? _proteins__ 4. List some examples. ATP synthase, Peptidase, Amylase, 5. Describe the effect of temperature and/or pH on enzyme activity as seen in the graph to the right. Increasing temp or pH will increase enzyme efficiency for a while, then it will start to denature the proteins and start decreasing efficiency 6. What is biological catalyst? An enzyme that usually speeds up a reaction by DECREASING the activation energy required to start a chemical reaction 7. What does a catalyst do? (explain the graph to the right) *speeds up a reaction by DECREASING the activation energy required to start a chemical reaction *The dotted line is lower meaning it takes less energy to reach the products of a reaction The Earth is approximately 4.5 billions years old. Life did not evolve for another billion years. What is the age of the oldest fossilized life that we have found? 3.5 billion years old Which kingdom is the most recent ancestors of Fungi, Plants and Animals? Protista (protists) What is the difference between the Theories of Evolution proposed by Charles Darwin and Jean Baptiste LaMarck? Charles Darwin – Animals are born with adaptions caused by random mutations. If the adaptation helps them then they outcompete other organisms and pass on that mutation more often to their offspring. Nature selects the best fit organisms to survive (Natural Selection) _Natural_ _Selection_ - nature puts stress/pressure on animals (called limiting factors), if they have the right adaptations they survive and reproduce Jean Baptist LaMarck – Animals adapt to their environment to become the best fit. Animals change themselves over their lifetime intentionally and then pass those traits on to their offspring. (Inheritance of Acquire Traits) ** Individual organisms DO NOT ADAPT to their environment. They have the adaptations from birth due to mutations in genetics. _Evolution__ – the change in a species (not an individual) over time due to natural selection. Descent with Modification Viable – _The offspring from mating is capable of mating and having offspring of their own_ _Ecology_ – study of the INTERACTIONS of animals with each other and with their environment Put these in order from largest level of organization to the smallest level of organization: Biological systems are composed of multiple levels. Put these 12 levels in order from largest to smallest Ecosystem, Tissues, Communities, Organ systems, Organelles, Biome, Molecules, Elements/Atoms, Cells, Biosphere, Organism/species (a single member of species), Organs, Population (group of one species) [ Largest] _Biosphere_, _Biome_, _Ecosystem_, _Communities__, _Population_, _Organism/species_, _Organ System_, _Organs_, _Tissue_, _Cells_, _Organelles_, _Molecules_, _Element/Atoms_, [Smallest] How is a Habitat different than a Niche? (explain and give an example) Habitat is where something lives (tree, savannah, small intestines of a host, etc) Niche is the role it plays in that habitat (decomposer, producer, predator, etc) Relationships: Symbiosis – association between two different species. Mutualism – Both organisms _Benefit_ (bee and flower) Commensalism – One organism _Benefits_ and the other organism is neither harmed nor helped. (moss & trees) Parasitism – One organism _Benefits__ and the other is _Harmed_. (fleas & dogs) Sample question: A lichen is composed of two organisms, a fungus and a cyanobacterium. The fungus provides a growing surface, moisture, and nutrients to the cyanobacterium. The cyanobacterium provides food to the fungus. This relationship is considered to be an example of which of the following? A. B. Commensalism Mutualism C. Neutralism D. Parasitism Draw a food web that has at least 3 food chains in it and shows the following trophic level organisms: 3 producers, 3 herbivores, 2 carnivore only, 2 omnivores, and 1 decomposer connected to every other organism Trophic level – _a feeding level in a food chain or food web__ (producer, herbivore, etc) Food webs show _ALL_ energy paths in an ecosystem Food chains show _One_ energy path **** Food webs are made up of many food chains Why are Decomposers so important for the environment? They return the nutrients stored in organisms back to the environment to be used again What is this diagram showing to the right? Biological magnification – how toxins are increasing in concentration as you move up the food chain Water cycle: What is the difference between evaporation and Transpiration? Evaporation is from bodies of water, Transpiration is from plants Carbon cycle: What are the TWO most important processes that make up the Carbon Cycle? _photosynthesis_ and _Cellular respiration Nitrogen cycle: Why is Nitrogen Fixation so important for life on this planet? It allows bacteria to take non-usable N2 gas and turn it into a usable form by plants and animals. An asteroid has hit the state of Texas and completely destroyed all life in a 100 mile radius around Austin. Explain which type of succession will take place: Since there is no life, it would be Primary Succession What is a Limiting Factor? Something in an ecosystem that makes it difficult to survive (weather, mates, competition for food or water, etc) How are limiting factors associated with Natural Selection and Evolution? Limiting factors create the stresses that drive natural selection. It creates the opportunities for competition for survival Carrying Capacity – _maximum number of organisms that can be sustained (can live) in an environment due to limiting factors_ Which type of graph does not have a carrying capacity? (Exponential or Logistic) Exponential, the J shape keeps going up and does not level off like a Logistic curve which has a carrying capacity. Draw a picture of this type of graph: What is an Invasive Species? An organism that is not native to an area. It usually causes severe ecological damage because it does not have any natural predators to keep its population growth in check. Why are invasive species so bad for an ecosystem? This causes invasive species to out compete the native species that do have predators eating them