* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Marketing, 16e - University of Hawaii at Hilo
Genetic algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Personal knowledge base wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Personal information management wikipedia , lookup
Ecological interface design wikipedia , lookup
Collaborative information seeking wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Time series wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Agent-based model in biology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Expert system wikipedia , lookup
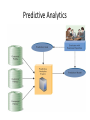
Chapter 4 Analytics, Decision Support, and Artificial Intelligence: Brainpower for Your Business McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. Compare and contrast decision support systems and geographic information systems. 2. Describe the decision support role of specialized analytics (predictive and text analytics). 3. Describe the role and function of an expert system in analytics. STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES 4. Explain why neural networks are effective decision support tools. 5. Define genetic algorithms and the types of problems they help solve. 6. Describe data-mining agents and multiagent systems. ONLINE LEARNING Notice the increase in online learning and the decrease in traditional enrollments. Questions 1. Have you taken or are taking an online course? Fully online or hybrid? 2. Why do students opt to take online courses over traditional classroom courses? 3. Is this transformation occurring at the K-12 level? INTRODUCTION • • • • Businesses make decisions everyday Some big and some small IT tools can aid in the decision-making process Use of IT Analytics is now key to the success of any business DECISIONS AND DECISION SUPPORT Find or recognize the problem, need, or opportunity Consider ways of solving the problem Examine the merits of each solution and choose the best one Carry out the chosen solution and monitor the results Types of Decisions You Face • Structured decision – processing a certain information in a specified way so you always get the right answer • Nonstructured decision – may be several “right” answers, without a sure way to get the right answer • Recurring decision – happens repeatedly • Nonrecurring (ad hoc) decision – one you make infrequently Types of Decisions You Face EASIEST MOST DIFFICULT Decision Support Systems • Decision support system (DSS) • Highly flexible and interactive system • Designed to support decision making when the problem is not structured • Decision support systems help you analyze, but you must know how to solve the problem, and how to use the results of the analysis Components of a DSS • Model management component – consists of both the DSS models and the model management system • Data management component – stores and maintains the information that you want your DSS to use • User interface management component – allows you to communicate with the DSS Components of a DSS GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS • Geographic information system (GIS) – DSS designed specifically to analyze spatial information • Spatial information is any information in map form • Businesses use GIS software to analyze information, generate business intelligence, and make decisions Google Earth as a GIS DATA-MINING TOOLS AND MODELS • Business need IT-based analytics tools – Databases and DBMSs – Query-and-reporting tools – Multidimensional analysis tools – Digital dashboards – Statistical tools – GISs – Specialized analytics – Artificial intelligence Data-Mining Tools and Models Support • Association/dependency modeling – identifying cross-selling opportunities, ex: jalapeno chip sales correlate with Arizona Tea sales • Clustering – discovering groups of entities that are similar (without using known structures) • Classification – use historical data to derive future inferences • Regression – find corollary and often causal relationships between data sets • Summarization – descriptive stats, basic but powerful – Sums, averages, standard deviations – Histograms, frequency distributions Predictive Analytics • Predictive analytics – computational data-mining technology – uses information and BI to build a predictive model for a given business application • Insurance, retail, healthcare, travel, financial services, CRM, SCM, credit scoring, etc • Prediction goal – the question addressed by the predictive analytics model • Prediction indicator – measurable value based on an attribute of the entity under consideration ex: Predictive Analytics Predictive Analytics Example • Prediction goal – What customers are most likely to respond to a social media campaign within 30 days by purchasing at least 2 products in the advertised product line? • Prediction indicators – Frequency of purchases (FP) – Proximity of date of last purchase (LP) – Presence on Facebook and Twitter (FB) – Number of multiple-product purchases (MP) • Predictive Analytics Example – RapidMiner Text Analytics • Text analytics – uses statistical, AI, and linguistic technologies to convert textual information into structured information • Gaylord Hotels uses text analytics to make sense of customer satisfaction surveys Text Analytics Support • Lexical analysis – word frequency distributions • Named entity recognition – identifying peoples, places, things • Disambiguation – meaning of a named entity recognition – “Ford” can refer to how many different things? • Co-reference – handling of differing noun phrases that refer to the same object • Sentiment analysis – discerning subjective business intelligence such as mood opinion Endless Analytics • Web analytics – understanding and optimizing Web page usage – Search engine optimization (SEO) – improving the visibility of Web site using tags and key terms • HR analytics – analysis of human resource and talent management data • Marketing analytics – analysis of marketingrelated data to improve product placement, marketing mix, etc • CRM analytics – analysis of CRM data to improve customer service and support • Social media analytics, Mobile analytics, etc... ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE • Artificial intelligence, the science of making machines imitate human thinking and behavior, can replace human decision making in some instances – Expert systems – Neural networks (and fuzzy logic) – Genetic algorithms – Agent-based technologies Expert Systems • Expert (knowledge-based) system – an artificial intelligence system that applies reasoning capabilities to reach a conclusion • Used for – Diagnostic problems (what’s wrong?) – Prescriptive problems (what to do?) • ES Components – Similar to DSS – Model management Inference / Rule Engine – Data management Expert Knowledge Base – User interface Question / Explanation Module Traffic Light Expert System What Expert Systems Can and Can’t Do • An expert system can – Reduce errors – Improve customer service – Reduce cost • An expert system can’t – Use common sense – Automate all processes Expert System Examples • Problem Solving ES • Diagnosing Chronic Fatigue • Knowledge Base Example – Soil Classification • Complex Diagnostic System - MEDgle Neural Networks • Neural network (artificial neural network or ANN) – AI system capable of finding and differentiating patterns • ANNs can: – Learn / adjust to new circumstances on their own – Take part in massive parallel processing – Function without complete information – Cope with huge volumes of information – Analyze nonlinear relationships Fuzzy Logic • Fuzzy logic – mathematical method of handling imprecise or subjective information • Used to make ambiguous information such as “short” usable in computer systems • Applications – Google’s search engine – Washing machines – Antilock breaks Genetic Algorithms • Genetic algorithm – AI system that mimics evolutionary, survival-of-the-fittest process to generate increasingly better solutions to a problem – Staples – determine optimal package design characteristics – Boeing – design aircraft parts such as fan blades – Many retailers – better manage inventory and optimize display areas Genetic Algorithms Can… • Take thousands or even millions of possible solutions and combine and recombine them until it finds the optimal solution • Work in environments where no model of how to find the right solution exists AGENT-BASED TECHNOLOGIES • Agent-based technology (software agent) – piece of software that acts on your behalf (or on behalf of another piece of software) performing tasks assigned to it AGENT-BASED TECHNOLOGIES Types of Agent-Based Technologies • Autonomous agent – can adapt and alter the manner in which it works • Distributed agent – works on multiple distinct computer systems • Mobile agent – can relocate itself onto different computer systems Types of Agent-Based Technologies • Intelligent agent – incorporates artificial intelligence capabilities such as reasoning and learning • Multi-agent system – group of intelligent agents that can work independently and also together to perform a task Types of Intelligent Agents • Information agents (buyer agents) – search for information and bring it back • Monitoring-and-surveillance agents – constantly observe and report on some entity of interest, a network, or manufacturing equipment • User agents – take action on your behalf (e.g., sorting your email) Intelligent Agents • • • • • • • Shopping Agents – MySimon Chatbots – A.L.I.C.E. Personality Test through Chat Driving Agent – AIDA Virtual Agents – Education / Training Swarm Intelligent Bots The Future of Intelligent Robots Types of Intelligent Agents • Data-mining agents – operate in a data warehouse discovering information – Important analytics tool for data warehouse data – Can find hidden patterns in the data – Can also classify and categorize Swarm Intelligence Swarm (collective) intelligence – collective behavior of groups of simple agents capable of devising solutions to problems as they arise, resulting in coherent global patterns Attributes – Flexibility – adaptable to change – Robustness – tasks are completed even if some individuals are removed – Decentralization – each individual has a simple job to do