* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
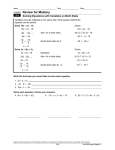
Name _______________________________________ Date __________________ Class __________________ LESSON 1-2 Review for Mastery Adding and Subtracting Real Numbers You can model integer addition using two-color counters. Use the yellow side for 1 and the red side for 1. A yellow counter and a red counter are opposites, so they sum to 0 and cancel. Add 4 6. 4 6 2 To subtract integers using counters, remember that subtracting a number is the same as adding the opposite of the number. Subtract 5 8. To subtract 8, add 8. 5 8 5 (8) 3 Add or subtract by drawing a model of two-color counters. 1. 2 (5) 2. 4 (1) _________________ _________________ Add or subtract using two color counters. 3. 3 7 ________________________ 6. 8 2 ________________________ 9. 6 (4) ________________________ 4. 3 (4) 5. 2 6 ________________________ 7. 5 3 ________________________ 8. 7 (4) ________________________ 10. 5 (5) ________________________ 11. 2 7 ________________________ ________________________ Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. 1-14 Holt McDougal Algebra 1 Name _______________________________________ Date __________________ Class __________________ Review for Mastery LESSON 1-2 Adding and Subtracting Real Numbers continued These rules apply to the addition of all real numbers, not just integers: To Add Numbers with the Same Sign Add the numbers’ absolute values and use the same sign as the numbers. To Add Numbers with Different Signs Find the difference of the numbers’ absolute values and use the sign of the number with the greater absolute value. Add 3 1 . 5 5 Use the rule for adding numbers with the same sign. 1 1 5 5 and 3 3 5 5 1 3 4 5 5 5 Find the absolute values. Add the absolute values. Use the same sign as the numbers. 3 1 4 5 5 5 Both addends are negative, so the result is negative. Subtract 2.9 (3.5). Change subtraction to addition. To subtract 3.5, add 3.5. 2.9 3.5 Use the rule for adding numbers with different signs. 2.9 2.9 and 3.5 3.5 3.5 2.9 0.6 Find the absolute values. Find the difference. Use the sign of the number with the greater absolute value. 2.9 (3.5) 0.6 3.5 had the greater absolute value in the addition problem, so the result is positive. Add or subtract. 12. 5 (9) ________________________ 15. 12 (15) ________________________ 13. 6.5 (3.2) 14. ________________________ 16. 7.8 2.5 ________________________ 5 1 9 9 ________________________ 17. 3 5 8 8 ________________________ Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. 1-15 Holt McDougal Algebra 1 4.Possible answer: It depends on the number of minutes used. Plan A is cheaper if you use less than 300 minutes each month. Plan B is cheaper if you use more than 300 minutes each month. If you use exactly 300 minutes each month, the plans cost the same. Problem Solving 1. 45d 14. 28 15. 2.4 16. 6 17. 37 18. 2.5 19. 116°F 20. $6.26 21. 31 22. 9.45 1 5 1. 4 2. 11 3. 12 4. 42 5. 1.6 6. 2 6. F 7. B Reading Strategies 7. 1. Possible answers: 10y, 10 • y, and 10(y) 13. 6. 58 t Practice A 2. 6 3. 0 4. 3 5. 7 6. 18 7. 2 8. 4.2 9. 5 10. 29 11. 7 12. 22 13. 5 14. 7 15. 15 16. 11 17. 16 feet 18. 3 points 5 6 11. 15.1 4. 4 b 1. 6 1 30 9. 4 2. Possible answers: k divided by 6, the quotient of k and 6 5. 20m LESSON 1–2 13. 45 Practice C 550 4. ; $22, $11, $10 p 3. b 4 12. 12.4 23. 2 2. 5.15 w 3. 216 t 5. C 11. 2 5 6 1 5 8. 0.3 10. 22 12. 3 14. 3 15. 9.5 16. 7 feet 17. $24,577 18. 31 19. 1.75 20. 2 2 3 Review for Mastery 1. 3 1 2 2. 5 Practice B 3. 4 4. 1 1. 14 2. 10 5. 8 6. 6 3. 6 4. 4 7. 8 8. 11 5. 0 6. 4.25 9. 2 10. 0 7. 18 8. 24 11. 5 12. 4 13. 9.7 14. 9. 20.9 10. 4 2 5 5 8 4 9 Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. A2 Holt McDougal Algebra 1 16. 10.3 15.3 17. 2 1 8 4 Challenge 5. 8 6. 6 7. 14.31 8. 63 9. 2 10. 5 11. 3 12. 3 13. 2 3 14. Math Expression Balance $450 ($25) $425 $425 ($200) $225 $225 $50 $275 $275 $50 $325 21. 1 2 22. 2 $325 ($350) $25 23. 0 24. 0 $25 $75 $50 25. undefined $50 ($25) $25 $25 $100 $125 $125 ($200) $75 $75 $225 $150 15. 3 16. undefined 17. 1 18. 0 19. 10 points 20. 72 Practice B 1. no 2. yes; 3/23 and 5/17 3. $150 4. yes 1. 3 2. 120 3. 32 4. 120 5. 105 6. 4 7. 1 4 1 3 3 9. 27 64 Problem Solving 1. 1195 feet inches 2. 68 feet 6 3. 44.18 points 4. 10 points lower 5. A 6. F Reading Strategies 1. negative 2. because subtraction problems become addition problems 4. 30 5. 3 6. 11 7. 9 8. 19 8. 50 10. 0 11. 0 12. undefined 13. $1250 14. 0.54 15. 1 16. 17. 7. D 3. 13 1 16 1 4 5 1 2 2 2 18. 64 1 2 19. 32 20. 21. 8 22. 2 23. 8 24. 4 25. 1 8 Practice C LESSON 1–3 1. 120 2. 2 Practice A 3. undefined 4. 1. 24 2. 20 3. 0 4. 5. 3 8 7 36 1 15 6. 7 7. 28 8. 0 Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. A3 Holt McDougal Algebra 1