SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY
... Self-disclosure occurs more when two people like one another. Self-disclosure follows a reciprocity norm: Low levels of self-disclosure are met with low levels in return, whereas moderate self-disclosure elicits more personal replies. However, overdisclosure tends to inhibit self-disclosure by other ...
... Self-disclosure occurs more when two people like one another. Self-disclosure follows a reciprocity norm: Low levels of self-disclosure are met with low levels in return, whereas moderate self-disclosure elicits more personal replies. However, overdisclosure tends to inhibit self-disclosure by other ...
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY
... Self-disclosure occurs more when two people like one another. Self-disclosure follows a reciprocity norm: Low levels of self-disclosure are met with low levels in return, whereas moderate self-disclosure elicits more personal replies. However, overdisclosure tends to inhibit self-disclosure by other ...
... Self-disclosure occurs more when two people like one another. Self-disclosure follows a reciprocity norm: Low levels of self-disclosure are met with low levels in return, whereas moderate self-disclosure elicits more personal replies. However, overdisclosure tends to inhibit self-disclosure by other ...
Attraction and Close Relationships
... and fear of rejection. Excitation transfer: the process whereby arousal caused by one stimulus is added to the arousal from a second stimulus and the combined arousal is attributed to the second stimulus. ...
... and fear of rejection. Excitation transfer: the process whereby arousal caused by one stimulus is added to the arousal from a second stimulus and the combined arousal is attributed to the second stimulus. ...
Document
... Motivation is defined as an internal state that induces a person to engage in particular behaviors Work motivation theories are concerned with the reasons why some people perform their ...
... Motivation is defined as an internal state that induces a person to engage in particular behaviors Work motivation theories are concerned with the reasons why some people perform their ...
Behavior in Social & Cultural Context
... element and an emotional element. • Affected by many social and environmental influences: – Some arise from the characteristic attitudes of each generation. – Events that occur when a person is between the ages of 16 to 24 appear to be critical for the formation of generational identity. ...
... element and an emotional element. • Affected by many social and environmental influences: – Some arise from the characteristic attitudes of each generation. – Events that occur when a person is between the ages of 16 to 24 appear to be critical for the formation of generational identity. ...
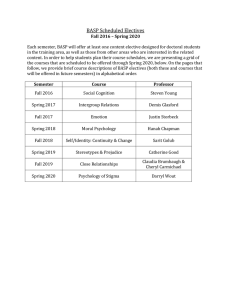
Fall 2016 - Spring 2020 - Basic and Applied Social Psychology
... focuses on groups that are stigmatized because of ethnicity/race, gender and sexual orientation. Topics covered will include the function and nature of stigma, stigma and the self-concept, stereotype threat, attributional ambiguity, stigma concealability and controllability, stigma and social intera ...
... focuses on groups that are stigmatized because of ethnicity/race, gender and sexual orientation. Topics covered will include the function and nature of stigma, stigma and the self-concept, stereotype threat, attributional ambiguity, stigma concealability and controllability, stigma and social intera ...
Roots of Early Childhood Education
... Gesell's classic study involved twin girls, both given training for motor skills but one given training for longer than the other. There was no measurable difference in the age at which either child acquired the skills, suggesting that development had happened in a genetically programmed way, irresp ...
... Gesell's classic study involved twin girls, both given training for motor skills but one given training for longer than the other. There was no measurable difference in the age at which either child acquired the skills, suggesting that development had happened in a genetically programmed way, irresp ...
Social Interaction, Social Structure, and Groups
... evaluations, and definitions – Varies across cultures – Ability to define social reality reflects group’s power – Social change involves redefining or reconstructing social reality ...
... evaluations, and definitions – Varies across cultures – Ability to define social reality reflects group’s power – Social change involves redefining or reconstructing social reality ...
Social Psychology
... • By the end of this lesson, I will be able to: • 1. Discuss attitude formation and ...
... • By the end of this lesson, I will be able to: • 1. Discuss attitude formation and ...
social perception
... -Attribution helps individuals understand and rationalize the behavior of others through the use of information gathered by observation. - People make attributions to understand the world around them in order to seek reasons for a particular individual’s behavior. - When people make attributions the ...
... -Attribution helps individuals understand and rationalize the behavior of others through the use of information gathered by observation. - People make attributions to understand the world around them in order to seek reasons for a particular individual’s behavior. - When people make attributions the ...
Group Behavior - MrGalusha.org
... A mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in a decision-making group overrides the realistic appraisal of alternatives. Attack on Pearl Harbor Kennedy and the Cuban Missile Crisis Watergate Cover-up ...
... A mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in a decision-making group overrides the realistic appraisal of alternatives. Attack on Pearl Harbor Kennedy and the Cuban Missile Crisis Watergate Cover-up ...
Social Psychology - ISA
... an unjustifiable (and usually negative) attitude toward a group and its members involves stereotyped beliefs, negative feelings, and a predisposition to discriminatory action ...
... an unjustifiable (and usually negative) attitude toward a group and its members involves stereotyped beliefs, negative feelings, and a predisposition to discriminatory action ...
Introduction to Psychology - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... an unjustifiable (and usually negative) attitude toward a group and its members involves stereotyped beliefs, negative feelings, and a predisposition to discriminatory action ...
... an unjustifiable (and usually negative) attitude toward a group and its members involves stereotyped beliefs, negative feelings, and a predisposition to discriminatory action ...
Social influence Lecture
... People from different cultures seek different amounts of personal space. ...
... People from different cultures seek different amounts of personal space. ...
TA I Unit 3 Terms
... Autonomy: Independence that includes personal responsibility and decision making. Bandura: (1925- ) theorist who developed a model, “Bandura’s Social Learning Theory” which claims that people learn from one another, via observation, imitation, and modeling (famous for the Bobo doll experiment/demons ...
... Autonomy: Independence that includes personal responsibility and decision making. Bandura: (1925- ) theorist who developed a model, “Bandura’s Social Learning Theory” which claims that people learn from one another, via observation, imitation, and modeling (famous for the Bobo doll experiment/demons ...
Groups - Doral Academy Preparatory
... social scientists today believe that environmental factors have the biggest influence. • According to social scientists, the principal factors that influence personality and behavior are heredity, birth order, parental characteristics, and cultural environment. • Studies of isolated children suggest ...
... social scientists today believe that environmental factors have the biggest influence. • According to social scientists, the principal factors that influence personality and behavior are heredity, birth order, parental characteristics, and cultural environment. • Studies of isolated children suggest ...
AP Psych cpt 13 sq AP Psych cpt 13 sq, new book
... 10. Explain the difference between informational and normative social influence. 11. Identify two causes of group polarization. 12. According to social exchange theory, what factors influence whether a relationship will deepen, be satisfying, and continue? 13. Describe the three components of Sternb ...
... 10. Explain the difference between informational and normative social influence. 11. Identify two causes of group polarization. 12. According to social exchange theory, what factors influence whether a relationship will deepen, be satisfying, and continue? 13. Describe the three components of Sternb ...
Richard J. Gerrig, Ph.D. and Philip Zimbardo, Ph.D.
... • Conflict experienced after making decision, taking action, or being exposed to information that is contrary to prior beliefs, feelings, or ...
... • Conflict experienced after making decision, taking action, or being exposed to information that is contrary to prior beliefs, feelings, or ...
Sociological Theory Midterm Test Spring 2008 1. Sociological
... 19. In Georg Simmel’s theory, an increasing division of labor leads to: (p. 51) a. increased specialization and the ability to produce more sophisticated and complex components of objective culture. b. anomie and the tragedy of suicide. c. mental confusion. d. the labor theory of value. A 20. Thorst ...
... 19. In Georg Simmel’s theory, an increasing division of labor leads to: (p. 51) a. increased specialization and the ability to produce more sophisticated and complex components of objective culture. b. anomie and the tragedy of suicide. c. mental confusion. d. the labor theory of value. A 20. Thorst ...
Group Think Powerpoint - Ms. Anderson
... Essential Task 4-4: Describe the structure and function of different kinds of group behavior with specific attention to group polarization and group think ...
... Essential Task 4-4: Describe the structure and function of different kinds of group behavior with specific attention to group polarization and group think ...
Social Psychology - Solon City Schools
... • Discomfort we feel when your thoughts are behaviors are inconsistent • People want to have consistent attitudes and behaviors….when they are not they experience ...
... • Discomfort we feel when your thoughts are behaviors are inconsistent • People want to have consistent attitudes and behaviors….when they are not they experience ...
sociocultural cognition 4.1
... • Henry Tajfel developed this theory • Which assumes that individuals strive to improve their self-image by trying to enhance their selfesteem based on either personal identity or various social identities • In other words, We also enhance the sense of identity by making comparisons with out-groups. ...
... • Henry Tajfel developed this theory • Which assumes that individuals strive to improve their self-image by trying to enhance their selfesteem based on either personal identity or various social identities • In other words, We also enhance the sense of identity by making comparisons with out-groups. ...
Document
... 3. costs of intervention. sometimes they are raised bythe presence of others (surveillance) 4. rules for behaving: don't stare, unless you know what to do/day, keep your mouth shut etc. 5) mood: Isen dime in coin slot mailing letter 10-->90 ...
... 3. costs of intervention. sometimes they are raised bythe presence of others (surveillance) 4. rules for behaving: don't stare, unless you know what to do/day, keep your mouth shut etc. 5) mood: Isen dime in coin slot mailing letter 10-->90 ...
Social Psychology experiments
... #4 Nisbett and Wilson wanted to see if one positive trait or experience could slant a person’s cognitive bias in a favorable way. Often subjects rated professors as more honest, trustworthy, intelligent if that person had other favorable traits. For example, when two professors gave the same lecture ...
... #4 Nisbett and Wilson wanted to see if one positive trait or experience could slant a person’s cognitive bias in a favorable way. Often subjects rated professors as more honest, trustworthy, intelligent if that person had other favorable traits. For example, when two professors gave the same lecture ...
Self-categorization theory

Self-categorization theory is a social psychological theory that describes the circumstances under which a person will perceive collections of people (including themselves) as a group, as well as the consequences of perceiving people in group terms. Although the theory is often introduced as an explanation of psychological group formation (which was one of its early goals), it is more accurately thought of as general analysis of the functioning of categorization processes in social perception and interaction that speaks to issues of individual identity as much as group phenomena.The theory was developed by John Turner and colleagues, and along with social identity theory it is a constituent part of the social identity approach. It was in part developed to address questions that arose in response to social identity theory about the mechanistic underpinnings of social identification. For example, what makes people define themselves in terms of one group membership rather than another? Self-categorization theory has been influential in the academic field of social psychology and beyond. It was first applied to the topics of social influence, group cohesion, group polarization, and collective action. In subsequent years the theory, often as part of the social identity approach, has been applied to further topics such as leadership, personality, outgroup homogeneity, and power. One tenet of the theory is that the self should not be considered as a foundational aspect of cognition, but rather the self should be seen as a product of the cognitive system at work. Or in other words, the self is an outcome of cognitive processes rather than a ""thing"" at the heart of cognition.