* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Radii Answers File
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Reflection high-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
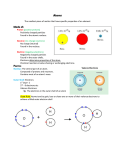
CHEMISTRY 3.4 WORKSHEET FOUR 1. 2. RADII OF ATOMS AND IONS (a) 1.87 x 10-10 m (b) (i) (ii) Atomic Radii decrease across a group. The electrons are going into the same shell so the increasing nuclear change pulls them closer to the nucleus. (c) (i) (ii) A.R. increases going down a group. An extra shell is being added in successive elements and the electrons in the outer shell are “shielded” from the nucleus by the inner shells. There is a decreasing attractive pull on them from the nucleus. (d) Atomic radii are measured from inter-nuclear distances between bonded atoms. The inert gases do not form bonds so it is not possible to make these measurements. (a) (d) smaller (b) larger (c) increases When an atom loses an electron to form a positive ion, the nuclear charge has not changed. However, now the nucleus is attracting one less electron so the remaining ones are pulled in closer. When an atom gains an electron to form a negative ion, the nuclear charge has not changed. However, now the nucleus is attracting one more electron so they are not pulled as strongly as before. The negative ions will all be bigger than Ar and the positive ions will be smaller. P3- has gained three electrons so its electrons will be held less strongly than S2- which will be held less strongly than Cl- so I.R. will decrease ie P3- > S2- > C1- > Ar. Also Ca2+ has lost 2 electrons compared to K+ which has lost one, so Ar > K+ > Ca2+ (e) (f) 3. ANSWERS 1.1 x 10-10 m 1.0 x 10-10 m 1.35 x 10-10 m (a) B, Al, Ga (b) Cs, Cs+ (c) P3-, S2-, Cl- (d) Li+, N3-, O2- (e) F, Cl, Br, I. (f) S, S2- (g) Cl, Cl- (h) Mg, Mg2+ (i) Na+, Mg2+, Al3+


![The electronic configuration of phosphorus is [Ne] 3s2 3p3](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010079862_1-7325b22ef907f6eb15733a24a4dfe50f-150x150.png)