Who Controls Your DNA
... The use of DNA for personal identification by the military may be justified. An individual’s genetic information, however, is a private matter. A recent study at Harvard and Stanford universities turned up more than 200 cases of discrimination because of genes individuals carried or were suspected o ...
... The use of DNA for personal identification by the military may be justified. An individual’s genetic information, however, is a private matter. A recent study at Harvard and Stanford universities turned up more than 200 cases of discrimination because of genes individuals carried or were suspected o ...
Using microsatellites as molecular markers
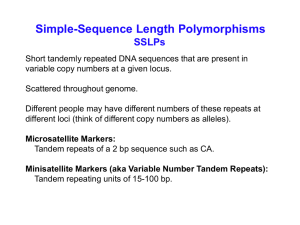
... Advantages of SSLPs compared to RFLPs 1. Unlike RFLPs, both microsatellites and minisatellites usually have > 2 alleles. By having more allele possibilities, each allele can be used as a more specific tag. 2. In a population, heterozygosity for a particular RFLP may be low, whereas heterozygosity f ...
... Advantages of SSLPs compared to RFLPs 1. Unlike RFLPs, both microsatellites and minisatellites usually have > 2 alleles. By having more allele possibilities, each allele can be used as a more specific tag. 2. In a population, heterozygosity for a particular RFLP may be low, whereas heterozygosity f ...
Genetic Engineering - ABC-MissAngelochsBiologyClass
... Transgenic Organisms Plants and animals that contain fragments of DNA from different sources. Example: tobacco plant with firefly gene that makes the plant glow ...
... Transgenic Organisms Plants and animals that contain fragments of DNA from different sources. Example: tobacco plant with firefly gene that makes the plant glow ...
GENETIC ENGINEERING QUESTIONS
... a. They have single nucleotide differences in their DNA b. The have different numbers of tandem repeats in their genes c. Both a and b d. Neither are correct 3. In gel electrophoresis smaller fragments of DNA a. Move slower down the gel b. Move faster down the gel c. Move towards the negative charge ...
... a. They have single nucleotide differences in their DNA b. The have different numbers of tandem repeats in their genes c. Both a and b d. Neither are correct 3. In gel electrophoresis smaller fragments of DNA a. Move slower down the gel b. Move faster down the gel c. Move towards the negative charge ...
Intermediate Inheritance or Incomplete Dominance
... • Genes are considered to be segments of these molecules with the sequence of bases coding for the amino acids in protein ...
... • Genes are considered to be segments of these molecules with the sequence of bases coding for the amino acids in protein ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... During replication, what would be the complementary bases to the following nucleotide sequence: A-A-G-G-T-C-T-C-A-C __________________________________ ...
... During replication, what would be the complementary bases to the following nucleotide sequence: A-A-G-G-T-C-T-C-A-C __________________________________ ...
Unit 4 Resources - Schoolwires.net
... __________________________ . 8. The amino acid __________________________ is represented by the mRNA codon ACA. 9. ________________________ and ________________________ are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. 10. There can be more than one __________________________ for the same amino acid. 11. For any o ...
... __________________________ . 8. The amino acid __________________________ is represented by the mRNA codon ACA. 9. ________________________ and ________________________ are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. 10. There can be more than one __________________________ for the same amino acid. 11. For any o ...
Micro Quiz #3R Stu F2011 - the Biology Scholars Program Wiki
... 3. The primary structure of bases in DNA (and RNA) refers to: A. The association of one or more strands by hydrogen bonding B. The linear sequence of purines and pyrimidines C. The complementary binding of purines and pyrimidines D. Supercoiling E. Double stranded helix 4. AT-rich DNA strands will d ...
... 3. The primary structure of bases in DNA (and RNA) refers to: A. The association of one or more strands by hydrogen bonding B. The linear sequence of purines and pyrimidines C. The complementary binding of purines and pyrimidines D. Supercoiling E. Double stranded helix 4. AT-rich DNA strands will d ...
Biotechnology and its applications - MrsGorukhomework
... the base sequences. Mapping of genes – what the sequence codes for. (did mapping of genome of yeast in 1992 just for chromosome 3 which consisted of 315 357 nucleotides, took about 10 years.) Thought that DNA → RNA → proteins → control the body, based on that and looking at all the different phenoty ...
... the base sequences. Mapping of genes – what the sequence codes for. (did mapping of genome of yeast in 1992 just for chromosome 3 which consisted of 315 357 nucleotides, took about 10 years.) Thought that DNA → RNA → proteins → control the body, based on that and looking at all the different phenoty ...
Radiation and Gene Damage
... Radiation is known to be dangerous to human bodies. Millions of body cells exposed to high-energy waves from X rays, radon gas, and ultra-violet radiation have been permanently harmed by these emissions. The DNA of the individual cells is too delicate to withstand the energy produced by these kinds ...
... Radiation is known to be dangerous to human bodies. Millions of body cells exposed to high-energy waves from X rays, radon gas, and ultra-violet radiation have been permanently harmed by these emissions. The DNA of the individual cells is too delicate to withstand the energy produced by these kinds ...
Genes
... new medicines, vaccines and disease diagnostic tools; and higher yielding and more nutrient-rich crop plants. ...
... new medicines, vaccines and disease diagnostic tools; and higher yielding and more nutrient-rich crop plants. ...
DNA intro review - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... 14. What type of bond does the phosphate group and the sugar have? What is this bond called? 15. Write out the complete name for DNA: __________________________________________ 16. Write the complementary strand nitrogen bases that match up with the following template strand: ...
... 14. What type of bond does the phosphate group and the sugar have? What is this bond called? 15. Write out the complete name for DNA: __________________________________________ 16. Write the complementary strand nitrogen bases that match up with the following template strand: ...
Mitosis and Asexual Reproduction
... following “Mitosis and Asexual Reproduction” vocabulary: Eukaryotic: a domain of organisms having cells each with a distinct nucleus within which the genetic material is contained along with other membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic: any organism having cells in each of which the genetic material ...
... following “Mitosis and Asexual Reproduction” vocabulary: Eukaryotic: a domain of organisms having cells each with a distinct nucleus within which the genetic material is contained along with other membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic: any organism having cells in each of which the genetic material ...
DNA – The Building Blocks of Life
... The main role of DNA is the long-term storage of information. You can compare it to a set of instructions that tell the cell what to make, for example, a specific type of protein. Specific segments of DNA are called genes. These genes are responsible for some of the traits you can inherit from yo ...
... The main role of DNA is the long-term storage of information. You can compare it to a set of instructions that tell the cell what to make, for example, a specific type of protein. Specific segments of DNA are called genes. These genes are responsible for some of the traits you can inherit from yo ...
genetics i - Indian School Al Wadi Al Kabir
... (a) How many codons code for amino acids and how many do not? (b) Explain the following with example Unambiguous and specific codon Degenerate codon Universal Initiator codon ...
... (a) How many codons code for amino acids and how many do not? (b) Explain the following with example Unambiguous and specific codon Degenerate codon Universal Initiator codon ...
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE and TRENDS Unit Cover Page Topic
... All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain instructions that code for the formation of proteins. (LS1.A) ...
... All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain instructions that code for the formation of proteins. (LS1.A) ...
File
... DNA is separated into single strands by gel DNA is negatively charged – migrates to positive ...
... DNA is separated into single strands by gel DNA is negatively charged – migrates to positive ...
Microbiology Exam II - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... 25. Transcription is the process of making RNA from a DNA template. 26. The most common type of control in bacterial is transcriptional. 27. A repressor controls the lactose operon. 28. Mutations always affect the genotype. 29. Prions only contain RNA. 30. Reverse transcriptase can make DNA using an ...
... 25. Transcription is the process of making RNA from a DNA template. 26. The most common type of control in bacterial is transcriptional. 27. A repressor controls the lactose operon. 28. Mutations always affect the genotype. 29. Prions only contain RNA. 30. Reverse transcriptase can make DNA using an ...
Chapter 1-2: Genetics Progressed from Mendel to DNA in Less Than
... 1.3: Discovery of the Double Helix and Molecular Genetics ...
... 1.3: Discovery of the Double Helix and Molecular Genetics ...
Genetics Syllabus
... Shared Activities and Assessments: Activities: Building a basic DNA molecule Form the DNA into a double helix Form the DNA into a flexible double helix Replication of a DNA molecule Form the daughter molecules into double helixes Transcription of a DNA molecule ...
... Shared Activities and Assessments: Activities: Building a basic DNA molecule Form the DNA into a double helix Form the DNA into a flexible double helix Replication of a DNA molecule Form the daughter molecules into double helixes Transcription of a DNA molecule ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? ...
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? ...
TRANSFORMATION
... Concluded that some factor, a "transforming principle", from the dead S had converted some R bacteria into S bacteria (a genetic change) ...
... Concluded that some factor, a "transforming principle", from the dead S had converted some R bacteria into S bacteria (a genetic change) ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.