ap: chapter 16: the molecular basis of inheritance
... 1. After Morgan and fellow scientists developed the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance, the search was on for the chemical mechanism of inheritance. What are the two components of the chromosome? __________________________________________________________________________ 2. From initial logic, which c ...
... 1. After Morgan and fellow scientists developed the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance, the search was on for the chemical mechanism of inheritance. What are the two components of the chromosome? __________________________________________________________________________ 2. From initial logic, which c ...
Fast Facts about Human Genetics • DNA stands for Deoxy
... In April 2003, the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) celebrates the completion of the human genome sequence and the 50th anniversary of the description of the DNA double helix. ...
... In April 2003, the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) celebrates the completion of the human genome sequence and the 50th anniversary of the description of the DNA double helix. ...
Cell Theory Quiz Study Guide Name
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
MCAS BIOLOGY REVIEW GENETICS AND EVOLUTION
... from DNA Translation takes place at the ribosome in the cytoplasm; translates mRNA to tRNA to amino acid ...
... from DNA Translation takes place at the ribosome in the cytoplasm; translates mRNA to tRNA to amino acid ...
Ch 16-17 Practice Quiz
... 1. What are the 2 pyrimidines? ____________, and the 2 purines? __________, which is a double ring structure and which is a single ring? ___________________ What are Chargaff’s rules? ______________ 2. How many H bonds are there between A and T? ______ and how many between C and G? ________ 3. Which ...
... 1. What are the 2 pyrimidines? ____________, and the 2 purines? __________, which is a double ring structure and which is a single ring? ___________________ What are Chargaff’s rules? ______________ 2. How many H bonds are there between A and T? ______ and how many between C and G? ________ 3. Which ...
genetics science learning center – internet lesson
... Click on the link that says “Tour the basics”. A new window will open, you can navigate sections by using the top toolbar. WHAT IS DNA? 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four b ...
... Click on the link that says “Tour the basics”. A new window will open, you can navigate sections by using the top toolbar. WHAT IS DNA? 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four b ...
History of Genetics
... • 1910: Thomas Hunt Morgan: proved that genes are located on the chromosome • 1941: Beadle and Tatum - show how genes direct the synthesis of enzymes that control metabolic processes “1 gene = 1 enzyme” • 1952: Hershey and Chase - conducted experiments which helped to confirm that DNA was the geneti ...
... • 1910: Thomas Hunt Morgan: proved that genes are located on the chromosome • 1941: Beadle and Tatum - show how genes direct the synthesis of enzymes that control metabolic processes “1 gene = 1 enzyme” • 1952: Hershey and Chase - conducted experiments which helped to confirm that DNA was the geneti ...
Cytosine – ______ Sugar
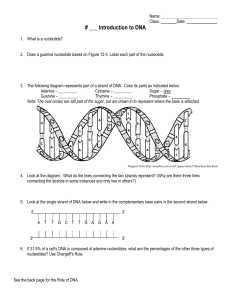
... 2. Draw a guanine nucleotide based on Figure 12-5. Label each part of the nucleotide. ...
... 2. Draw a guanine nucleotide based on Figure 12-5. Label each part of the nucleotide. ...
Chapters Bacteria, viruses, prions
... •Can be cut with RESTRICTION ENZYMES and used to incorporate foreign DNA into bacteria •Bacteria then reproduce, copying the inserted gene along with their own plasmid MECHANISMS OF GENE TRANSFER/GENETIC RECOMBINTION IN BACTERIA TRANSDUCTION Phage viruses can pick up & transfer DNA to new host along ...
... •Can be cut with RESTRICTION ENZYMES and used to incorporate foreign DNA into bacteria •Bacteria then reproduce, copying the inserted gene along with their own plasmid MECHANISMS OF GENE TRANSFER/GENETIC RECOMBINTION IN BACTERIA TRANSDUCTION Phage viruses can pick up & transfer DNA to new host along ...
PCR - University of Hawaii
... • AMV reverse transcriptase from the avian myeloblastosis virus • Reverse Transcriptase (RT): A DNA polymerase enzyme that uses an RNA template to synthesize a complementary molecule of double stranded DNA • RNA template ...
... • AMV reverse transcriptase from the avian myeloblastosis virus • Reverse Transcriptase (RT): A DNA polymerase enzyme that uses an RNA template to synthesize a complementary molecule of double stranded DNA • RNA template ...
WINK DNA Structure and Replication
... * Develop and use models to explain how genetic information (DNA) is copied for transmission to subsequent generations of cells (mitosis). ...
... * Develop and use models to explain how genetic information (DNA) is copied for transmission to subsequent generations of cells (mitosis). ...
GE Nova Video Questions
... Teachers Answer Sheet 1. Bacteria 2. Plasmids can multiply at the same rate as the DNA of the cell Plasmids are present in larger numbers than the chromosomes in cells The size of plasmids make them easier to handle than chromosomal DNA. 3. To cut DNA. 4. (i) cut (ii) enzyme, gene (iii) mixed (iv) ...
... Teachers Answer Sheet 1. Bacteria 2. Plasmids can multiply at the same rate as the DNA of the cell Plasmids are present in larger numbers than the chromosomes in cells The size of plasmids make them easier to handle than chromosomal DNA. 3. To cut DNA. 4. (i) cut (ii) enzyme, gene (iii) mixed (iv) ...
01 - Educator Pages
... stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of proteins needed by the cell. As a eukaryotic cell prepares to divide, the DNA and the proteins associated with the DNA coil into a structure called a chromosome. Before the DNA coils up, however, the ...
... stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of proteins needed by the cell. As a eukaryotic cell prepares to divide, the DNA and the proteins associated with the DNA coil into a structure called a chromosome. Before the DNA coils up, however, the ...
Apple Molecular Biology: Animation 2
... 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Cloning. 4. After reading the introduction click on the third and fourth animation to learn more about cloning. 5. Then complete the review questions on this ...
... 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Cloning. 4. After reading the introduction click on the third and fourth animation to learn more about cloning. 5. Then complete the review questions on this ...
國立嘉義大學九十七學年度
... genomic DNA (4 x 106 nucleotide pairs) with HaeIII (4-base recognition site)? or with EcoR I (6base recognition site)? (6%) (3) Which of the following statements are correct? For the incorrect statements, correct them specifically (hint: the correction should not be simply from “can” to “cannot”, or ...
... genomic DNA (4 x 106 nucleotide pairs) with HaeIII (4-base recognition site)? or with EcoR I (6base recognition site)? (6%) (3) Which of the following statements are correct? For the incorrect statements, correct them specifically (hint: the correction should not be simply from “can” to “cannot”, or ...
Ch 11 homework
... 1. The term "gene expression" refers to the (.5) A) fact that each individual of a species has a unique set of genes. B) fact that individuals of the same species have different phenotypes. C) process by which genetic information flows from genes to proteins. D) fact that certain genes are visible a ...
... 1. The term "gene expression" refers to the (.5) A) fact that each individual of a species has a unique set of genes. B) fact that individuals of the same species have different phenotypes. C) process by which genetic information flows from genes to proteins. D) fact that certain genes are visible a ...
Extra Credit Ch. 6 Cell cycle and Mitosis student
... 1. Following replication of its DNA, each chromosome contains two ____________________, which are attached to each other by a centromere. 2. The DNA in eukaryotic cells is packaged into structures that are called ____________________. 3. A(n) ____________________ is a segment of a DNA molecule that ...
... 1. Following replication of its DNA, each chromosome contains two ____________________, which are attached to each other by a centromere. 2. The DNA in eukaryotic cells is packaged into structures that are called ____________________. 3. A(n) ____________________ is a segment of a DNA molecule that ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of __________. 3. What is heredity? 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? 5. What is the name of the process for the way cells divide in asexual reproduction? 6 ...
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of __________. 3. What is heredity? 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? 5. What is the name of the process for the way cells divide in asexual reproduction? 6 ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.