Child Psychology - lowellpsychology
... Genital Stage (puberty on). The final stage of psychosexual development begins at the start of puberty when sexual urges are once again awakened. Through the lessons learned during the previous stages, adolescents direct their sexual urges onto opposite sex peers, with the primary focus of pleasure ...
... Genital Stage (puberty on). The final stage of psychosexual development begins at the start of puberty when sexual urges are once again awakened. Through the lessons learned during the previous stages, adolescents direct their sexual urges onto opposite sex peers, with the primary focus of pleasure ...
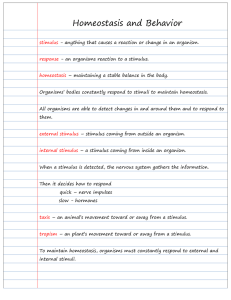
Homeostasis and Behavior
... external stimulus – stimulus coming from outside an organism. internal stimulus – a stimulus coming from inside an organism. When a stimulus is detected, the nervous system gathers the information. Then it decides how to respond quick – nerve impulses slow - hormones taxis – an animal’s movement tow ...
... external stimulus – stimulus coming from outside an organism. internal stimulus – a stimulus coming from inside an organism. When a stimulus is detected, the nervous system gathers the information. Then it decides how to respond quick – nerve impulses slow - hormones taxis – an animal’s movement tow ...
Neutral Stimulus
... - inserted 20 times each amongst 430 presentations - did not notice pairings - preferred the Pokemon paired with positive words ...
... - inserted 20 times each amongst 430 presentations - did not notice pairings - preferred the Pokemon paired with positive words ...
BEHAVIORISM LEARNING THEORY
... • The behavioral learning theory is represented as an S-R paradigm. The organism is treated as a “black box.” We only know what is going on inside the box by the organism’s overt behavior. ...
... • The behavioral learning theory is represented as an S-R paradigm. The organism is treated as a “black box.” We only know what is going on inside the box by the organism’s overt behavior. ...
Famous Experiments
... Continuous reinforcement—Reward every time behavior occurs fixed ratio schedule—same amount of reward every time behavior occurs fixed interval schedule—reward given if behavior occurs in set amount of time ...
... Continuous reinforcement—Reward every time behavior occurs fixed ratio schedule—same amount of reward every time behavior occurs fixed interval schedule—reward given if behavior occurs in set amount of time ...
Classical Conditioning (Ivan Pavlov)
... Classical Conditioning (Pavlov) Summary: Classical conditioning is a reflexive or automatic type of learning in which a stimulus acquires the capacity to evoke a response that was originally evoked by another stimulus. Originators and Key Contributors: First described by Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936), Rus ...
... Classical Conditioning (Pavlov) Summary: Classical conditioning is a reflexive or automatic type of learning in which a stimulus acquires the capacity to evoke a response that was originally evoked by another stimulus. Originators and Key Contributors: First described by Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936), Rus ...
LECTURE23.EmotionDriveDrugs
... Cocaine and amphetamines act by blocking dopamine reuptake transporters, resulting in prolonged dopaminergic signaling. These drugs cause sensory-independent sensation of pleasure and also enhance pleasure associated with certain stimuli Nicotine mediates excess release of VTA dopamine by stimulatin ...
... Cocaine and amphetamines act by blocking dopamine reuptake transporters, resulting in prolonged dopaminergic signaling. These drugs cause sensory-independent sensation of pleasure and also enhance pleasure associated with certain stimuli Nicotine mediates excess release of VTA dopamine by stimulatin ...
- Employees
... as a result of interactions with another individual. There are several distinct types. Social facilitation is where one individual becomes motivated to engage in a behavior because another is doing it. Group howling in dogs is socially facilitated. Stimulus enhancement is where one animal learns a r ...
... as a result of interactions with another individual. There are several distinct types. Social facilitation is where one individual becomes motivated to engage in a behavior because another is doing it. Group howling in dogs is socially facilitated. Stimulus enhancement is where one animal learns a r ...
Drosophila melanogaster
... nutritional and physiological states. Fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster makes mating statusspecific food preference decisions. Given with a choice between yeast and sucrose, male and virgin female prefer sucrose to yeast. After mating, female undergoes a switch, and prefers yeast to sucrose. A verte ...
... nutritional and physiological states. Fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster makes mating statusspecific food preference decisions. Given with a choice between yeast and sucrose, male and virgin female prefer sucrose to yeast. After mating, female undergoes a switch, and prefers yeast to sucrose. A verte ...
PSY105 Neural Networks 2/5
... • Neural network modellers hope that we can understand behaviour by creating models of networks of artificial neurons. ...
... • Neural network modellers hope that we can understand behaviour by creating models of networks of artificial neurons. ...
Conditioned Response
... sometimes because the person knows when the reward will occur. ie Examples: Paycheck every two weeks, Test in two weeks What are some other examples? ...
... sometimes because the person knows when the reward will occur. ie Examples: Paycheck every two weeks, Test in two weeks What are some other examples? ...
Drug Lecture Notes
... Look – Alike Drug – Drug made to look like another but not give the same effects. Prescription Drugs – Available only with written instructions from a doctor or dentist to a pharmacist Over the Counter Drugs – Drugs that may be purchased without a ...
... Look – Alike Drug – Drug made to look like another but not give the same effects. Prescription Drugs – Available only with written instructions from a doctor or dentist to a pharmacist Over the Counter Drugs – Drugs that may be purchased without a ...
Behaviorism
... – Punishment can involve adding something (paying a fine, staying after school) or involve removing something you like (losing recess time, leaving your friends) – In both cases, adding something or removing something, you perceive it as “bad” and as a result, you exhibit the behavior less. ...
... – Punishment can involve adding something (paying a fine, staying after school) or involve removing something you like (losing recess time, leaving your friends) – In both cases, adding something or removing something, you perceive it as “bad” and as a result, you exhibit the behavior less. ...
US - UCI Cognitive Science Experiments
... (for original video, see: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UiB2ZX1phmc&feature=related) ...
... (for original video, see: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UiB2ZX1phmc&feature=related) ...
AutoCAD Architecture 2008: Part I: Getting Started
... behaviorism? Do you agree or not? What are some real life examples of Skinner’s oper ant conditioning? ...
... behaviorism? Do you agree or not? What are some real life examples of Skinner’s oper ant conditioning? ...
Answers to Concepts and Exercises
... Taste aversion. Gufla learned that roses (CS) predict the presence of fertilizer (UCS). Fertilizer causes stomachaches (CR). Gufla will stay away from (CR) all roses (CS) in the future. (see The Signaling of Significant Events) ...
... Taste aversion. Gufla learned that roses (CS) predict the presence of fertilizer (UCS). Fertilizer causes stomachaches (CR). Gufla will stay away from (CR) all roses (CS) in the future. (see The Signaling of Significant Events) ...
F1 - Imprinting of Domestic Chickens
... Chicks of 5-10 days of age are individually exposed to a stimulus, known to elicit imprinting behaviour (e.g. model of a hen), for a period of 2 hours. Following exposure the success of the imprinting procedure is determined by placing each chick in a runway or other arena for 5 minutes. The chick i ...
... Chicks of 5-10 days of age are individually exposed to a stimulus, known to elicit imprinting behaviour (e.g. model of a hen), for a period of 2 hours. Following exposure the success of the imprinting procedure is determined by placing each chick in a runway or other arena for 5 minutes. The chick i ...
Tolerance & Dependence
... ○ Some drugs (e.g., LSD) are not selfadministered by nonhumans. Patterns of Self-Administration ○ Patterns of use are comparable between humans and monkeys (see figure 5-2) ...
... ○ Some drugs (e.g., LSD) are not selfadministered by nonhumans. Patterns of Self-Administration ○ Patterns of use are comparable between humans and monkeys (see figure 5-2) ...
Learning Study Guide
... Hand Luke”. Identify scenes from the movie that represents each drawback. Cognitive Learning What is Cognitive Learning? Who was Wolfgang Kohler? What is Insight Learning? Explain his experiment. What is Latent Learning? Who was Edward Tolman? Explain Explain his experiment. How do we use Cognitive ...
... Hand Luke”. Identify scenes from the movie that represents each drawback. Cognitive Learning What is Cognitive Learning? Who was Wolfgang Kohler? What is Insight Learning? Explain his experiment. What is Latent Learning? Who was Edward Tolman? Explain Explain his experiment. How do we use Cognitive ...
Chapter 2 Figures
... CR, learner often responds to similar stimuli as if they are the original CR. Stimulus discrimination • Ability to differentiate between a particular CS and other significantly different stimuli is stimulus differentiation. ...
... CR, learner often responds to similar stimuli as if they are the original CR. Stimulus discrimination • Ability to differentiate between a particular CS and other significantly different stimuli is stimulus differentiation. ...
Conditioning Theories
... - 2 Pokemon characters paired with negative and positive words - inserted 20 times each amongst 430 presentations - did not notice pairings - preferred the Pokemon paired with positive words ...
... - 2 Pokemon characters paired with negative and positive words - inserted 20 times each amongst 430 presentations - did not notice pairings - preferred the Pokemon paired with positive words ...
2) Classical Conditioning
... The specific model for classical conditioning is: 1. Unconditioned Stimulus (US) elicits > Unconditioned Response (UR): a stimulus will naturally (without learning) elicit or bring about a reflexive response 2. Neutral Stimulus (NS) ---> does not elicit the response of interest: this stimulus is a n ...
... The specific model for classical conditioning is: 1. Unconditioned Stimulus (US) elicits > Unconditioned Response (UR): a stimulus will naturally (without learning) elicit or bring about a reflexive response 2. Neutral Stimulus (NS) ---> does not elicit the response of interest: this stimulus is a n ...
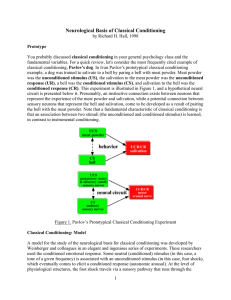
Neurological Basis of Classical Conditioning
... The question then becomes, how does the auditory and somatosensory signal come to be associated at the neurological level? The key to this involves the nucleus basalis, a brain structure rich in acetylcholine (ACh) neurons, which sends projections diffusely into the cerebral cortex. When the neural ...
... The question then becomes, how does the auditory and somatosensory signal come to be associated at the neurological level? The key to this involves the nucleus basalis, a brain structure rich in acetylcholine (ACh) neurons, which sends projections diffusely into the cerebral cortex. When the neural ...
Pavlov`s Dilemma and Discovery: Classical Conditioning
... tary emotional or physiological responses such as fear, increased heartbeat, salivation, or sweating, which are Classical Conditioning sometimes called respondents because they are automatic responses to stimuli. Through the process of classical conHow does a neutral stimulus become a ditioning, hum ...
... tary emotional or physiological responses such as fear, increased heartbeat, salivation, or sweating, which are Classical Conditioning sometimes called respondents because they are automatic responses to stimuli. Through the process of classical conHow does a neutral stimulus become a ditioning, hum ...
Conditioned place preference

Conditioned place preference (CPP) is a form of Pavlovian conditioning used to measure the motivational effects of objects or experiences. This paradigm can also be used to measure conditioned place aversion with an identical procedure involving aversive stimuli instead. Both procedures usually involve mice or rats as subjects. This procedure can be used to measure extinction and reinstatement of the conditioned stimulus. Certain drugs are used in this paradigm to measure their reinforcing properties. Two different methods are used to choose the compartments to be conditioned, and these are biased vs. unbiased. The biased method allows the animal to explore the apparatus, and the compartment they least prefer is the one that the drug is administered in and the one they most prefer is the one where the vehicle is injected. This method allows the animal to choose the compartment they get the drug and vehicle in. In comparison, the unbiased method does not allow the animal to choose what compartment they get the drug and vehicle in and instead the researcher chooses the compartments.Humans have also been shown to develop conditioned place preferences; for example, individuals taking therapeutic doses of amphetamine develop a CPP for where they consumed the drug.