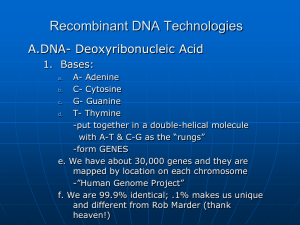
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
VII. DNA/ GENES/ AND GENETICS • Describe the relationship
... structure and function. How is this possible? What mechanism do cells use to turn genes on and off? Give examples of emerging biotechnologies. What modern technologies are currently being implemented to determine evolutionary relationships among species? How are viruses used to treat disease? How ca ...
... structure and function. How is this possible? What mechanism do cells use to turn genes on and off? Give examples of emerging biotechnologies. What modern technologies are currently being implemented to determine evolutionary relationships among species? How are viruses used to treat disease? How ca ...
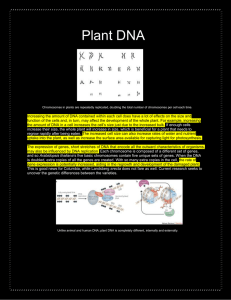
Plant DNA - The uniqueness of DNA
... The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a different set of genes, and so Arabidopsis thaliana’s five basic chromosomes contain five unique sets of genes. When t ...
... The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a different set of genes, and so Arabidopsis thaliana’s five basic chromosomes contain five unique sets of genes. When t ...
Sources of DNA
... prokaryote has a single, circular chromosome (DNA molecule) sectioned functionally into operon. The chromosome is significantly shorter than in a eukaryote and holds fewer genes. ...
... prokaryote has a single, circular chromosome (DNA molecule) sectioned functionally into operon. The chromosome is significantly shorter than in a eukaryote and holds fewer genes. ...
DNA * History, Structure, and Functions
... Mendel eventually became the “Father of Genetics” Friar Scientist ...
... Mendel eventually became the “Father of Genetics” Friar Scientist ...
notes
... Bacteria provide the means • Bacteria have been vital in developing DNA technology • Thermus aquaticus (which lives in hot springs) provides DNA polymerase enzyme for PCR • Escherichia coli (which lives in our guts) provides “plasmids” (mini-chromosomes) used in cloning • 100s of bacterial species ...
... Bacteria provide the means • Bacteria have been vital in developing DNA technology • Thermus aquaticus (which lives in hot springs) provides DNA polymerase enzyme for PCR • Escherichia coli (which lives in our guts) provides “plasmids” (mini-chromosomes) used in cloning • 100s of bacterial species ...
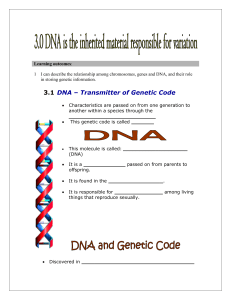
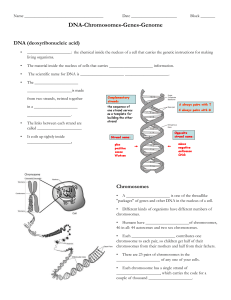
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
Genetic Engineering Short Notes
... 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independa ...
... 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independa ...
The exchange of Genetic Material between bacteria or How
... The exchange of Genetic Material between bacteria ...
... The exchange of Genetic Material between bacteria ...
Quiz 3-DNA.doc
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
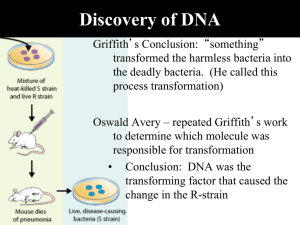
Discovery of DNA
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
Introduction to DNA webquest: Name http://learn.genetics.utah.
... 2. What is the protein in red blood cells called, and what does it ...
... 2. What is the protein in red blood cells called, and what does it ...
Chapter 11: Organization of DNA in Eukaryotes 11.2: mtDNA
... Human mtDNA does NOT have introns. Introns are non-coding SEQUENCES of the double helix. The absence of INTRONS in human mtDNA means that mutations will have a greater impact because all of the information is needed for normal cell structure and function; there is no “fluff” What does human mtDNA co ...
... Human mtDNA does NOT have introns. Introns are non-coding SEQUENCES of the double helix. The absence of INTRONS in human mtDNA means that mutations will have a greater impact because all of the information is needed for normal cell structure and function; there is no “fluff” What does human mtDNA co ...
5. Protein Synthesis
... 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it found? 10. Briefly describe transcription. 11. Briefly describe translation. ...
... 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it found? 10. Briefly describe transcription. 11. Briefly describe translation. ...
Genes and genomes
... of A, T, C, and G. These unique combinations code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
... of A, T, C, and G. These unique combinations code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
Virtual DNA Lab
... b. _________________________________________________________________________ 4. Examine the picture. Which type of bonds hold the DNA bases together? ____________________ 5. What molecule do genes create? ____________________________________________________ What is a Gene? 6. Why are genes called th ...
... b. _________________________________________________________________________ 4. Examine the picture. Which type of bonds hold the DNA bases together? ____________________ 5. What molecule do genes create? ____________________________________________________ What is a Gene? 6. Why are genes called th ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.