* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics Notes - davis.k12.ut.us
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
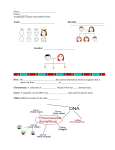
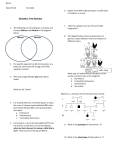
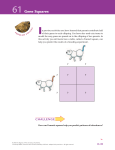
Objective 1. Students will define the following terms: recessive, dominant, genetics, gene, allele, genotype, phenotype, heredity, heterozygous, homozygous. 2. Students will state the Laws of Inheritance. 3. Students will explain punnett squares, monohybrid cross, di-hybrid cross, incomplete dominance and co-dominance. 4. Students will explain how punnett squares and pedigrees are used by geneticists. II. Genetics a. Genetics is the study of heredity or how traits are passed from parent to offspring. A trait is a genetically determined characteristic and may be passed as a dominant (an allele which is expressed) trait or a recessive (an allele which is present but not expressed) trait. Alleles may be homozygous (both alleles for a trait are the same) or heterozygous (the alleles for a trait are different). An allele, (an alternative form of a gene), may occur due to mutations which create genetic variation. A gene is a distinct sequence of nucleotides forming a part of a chromosome. A genotype is the combination of genes present in an organism, whereas the phenotype is the physical characteristics that appear within/on an organism. b. Hereditary factors do not combine, but are passed intact is known as the Law of Segregation. Each member of the parental generation transmits only half of its hereditary factors to each offspring with certain factors "dominant" over others is the Law of Dominance. Different offspring of the same parents receive different sets of hereditary factors is the Law of Independent Assortment. c. Punnett squares and Pedigree charts are used by geneticists for genetic counseling with couples that may have a possibility for a genetic disorder that may be passed to their offspring. A punnett square is a grid diagram/table that shows the possible outcomes of a genetic cross. Punnett squares can be used to illustrate monohybrid (shows only 1 trait) cross, di-hybrid cross (show 2 independent traits), incomplete dominance (when traits are not completely dominant and result in an intermediate phenotype of the trait), and co-dominance (when dominance does not occur and two traits are both expressed).