The DNA connection - Somerset Academy North Las Vegas
... The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. Example: CGT, always codes for the amino acid alanine. ...
... The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. Example: CGT, always codes for the amino acid alanine. ...
Biology Chapter 11-1
... - DNA fragments may be combined with bacterial DNA so they can be reentered into a bacterium. - The plasmids are removed and cut with the same restriction enzyme used to produce the DNa fragments. - The cuts leave sticky ends which are then joined together to complete the ring. DNA Insertion - The D ...
... - DNA fragments may be combined with bacterial DNA so they can be reentered into a bacterium. - The plasmids are removed and cut with the same restriction enzyme used to produce the DNa fragments. - The cuts leave sticky ends which are then joined together to complete the ring. DNA Insertion - The D ...
THINK ABOUT THESE………………
... 12. Why do we call DNA replication SEMI-CONSERVATIVE? Each new strand of DNA consists of ONE old (original strand) and one NEW strand 13. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Phosphate, sugar, base 14. What enzyme adds DNA nucleotides to a growing strand? DNA Polymerase 15. Where does transcrip ...
... 12. Why do we call DNA replication SEMI-CONSERVATIVE? Each new strand of DNA consists of ONE old (original strand) and one NEW strand 13. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Phosphate, sugar, base 14. What enzyme adds DNA nucleotides to a growing strand? DNA Polymerase 15. Where does transcrip ...
Topic 4: Genetics (15 hours)
... Predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring of monohybrid crosses involving any of the above patterns of ...
... Predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring of monohybrid crosses involving any of the above patterns of ...
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... crossed the resulting dominant genotype for the letter plants may be tall or B. short and produce yellow seeds or green seeds. This is supported by Mendel’s Law of ______________ __________________ . ...
... crossed the resulting dominant genotype for the letter plants may be tall or B. short and produce yellow seeds or green seeds. This is supported by Mendel’s Law of ______________ __________________ . ...
Document
... 13. Several forms of RNA or ______________________ help change DNA code into proteins. 14. Because it is so similar to ______________________, RNA can serve as a temporary copy of a DNA sequence. 15. The “factory” that assembles proteins is known as a(n) ______________________. 16. A mirror-like cop ...
... 13. Several forms of RNA or ______________________ help change DNA code into proteins. 14. Because it is so similar to ______________________, RNA can serve as a temporary copy of a DNA sequence. 15. The “factory” that assembles proteins is known as a(n) ______________________. 16. A mirror-like cop ...
DIR RD 4C-2
... 13. Several forms of RNA or ______________________ help change DNA code into proteins. 14. Because it is so similar to ______________________, RNA can serve as a temporary copy of a DNA sequence. 15. The “factory” that assembles proteins is known as a(n) ______________________. 16. A mirror-like cop ...
... 13. Several forms of RNA or ______________________ help change DNA code into proteins. 14. Because it is so similar to ______________________, RNA can serve as a temporary copy of a DNA sequence. 15. The “factory” that assembles proteins is known as a(n) ______________________. 16. A mirror-like cop ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 11. A string of nucleotides that has instructions for a certain trait is a gene. 12. The diagram used to trace a trait through generations of a family is a pedigree. 13. What does each gene have instructions for making? A protein 14. When a plant fertilizes itself, it is called self-pollinating plan ...
... 11. A string of nucleotides that has instructions for a certain trait is a gene. 12. The diagram used to trace a trait through generations of a family is a pedigree. 13. What does each gene have instructions for making? A protein 14. When a plant fertilizes itself, it is called self-pollinating plan ...
DNA Structure: Deoxyribonucleic acid
... Why is this trait an environmental trait? ____________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Watson and Crick’s discovery didn’t just win them the Nobel Prize because the double helix is pretty. The double helix showed something called: semiconservative replic ...
... Why is this trait an environmental trait? ____________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Watson and Crick’s discovery didn’t just win them the Nobel Prize because the double helix is pretty. The double helix showed something called: semiconservative replic ...
ppt
... these genes are responsible for a useful characteristic displayed by the host bacterium. For example, the ability to survive in normally toxic concentrations of antibiotics such as ampicillin, chloramphenicol or tetracycline is often due to the presence in the bacterium of a plasmid carrying antibio ...
... these genes are responsible for a useful characteristic displayed by the host bacterium. For example, the ability to survive in normally toxic concentrations of antibiotics such as ampicillin, chloramphenicol or tetracycline is often due to the presence in the bacterium of a plasmid carrying antibio ...
11-2 Genetics and Probability
... Ex. (disease resistance X food producing capacity) 2. Inbreeding – breeding individuals with similar characteristics to ...
... Ex. (disease resistance X food producing capacity) 2. Inbreeding – breeding individuals with similar characteristics to ...
Bulletin 1 - DNA: The Cookbook of Life - ctahr
... The DNA inside a cell is packaged very tightly into chromosomes. Within a human cell, 23 pairs of chromosomes fit in a structure that is one-tenth the width of a human hair, but if you unwound the chromosomes, the DNA would be six feet long. All living things contain DNA recipes and use them to make ...
... The DNA inside a cell is packaged very tightly into chromosomes. Within a human cell, 23 pairs of chromosomes fit in a structure that is one-tenth the width of a human hair, but if you unwound the chromosomes, the DNA would be six feet long. All living things contain DNA recipes and use them to make ...
docx Probes and fingerprint matching Card sort or vocab
... with a family history of genetic disorders on the likelihood it could be passed to their children. ...
... with a family history of genetic disorders on the likelihood it could be passed to their children. ...
11-2 Genetics and Probability
... Ex. (disease resistance X food producing capacity) 2. Inbreeding – breeding individuals with similar characteristics to ...
... Ex. (disease resistance X food producing capacity) 2. Inbreeding – breeding individuals with similar characteristics to ...
Name
... Directions: Use this as a study guide for your next exam. Typically 80-90% of the exam questions come from this sheet. Other questions may come from labs, online activities and news articles which have been discussed in class. DNA and Chromosomes ...
... Directions: Use this as a study guide for your next exam. Typically 80-90% of the exam questions come from this sheet. Other questions may come from labs, online activities and news articles which have been discussed in class. DNA and Chromosomes ...
AP BIO Unit 6 Review Ch. 14,15,16,18,19 Westbrook Gene
... If a cell loses its ability to control its cell cycle and begins dividing uncontrollably it results in a _______. Small, circular auxiliary DNA molecules of bacteria which are commonly used in genetic engineering technology are referred to as __________. How does UV light cause a mutation? Lung canc ...
... If a cell loses its ability to control its cell cycle and begins dividing uncontrollably it results in a _______. Small, circular auxiliary DNA molecules of bacteria which are commonly used in genetic engineering technology are referred to as __________. How does UV light cause a mutation? Lung canc ...
Deciphering the Structure of the Hereditary Material
... DNA from different biological sources showed distinct differences and could carry information. Four kinds of chemical structures are linked together in DNA - Deoxyribose, Phosphoric Acid, Purine Bases (Adenine - A and Guanine - G), and Pyrimidine Bases - (Thymine - T and Cytosine - C). Chargaff show ...
... DNA from different biological sources showed distinct differences and could carry information. Four kinds of chemical structures are linked together in DNA - Deoxyribose, Phosphoric Acid, Purine Bases (Adenine - A and Guanine - G), and Pyrimidine Bases - (Thymine - T and Cytosine - C). Chargaff show ...
Mutations and DNA Technology Notes
... • Inbreeding- continued breeding of ind. with similar characteristics. – Ex- different dog breeds – Can be dangerous due to increased chance for genetic defects. ...
... • Inbreeding- continued breeding of ind. with similar characteristics. – Ex- different dog breeds – Can be dangerous due to increased chance for genetic defects. ...
Pre-AP Biology 2009
... 9. What gene needs to be expressed when bacteria are lactose, a carbohydrate, needs to be broken down for energy use? 10. What is the role of a repressor protein? (See fig 12-23) 11. What happens when lactose is present? (See fig 12-23) D. Eukaryotic Gene Regulation: 1. Sketch a typical eukaryotic g ...
... 9. What gene needs to be expressed when bacteria are lactose, a carbohydrate, needs to be broken down for energy use? 10. What is the role of a repressor protein? (See fig 12-23) 11. What happens when lactose is present? (See fig 12-23) D. Eukaryotic Gene Regulation: 1. Sketch a typical eukaryotic g ...
genetic continuity
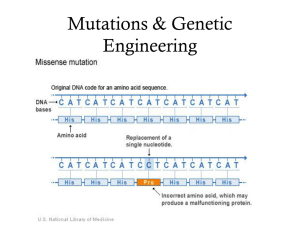
... ALTER THE GENETIC INSTRUCTIONS OF AN ORGANISM BY SUBSTITUTING DNA MOLECULES ...
... ALTER THE GENETIC INSTRUCTIONS OF AN ORGANISM BY SUBSTITUTING DNA MOLECULES ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... complementary base sequences found in the disease- causing allele ...
... complementary base sequences found in the disease- causing allele ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.